Demystify the world of project management with our comprehensive glossary of key terms.
Just as a skilled craftsman relies on specific tools, those working on and managing projects rely on key terms to help them.
Together we’ll explore the language of success and help you understand the important terms in project management.
Glossary guide
In this guide, we’ve organized the glossary into sections to make it easy to find the information you need. We also did this because some terms might have different meanings during different project stages.
Here’s a look at the different glossary sections and what you can expect to find in each.
1. Project management roles
Explore the key roles that drive project success.
2. Project planning terms
Dive into the terminology used during project planning, such as assumptions, constraints, and scope of work.
3. Project execution terms
Discover essential terms related to project execution, such as change management and UAT.
4. Project monitoring and controlling terms
Learn about terms used to monitor and control, such as variance analysis and earned value management.
5. Project closure terms
Understand project closure terms like customer satisfaction and final project reports.
6. Risk management terms
Get insights into managing project risks with terms like risk assessment, RAID log, and impact assessment.
7. Communication terms
Discover project communication terms such as communication channels, status reports, and stakeholder engagement.
8. Agile methodology terms
Explore the language of Agile project management.
9. Resource management terms
Read about resource terms like capacity planning, resource allocation, and resource utilization.
10. Quality management terms
Learn about quality management terms like continuous improvement, quality assurance, and quality metrics.
11. Change management terms
Understand change management terms such as change control, change implementation, and change request.
12. Cost management terms
Read about financial project terms like budgeting, cost estimation, and cost variance analysis.
13. Procurement management terms
Explore procurement process terms like contract management, procurement negotiation, and vendor selection.
14. Team management terms
Learn about teamwork terms like conflict resolution, team building, and performance evaluation.
15. Other methods and frameworks
Discover additional project management approaches, including critical path method, lean, and waterfall.
1. Terms for project management roles
Developer or designer
Crafts the project's product or solution based on specifications.
Oversees the product's lifecycle to make sure it aligns with business objectives.
Project manager
Orchestrates all project activities, sets timelines, manages resources, and drives successful project delivery.
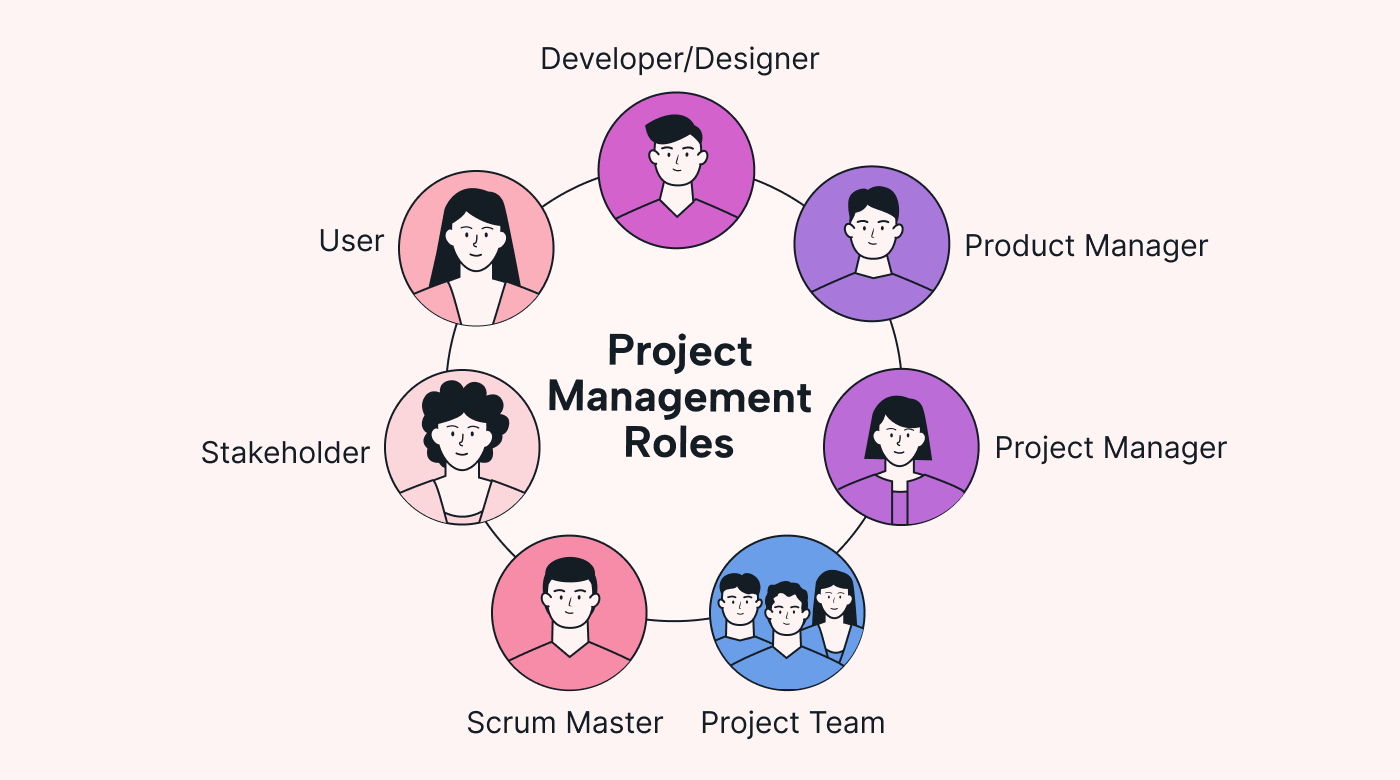 |
Project team
A dynamic group of individuals working together to execute project tasks and achieve project goals.
Agile facilitator and servant leader of Scrum teams.
Stakeholder
Those with a vested interest in the project's success, such as key influencers, investors, and users. May include outside interests, such as citizen groups affected by the project.
User
The end recipient of the project's output and the main driver of the project's design and functionality.
2. Terms for project planning
Assumptions
Implicit factors presumed to be true during project planning (can influence decisions).
Constraints
Limitations that can impact project progress, such as time, budget, resources, and external factors.
Cost estimation
The process of determining project expenses (during planning) involves doing detailed analysis and budgeting.
