Introduction
Most successful projects start with a planning phase before making any measurable progress toward the desired outcome.
To excel in project management means first stating the desired outcome or results, and then defining what is to be delivered (deliverables). Deliverables are then broken down even further into tasks and subtasks.
The next major part of planning ensures that everyone knows who is doing what and by when.
This is where the RACI model truly shines.
In this post, you'll learn:
- What is a RACI matrix in project management?
- What are the RACI rules?
- What are the 4 roles of the RACI model?
- When should you use a RACI matrix?
- What is the best way to present a RACI chart?
- How Motion can help take RACI models to the next level
Let's start with a simple definition.
What is a RACI model in project management?
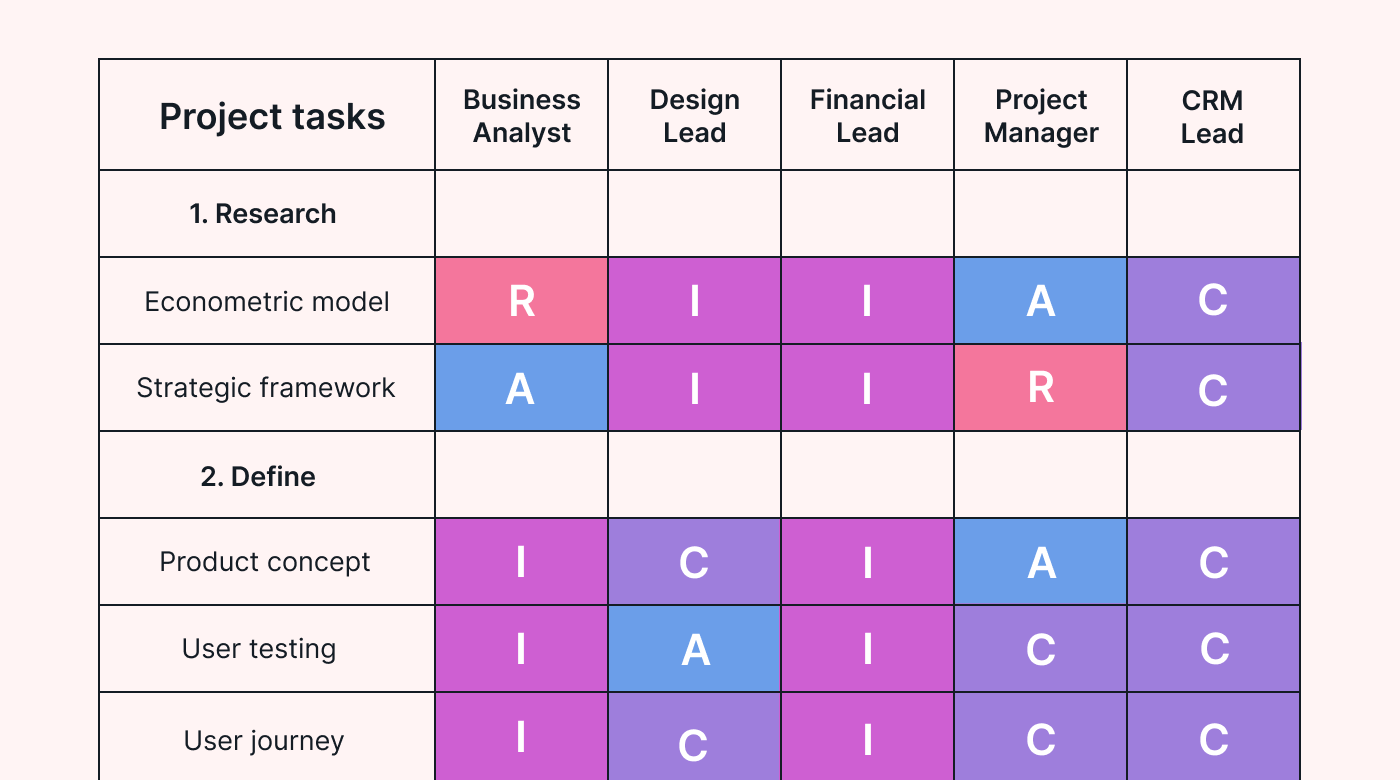
A RACI model (or RACI chart or RACI matrix) describes team members' level of responsibility for tasks, deliverables, and decisions in a project. RACI stands for responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed.
Poor resource management has been flagged as a top challenge in several studies conducted in the last 20 years. With a RACI chart, every stakeholder understands what is expected of them. Understanding the project manager's and sponsor’s expectations and assignments is especially important for cross-functional teams.