The sequence of tasks that determines the project's minimum duration and the most critical activities. Used to prioritize work when planning.
Deliverable
Tangible or intangible outputs that'll be produced because of project results.
Relationships between project tasks, where the completion of one task relies on another's progress. During planning, dependencies indicate the order in which work must be done.
Earned value management (EVM)
A project performance measurement technique that integrates cost, schedule, and scope. Used to give insights into project progress and forecasting.
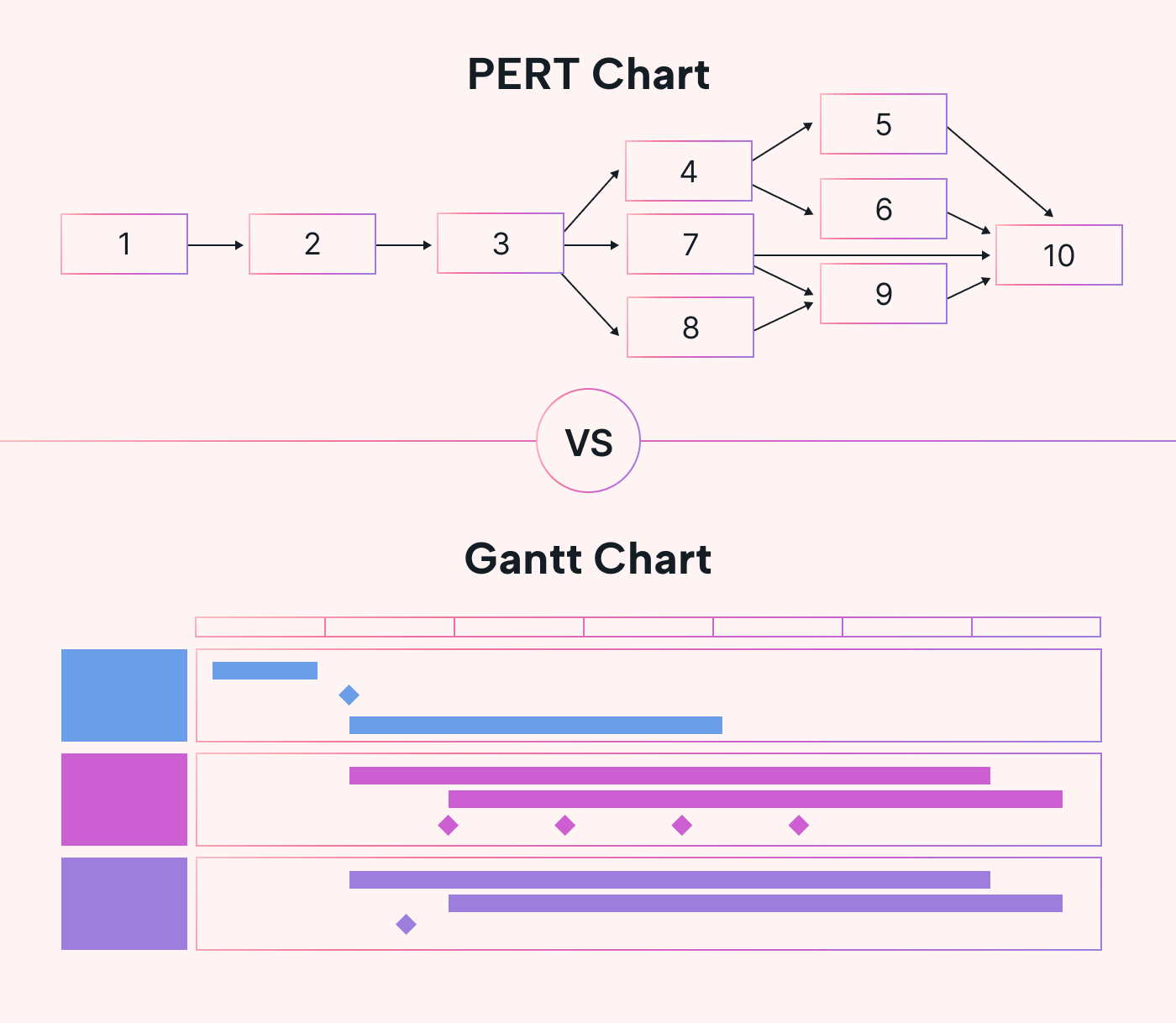
A visual timeline displaying project tasks, durations, and dependencies. Aids in project scheduling, planning, and resource allocation.
Milestone(s)
Significant points in the project timeline that mark the completion of key deliverables, phases, or achievements.
Program evaluation review technique (PERT)
A visual tool used to depict project tasks, durations, and uncertainties. Helps assess project risk and time estimation.
A strategic document outlining product development plans and goals.
Project charter
A formal document that authorizes the project and defines its objectives, scope, and key stakeholders.
The lifespan of a project from start to finish.
The specific and measurable outcomes or results that the project aims to achieve.
Project management methodology
A structured approach to project execution, providing consistency and efficiency, such as Agile, waterfall, or Scrum.
Tools used to plan, execute, and monitor projects and improve collaboration and organization.
The stages (often 5) a project progresses through, from initiation to closure. In traditional projects, these phases are initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure.
A comprehensive document detailing project goals, strategies, schedules, resources, and potential risks. It guides project execution and control.
The boundaries and extent of work involved in the project. It outlines what will be delivered and what will not.
Project schedule
A timeline that outlines the start and finish dates of project tasks (very helpful for planning).
A visual representation of project events and milestones over time. Gives a clear view of possible deadlines and expected timeframe.
The RACI matrix is a way to assign and track roles and responsibilities within the project team. The letters in the acronym stand for responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed.
 |
Resource allocation
The process of assigning and distributing resources effectively to complete project tasks.
Risk assessment
Identifying and evaluating potential project risks. Doing so during planning helps to address and possibly avoid them early on (before problems happen).
Quality management (planning)
The process of making sure project deliverables meet predetermined quality standards.
Uncontrolled changes or additions to the project scope which impact project timelines, budgets, and overall project success.
Scope of work (SoW)
A document outlining a project's specific tasks, deliverables, and objectives. Helpful in clarifying expectations for all stakeholders during planning.
Stakeholder analysis
Identifying stakeholders' interests, expectations, and influence on the project.
Success criteria
The predetermined criteria that define project success.
Team formation
Assembling the right team members with appropriate skills and expertise for the project.
Work breakdown structure (WBS)
A hierarchical breakdown of project tasks for easier planning, execution, and resource allocation.
3. Terms for project execution
Change management
The systematic approach to handling changes and modifications during project execution to minimize disruptions and risks.
Critical path
The sequence of tasks during project execution that are critical to meeting deadlines.
Cost management
Controlling the project budget and applying measures to reallocate the budget or find more sources of capital.
Cost performance index (CPI)
A performance metric measuring the cost efficiency of work performed in relation to its budgeted value. When it’s over 1, you’re doing well. When it’s under 1, you’re spending more than value delivered.
Deliverable
A tangible or intangible outcome caused by successful project execution.
Issue tracking
Identifying, documenting, and managing project-related issues that arise during execution.
Milestone(s)
Significant checkpoints during execution.
Product roadmap
A strategic document outlining a product’s planned development and evolution throughout the project’s execution. Used to guide decision-making and make sure it aligns with planned objectives.
Project charter
This formal document outlines the planned objectives and scope. During execution, it provides a clear direction for project teams.
Project management plan
A comprehensive document detailing the project's execution strategies, resources, and key milestones.
Project management software
Here these tools help to execute projects.
Project scope
The defined boundaries and objectives of the project during execution.
Resource allocation
The process of effectively assigning or reassigning resources during project execution.
Risk management
An ongoing process of identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential risks during project execution.
Quality assurance
Systematic processes and activities carried out during execution to confirm that the project deliverables meet predefined quality standards.
Schedule performance index (SPI)
A performance metric measuring project schedule performance, comparing planned progress to actual progress. Useful for predicting timeline issues. If over 1.0 you’re ahead of schedule; if under 1.0 you’re behind schedule.
Scope creep
Uncontrolled changes to the project scope during execution cause delays or budget overruns.
Stakeholder communication
Continuous engagement and regular updates for the project stakeholders. Used to manage expectations and build strong relationships.
Task dependencies
The relationships between project tasks, where the completion of one task is reliant on the progress of others. Keeping track of these during execution helps to avoid delays or bottlenecks that can slow down progress.
Work breakdown structure (WBS)
During this phase, the WBS is a valuable tool for re-organizing tasks. It’s also used to track progress against what was planned during the planning phase and to know which parts have been completed.
4. Terms for project monitoring and controlling
Change control
During this phase, change control is used to manage changes in scope and maintain control over project outcomes.
Cost tracking
The ongoing monitoring and recording of project expenses to make sure it stays within the budget.
Critical path
During project monitoring and control, the critical path remains relevant. The focus is on making sure the tasks on the critical path are being resourced and completed to avoid delaying project completion.
Earned value analysis (EVA) + SPI and CPI
EVA measures the value of work performed against planned progress. This analysis yields two important metrics (monitoring these metrics helps identify potential issues):
- Schedule performance index (SPI): shows a project's schedule efficiency
- Cost performance index (CPI): indicates a project’s cost efficiency
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Metrics used to measure team or individual performance.
Milestone(s)
In this phase, milestones serve as checkpoints and ensure that key deliverables and phases are completed as planned.
Performance metrics
Performance metrics are specific measurements used to evaluate project performance during execution. These metrics may include productivity indicators, resource use rates, schedule and cost performance, and adherence to constraints.
Project management software
Here, these tools help to monitor projects and display essential performance tracking metrics.
Project schedule
The project schedule, established during the planning phase, is actively tracked and updated during execution. It provides a timeline for project activities and is an ideal reference for tracking progress.
A project status report regularly updates the project's progress and performance to stakeholders, clients, or team members. It includes information on accomplishments, challenges, milestones, and risks.
Project timeline
The project timeline remains central during project monitoring and control. Project managers use it here to visualize important milestones, deadlines, and expected timeframes.
Resource leveling
Optimizing resource allocation during project execution to avoid overutilization or conflicts and maintain a balanced workload.
Risk mitigation
Risk mitigation here involves taking proactive measures to address potential risks that arise during project execution.
Team communication
Team communication during this phase means regular updates, meetings, and collaboration.
Work breakdown structure (WBS)
The WBS remains useful during the monitoring and control phase, providing a clear breakdown of project tasks. With it, project managers can track progress against planned execution.
Variance analysis
Variance analysis involves comparing actual project performance against planned performance. It helps identify deviations and assess whether the project is on track or requires corrective actions.
5. Terms for project closure
Customer or user satisfaction
Customer or user satisfaction refers to feedback from those who use the project's output. It helps gauge whether the project has met its objectives and delivered value to its stakeholders.
Final project report
A comprehensive document summarizing the entire project's journey, from initiation to closure. It details the project's achievements, challenges faced, lessons learned, and overall performance.
Handover documentation
A formal document that shows essential information and instructions for transferring a project, task, or deliverable from one party to another.
Lessons learned
The lessons learned document reflects on the project's successes and shortcomings. This is often used in combination with a retrospective.
Project evaluation
This thoroughly assesses the project's overall success in meeting its objectives and delivering value.
Project closure
Project closure is the formal conclusion of all project activities. It involves finalizing all documentation, archiving relevant files, and completing all contractual obligations.
Project completion criteria
The predefined conditions that specify what a complete project looks like.
Project review
The project review comprehensively analyzes the project's performance and outcomes.
Project sign off
This represents formal approval from key stakeholders to officially close the project. It signifies the acceptance of the project's results and the release of project resources.
A structured meeting held at the end of a project or iteration (for Agile projects). It aims to identify what worked well and areas that need improvement for future projects.
Quality control
During project closure, quality control is still applied to all deliverables.
Stakeholder feedback
Feedback from stakeholders on all the project processes, deliverables, and results.
Transition planning
Transition planning involves preparing for the post-project phase.