RACI is one type of responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) tool used to define and assign responsibilities. Other examples of responsibility matrix include:
- RASCI stands for the same responsibilities as RACI, with the addition of one letter for Support or Supportive. Supportive people assist the Responsible people with their tasks. For example, one person could lead the task while other team members could support the lead person on the task.
- CARS stands for Communicate, Approve, Responsible, Support. Some project managers prefer this model to RACI. This model shows that the person responsible for a task often needs other team members’ support.
- RAS is a simple version of CARS or Responsible, Approve, Support. It ignores communication outside the team, which must be covered in another way.
- CLAM, a parallel to the RACI model, or Contribute, Lead, Approve, Monitor.
- PACSI, which means Perform, Accountable, Control, Suggest, Inform. In PACSI, the performer has a quality control partner who makes final decisions. A person in the Suggest role has experience in the task but has no final say on the work.
- DACI stands for Driver, Approver, Contributor, Informed. Like the RACI model, it represents those who do the work, those who approve it, those who give advice, and those who receive updates.
- RAPID is a decision-making model that stands for Recommend, Agree, Perform, Input, Decide
 |
Now that you’ve seen some of the different approaches to responsibility assignment matrices, let's look at how a RACI matrix works and how it can help you.
Why do you need a RACI chart?
A successful project wraps up on time, within budget, and delivers expected value to the organization. Success rests on the quality of the deliverables and the quality of the project communication. A RACI chart can provide that CSF or critical success factor for effective communication.
Without RACI or another similar model, your project is susceptible to decision bottlenecks and even poor decision-making. A RACI matrix clarifies task responsibilities. It also ensures that no one is confused about their roles, so everyone knows what the project team expects of them.
A RACI matrix also lets people do their work without having to answer to many people with diverse opinions. Only a designated few consult, or offer their insight, and only one person has the final say over how work is done. A RACI model also helps teams quickly reallocate resources when staff members leave. Moreover, RACI charts cover communications with both internal and external stakeholders. Therefore, partners, vendors, and third parties can know their roles on the project, too.
What are the 4 RACI roles?
The RACI model approach to RAM employs four roles that indicate how involved a person is in a task or project.
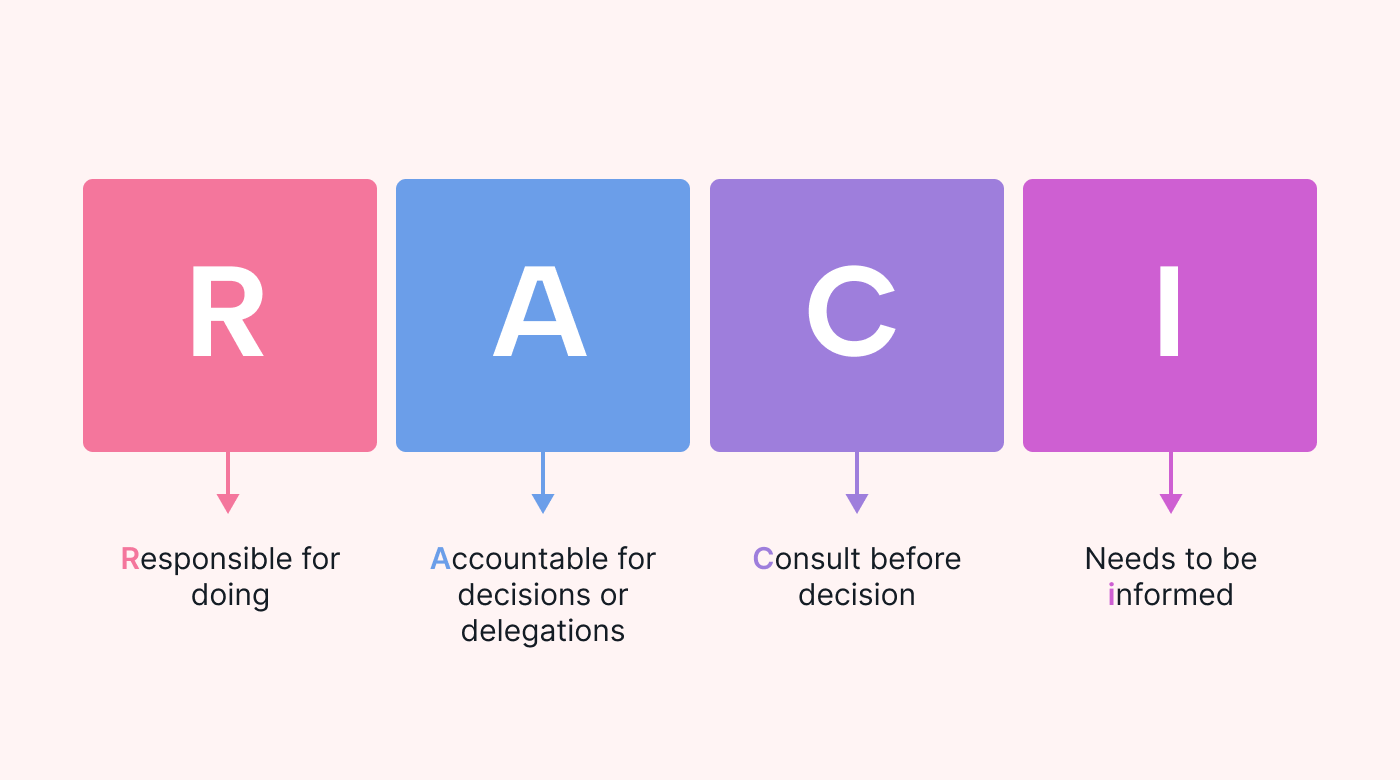 |
Responsible
The responsible role represents the performer, the person (or group) that performs and completes the work. In the RACI approach, every task, deliverable, or decision needs at least one person assigned to it to ensure that no essential requirements or efforts fall between the cracks.
Accountable
The accountable role reviews and decides whether or not to approve the task results or output. The accountable person must ensure that the responsible people understand their task's scope, requirements, and timeline. Often accountable parties have leadership or management positions, such as the project sponsor. They also have the background and authority to make key decisions.
Each task should have one, and only one, accountable person. It's crucial to project success that someone is accountable to establish an approval process, monitor progress, and motivate the responsible parties to keep the tasks or project on track. .
Consulted
The consulted role provides advice, insight, and suggestions for completing a task. They may be on the same team or from a different department, but they are typically subject matter experts. They’re also usually vested in giving good advice because it influences their current and future credibility. These stakeholders offer input before work starts and during the task lifecycle. The consulted role follows up when work concludes to provide feedback on the finished project. A consulted role isn't mandatory, but is often assigned when subject matter experts are needed.
Informed
The informed role has limited involvement in the project activities but is still vested in its success. They may include senior leadership, clients, or workers in other departments. Sometimes they are external parties who will be affected by the results of the project. These stakeholders are in the information loop to receive updates on work progress, but they only require information relevant to their interests.
What are the RACI rules of thumb?
The RACI model has a few rules of thumb that make it more effective:
- The only essential roles in a RACI matrix are accountable and responsible. Teams need to understand who will perform the work, and someone has to be accountable for ensuring the work is complete, accurate, and fits the requirements. Consulted and informed are secondary to ensuring work, and are not mandatory for every task.
- The RACI chart should be kept up to date and notifications provided when changes are made to it
- Assign only one accountable person per task. Restricting the accountable role to one person makes it clear who must approve the work. It reduces confusion about decisions for the responsible workers. This is sometimes called the “Golden Rule” of RACI.
- Some would say that only one person should be Responsible. However, that depends on how granular the matrix assignments are. For some tasks, only one person does the work, but for most, multiple people do the work.
There are rules to using a RACI chart. But there are also guidelines for when to use or not to use a RACI chart.
When Should You Use a RACI Matrix?