6. Terms for risk management
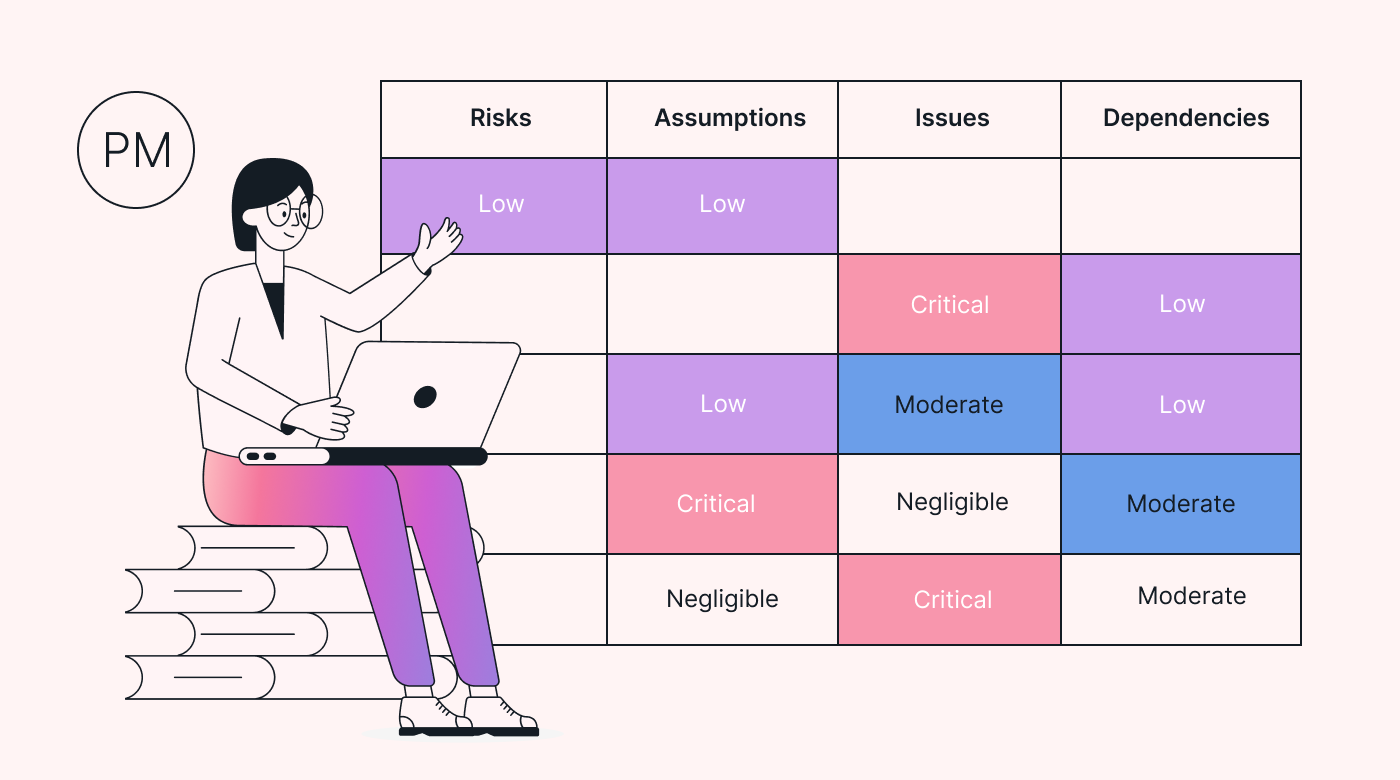
RAID stands for risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies. A RAID log is a document used to track and manage these aspects.
Risk assessment
This is the process of evaluating potential risks, their impact, and their likelihood.
Risk identification
The process of identifying specific risks that could affect the project.
Risk management
The overall process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to reduce their impact.
Risk mitigation
Taking action to reduce the likelihood or impact of identified risks.
Risk monitoring
The continuous tracking of identified risks throughout the project's execution.
7. Terms for communication
Communication channel
The method or platform used to exchange information and ideas between team members and stakeholders – think Slack, Gmail, Motion, Skype, etc.
Communication plan
A structured strategy outlining how, when, and what information will be communicated during the project.
Project meetings
Scheduled gatherings where team members discuss progress, plan, make decisions, and address project-related matters.
Status reports
These reports give those involved a snapshot of the project's progress.
Stakeholder management
The process of managing stakeholder concerns throughout the project.
Stakeholder engagement
Actively involving stakeholders in project activities and decision-making and seeking their feedback.
Team collaboration
When a team member works with one or more team members to achieve a result.
8. Terms for Agile methodology
An iterative approach to project management that focuses on adaptability, teamwork, and customer value.
Agile ceremonies
Structured meetings in Agile that promote communication, collaboration, and alignment within the team.
The guiding principles of Agile development, created by Jeff Sutherland.
Tools and techniques that support Agile practices.
Continuous integration (CI)
A software development practice where code changes are automatically integrated and tested to identify issues early.
Daily stand-up
A 5 to 15-minute daily meeting where team members share progress, discuss obstacles and synchronize their efforts.
Definition of done (DoD)
A shared understanding of what criteria a product increment must meet.
Iteration or iterative
An incremental development process where work is divided into smaller, manageable phases for continuous improvement.
A visual Agile framework for managing the flow of work to help drive efficiency and reduce bottlenecks.
Kanban board
A visual representation of work items and their status in a Kanban system. Often split into columns which represent the progress of work as it moves through its stages.
A framework that focuses on delivering value with minimal waste while seeking continuous improvement. This philosophy originated from Toyota and was first named “Lean Manufacturing.”
Product owner
The person in charge of controlling the product backlog and increasing the product value.
Retrospective
A team review after an iteration to reflect on successes and challenges and plan for improvement next time.
An Agile framework for managing complex projects, using time-boxed iterations called sprints.
Scrumban
A hybrid approach combining principles of Scrum and Kanban.
Scrum board
A visual representation of work items and their progress during a sprint in Scrum.
Formal events within Scrum that structure the team's work. Typically, includes sprint planning, daily stand-up, sprint review, and sprint retrospective.
Sprint
A fixed-length time period (usually 1–4 weeks) during which the team completes a set of planned work items.
A list of tasks and user stories committed to completing within a sprint.
A collaborative meeting where the team decides which work items to include in the upcoming sprint and how they will accomplish them.
Sprint review
A meeting at the end of a sprint where the team demonstrates completed work to stakeholders and receives feedback.
User stories
Short, simple descriptions of a feature or functionality from the end-user's perspective (helps capture user requirements).
User acceptance testing (UAT)
The final phase of testing and where end-users validate the product to check that it meets their requirements.
9. Terms for resource management
Strategically forecasting and planning resources to match project demands and avoid resource bottlenecks.
Resource allocation
The art of assigning resources to specific tasks, optimizing usage, and productivity. This can include resource leveling and other means of ensuring that resources are properly allocated.
Resource optimization
Fine-tuning resource allocation to achieve peak performance while reducing waste.
Resource scheduling
Creating well-structured timelines for resource availability. And making sure they're available when and where they're needed most.
Resource utilization
Measuring how resources are used for data-driven decisions and improvement.
10. Terms for quality management
Continuous improvement
The relentless pursuit of perfection. Constantly enhancing processes to deliver exceptional results.
Requirements management document
A comprehensive document that captures and defines project requirements.
Quality assurance
Verifying that project processes and deliverables meet planned standards.
Quality control
Checking deliverables against pre-set criteria to catch and correct issues.
Quality metrics
Quantifiable measures are used to assess and track project quality. An example metric is “Defect Density,” which measures the number of defects or issues in a specific deliverable.
11. Terms for change management
Change control
A structured process that reviews, evaluates, approves, and implements changes to project scope in a controlled manner.
Change implementation
The phase of change management where an approved change is set into action
Change request
A formal document submitted by stakeholders outlining the need for a change. Typically these are for changes in project scope, schedule, or requirements.
Impact assessment
A thorough evaluation of the potential effects of a proposed change.
12. Terms for cost management
Budgeting
Creating a financial plan for a project, setting the allocation of funds for various activities and resources.
Cost estimation
The method of predicting project expenses.
Cost of employee
The total cost associated with employing a staff member. Often, it includes salary, benefits, taxes, and overhead expenses.
Cost control
The practice of monitoring and managing project expenditures to make sure they stay within the approved budget.
Cost variance analysis
A comparison of actual project costs against the planned budget.
Earned value management (EVM)
A performance measurement technique for cost and schedule performance against scope.
13. Terms for procurement management
Contract management
The process of overseeing and administering contracts with suppliers.
Procurement contract
A legally binding agreement between the buyer and supplier that outlines the terms and conditions of the arrangement.
Procurement planning
Strategic planning to find procurement needs, develop sourcing strategies, and create a roadmap.
Procurement negotiation
Skillful discussions with suppliers to establish favorable terms, pricing, and conditions.
Purchase order (PO)
A formal document issued to a supplier to confirm the details of a purchase, including quantities, prices, and delivery dates.
Request for proposal (RFP)
A document issued to potential suppliers, inviting them to submit proposals for providing goods or services.
Request for quotation (RFQ)
A formal request sent to suppliers to obtain price quotations for specific goods or services required for the project.
Supplier relationship management
Managing supplier interactions to foster strong partnerships and promote collaboration.
Vendor selection
The methodical process of evaluating and choosing the most suitable vendors.
14. Terms for team management
Conflict resolution
The process of addressing and settling disagreements or disputes among team members.
Teams made of people with diverse skills and expertise from different departments or domains.
Matrix organizational structure
An organizational structure where employees report to both functional managers and project managers.
Performance evaluation
The assessment of individual and team performance to measure achievements and identify strengths.
Team building
Activities and initiatives designed to strengthen team dynamics and cohesion.
Team cohesion
A level of unity and harmony among team members, promoting a positive and supportive team atmosphere.
The interactions and relationships among team members that influence overall team performance and productivity.
15. Terms for other methods and frameworks
Critical path method
A project management technique that identifies the sequence of tasks with the longest duration.
Extreme programming (XP)
An Agile software development framework emphasizing engineering practices, collaboration, and rapid feedback.
Hybrid project management
A tailored approach that combines elements from various methodologies to suit the unique needs of a project.
Projects integrating sustainable methods (PRISM)
A project management approach that considers sustainability and environmental factors.
Projects in controlled environments (PRINCE2)
A structured framework emphasizing effective control, organization, and flexibility (popular in the UK and other European countries).
Project management body of knowledge (PMBOK)
A comprehensive project management guide published by the Project Management Institute (PMI). It outlines the best practices, processes, and tools used in project management.
Scrum of Scrums
A technique for large Agile projects, where representatives from different Scrum teams converse. The goal is to learn from each Scrum team to promote faster growth within separate teams.
A data-driven quality methodology aimed at minimizing defects and improving process efficiency.
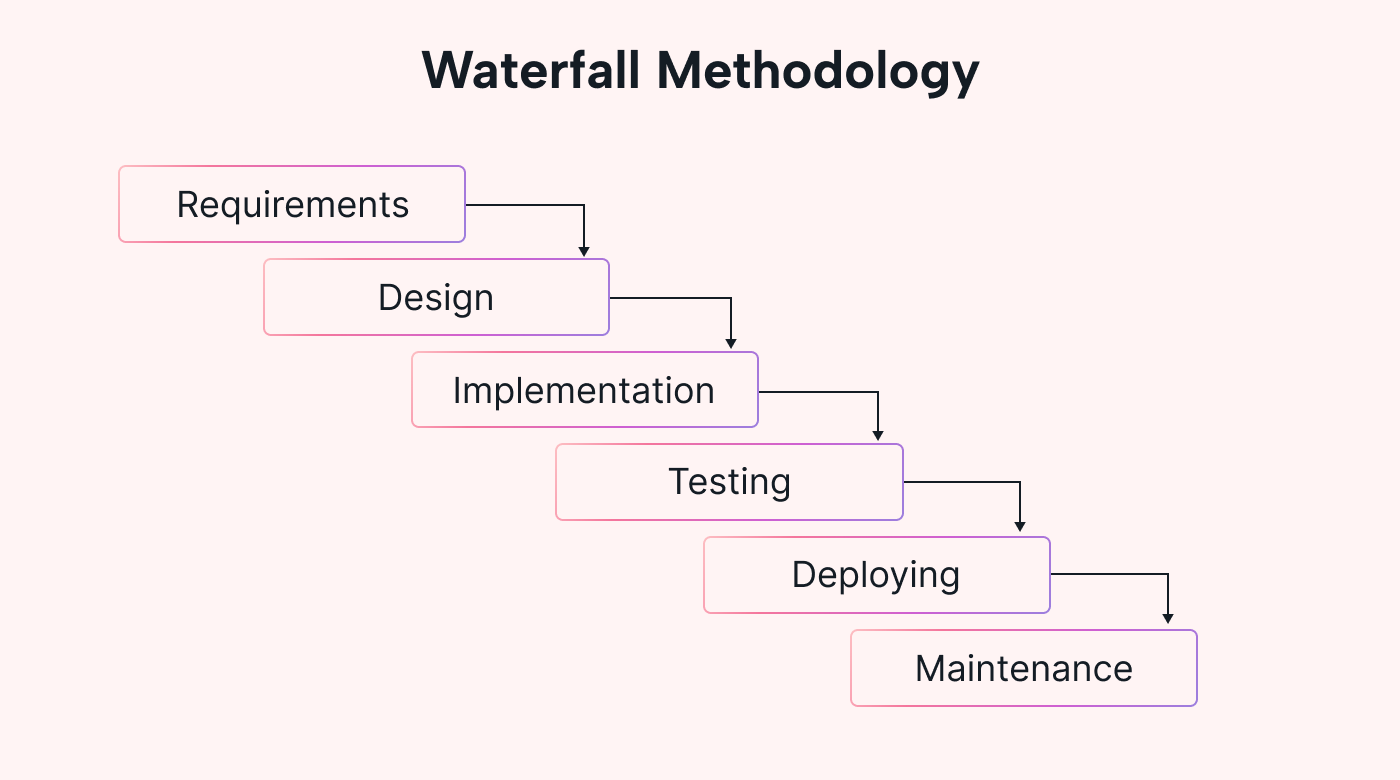
A linear project management approach where the precursor phase must be done before moving on to the next. This way, the project follows a linear project progression and can be backed up by robust planning and documentation.
Use Motion for your project management
Optimize your project management workflows with the power of Motion, the leading AI project management app. Motion’s intelligent features simplify work and help you to achieve better results.
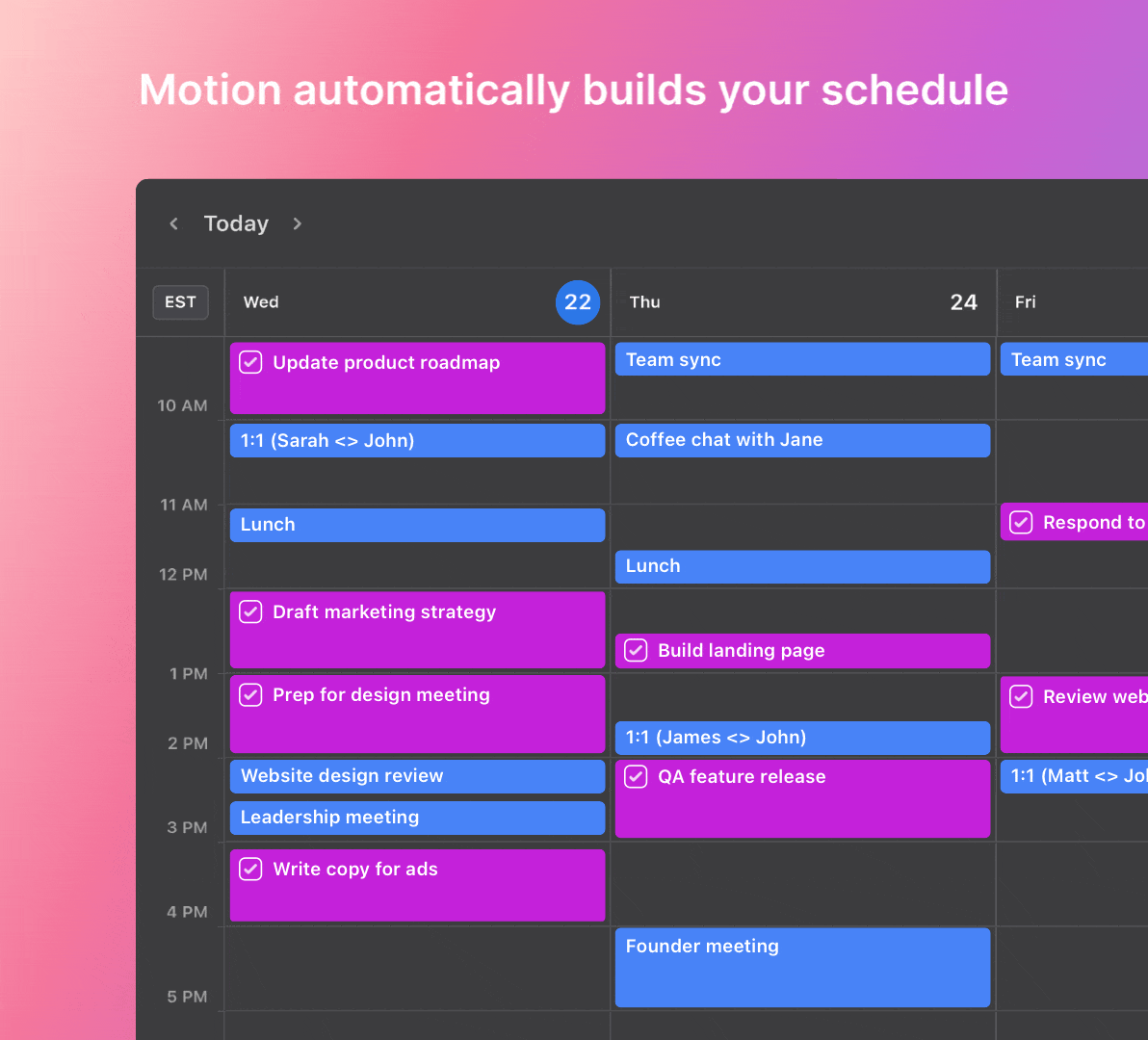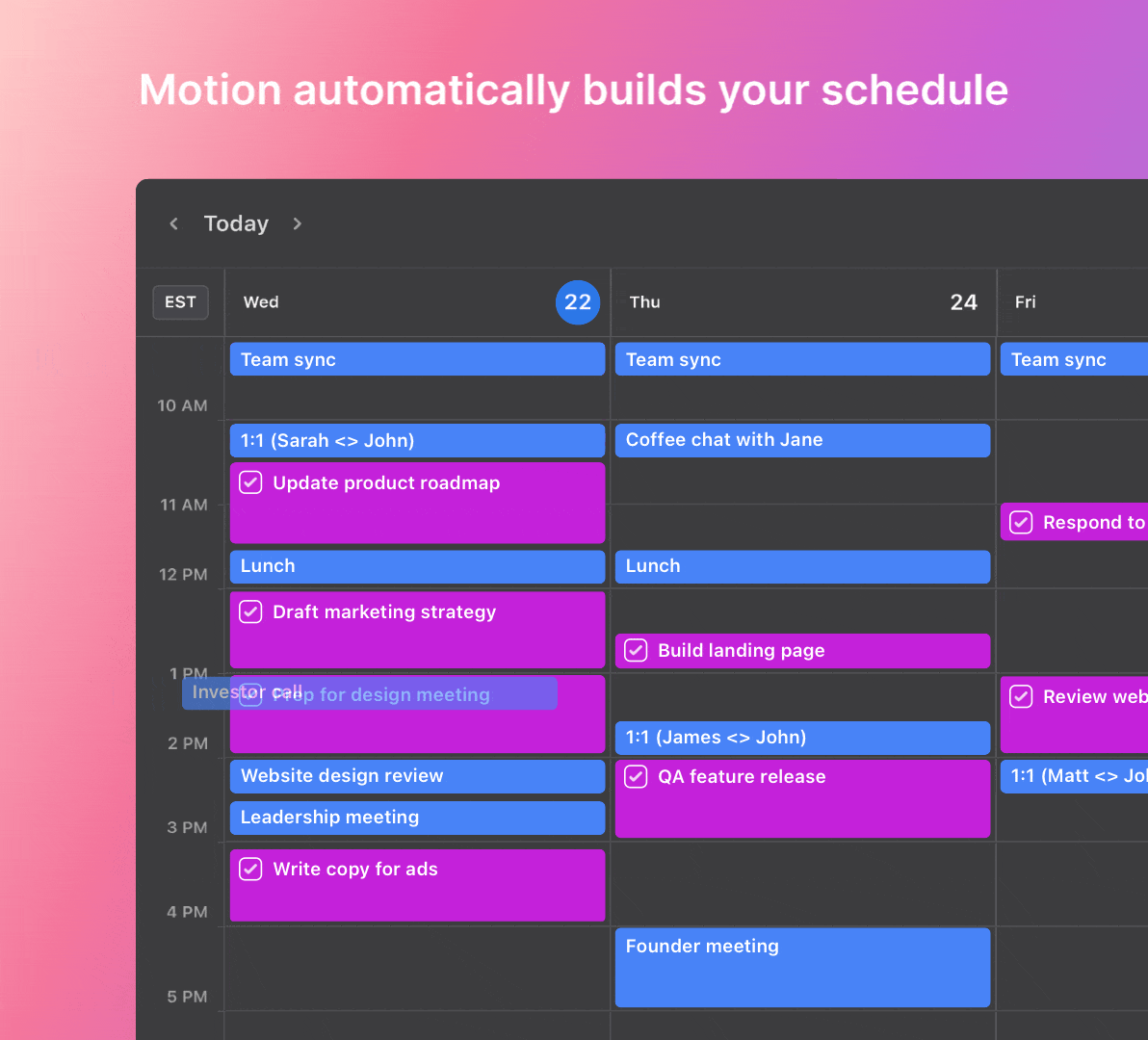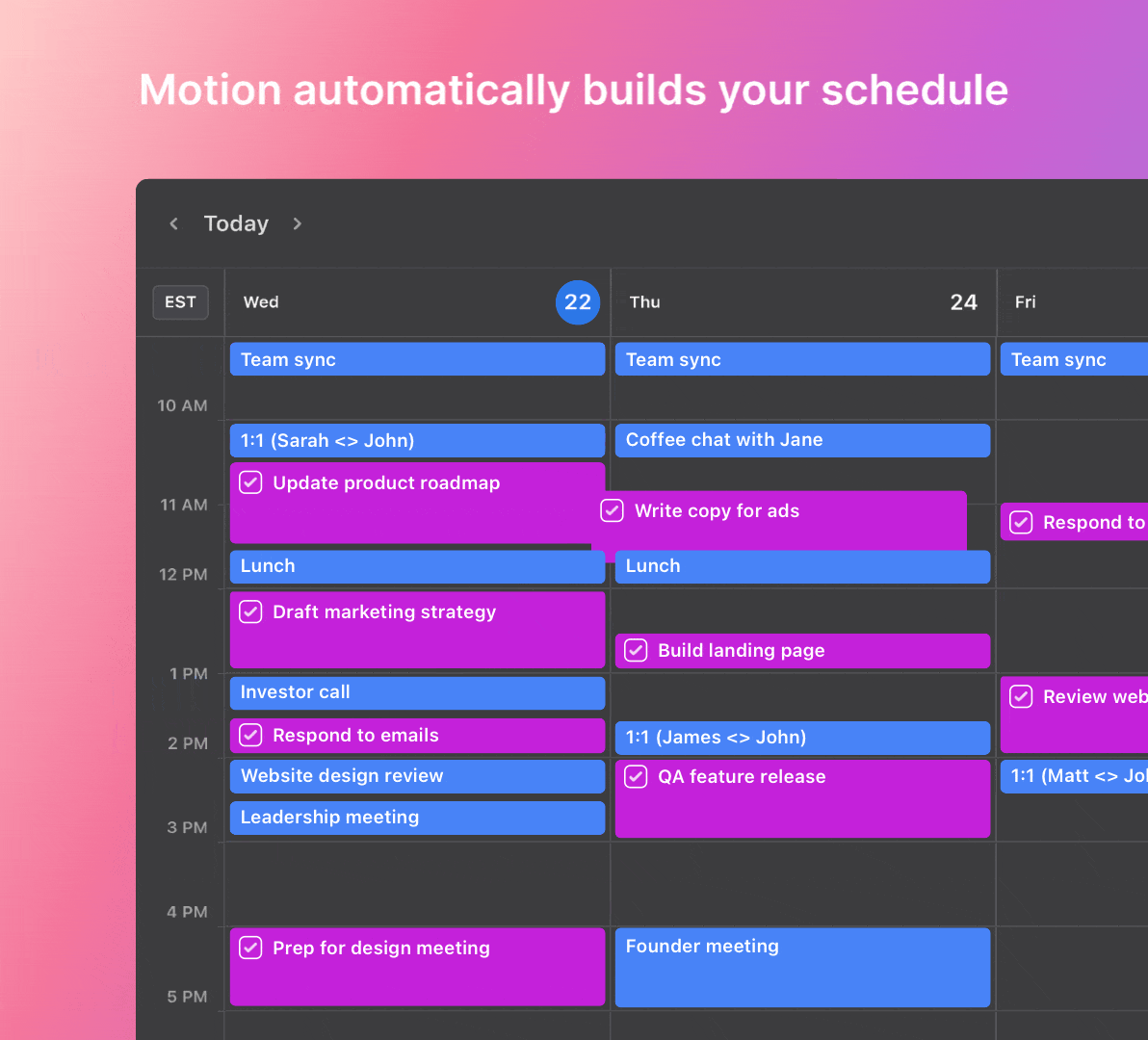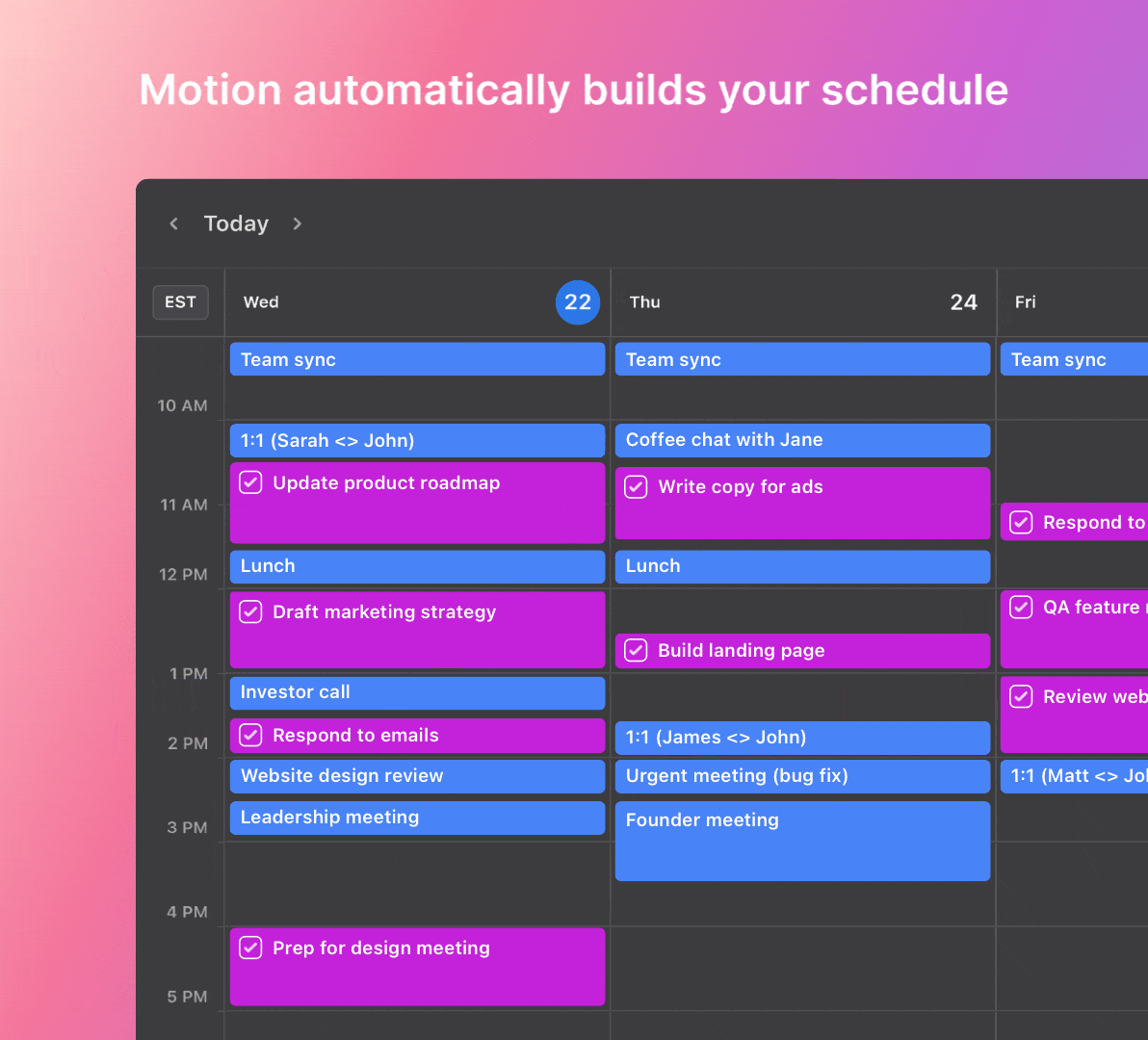 |
Motion’s intelligent automation dynamically organizes tasks based on priority, deadlines, and availability. It can also assign work to team members and manage their workloads precisely.
Aside from that, it hosts many features that can help with projects, business, personal life, ROI, and, most of all, time.
Don’t let project management bog you down. Find out how Motion does what we just said and more.
Sign up for Motion’s 7-day free trial today.