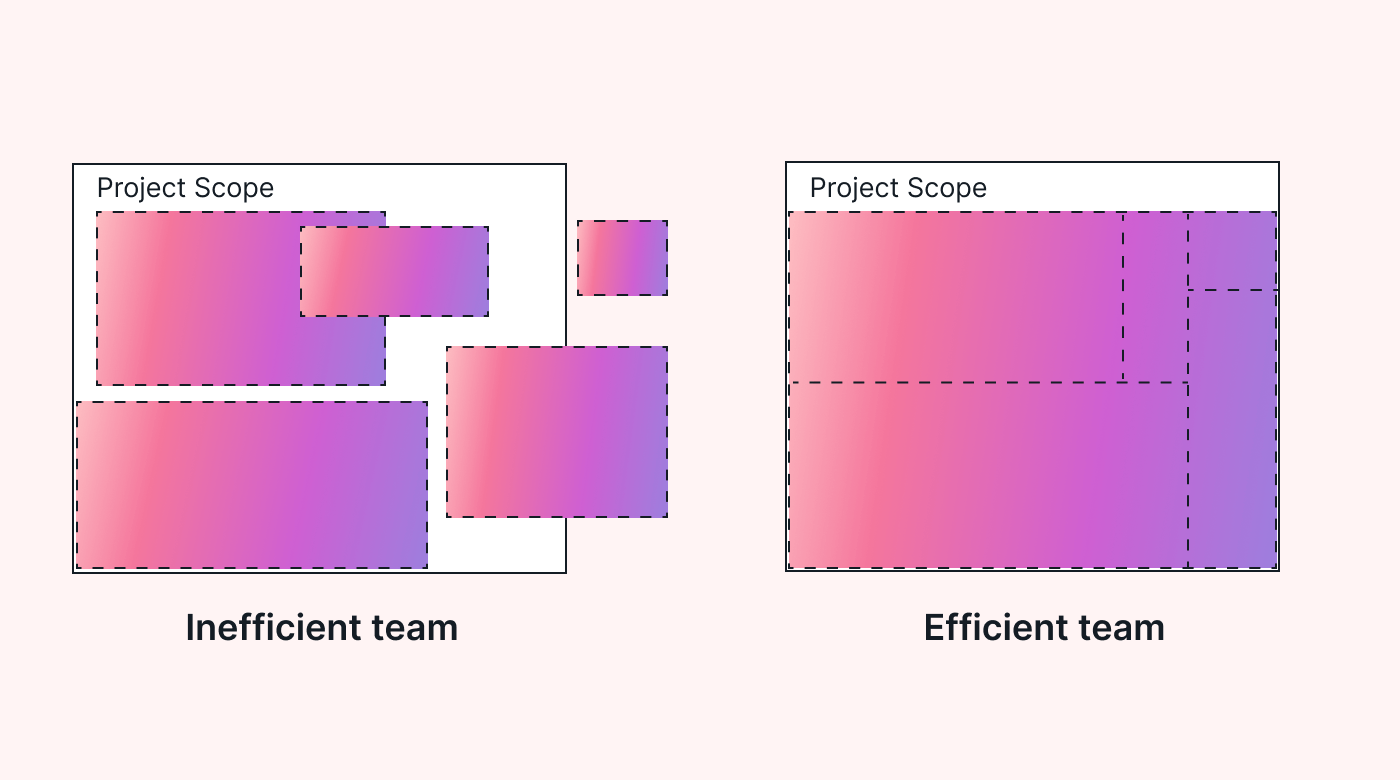
The RACI model is helpful for a variety of situations. Most projects can benefit from the role clarity provided by a RACI matrix. After you have determined what the project is expected to deliver, you can begin to determine the resources needed, and develop your RACI matrix.
Having it developed before project kick-off can help everyone understand both team and other stakeholder roles right from the start. It provides a good foundation for everyone on the team to understand who does what.
Later, the RACI matrix can help new team members understand their roles quickly.
 |
If a RACI model has not been implemented at project start, the most obvious indicator of the need for RACI is when project processes stall because of role confusion. And it happens! RACI analysis also works in situations where role authority isn't clearly defined.
RACI can also help when people feel overwhelmed because roles aren't clearly defined. The model offers clarity, especially when a project includes a range of stakeholders and spans multiple departments or organizations.
Projects that require frequent decisions can benefit from RACI by clearly indicating who can make these decisions, and who should be consulted. Making good business decisions fast is critical to business success. Yet only 20% of organizations in a recent study felt comfortable with their ability to make them. RACI done right can clarify who decides, and whom should be consulted.
The RACI approach also supports complex projects, especially those with many dependencies. Looking at the RACI makes it instantly clear who can provide information about those tasks you depend on, and those that depend on you..
RACI matrices with well thought out delegation for decision-making can instill a sense of empowerment in teams, and grow good decision-making skills among rising stars.
What is the upside of the RACI model?
Perhaps the biggest advantage of RACI charts is that they are simple and easy to understand at a glance.
RACI obviously provides clarity about roles and responsibilities for projects. Making it clear who does what can avoid "too many cooks in the kitchen" and other project illnesses that can befall teams with ambiguous roles.
The RACI model can prevent your team members from being overwhelmed with too many tasks, especially when color-coded by responsibility. On smaller, less complex projects, the project manager can often tell at a glance who might be overloaded.
A RACI model helps you think through the information needs of internal and external stakeholders. Informing key stakeholders outside the team about work progress helps them prepare for the project's outcome.
For stable organizations performing similar kinds of projects over and over, the types of stakeholders will remain similar, so consideration of stakeholder needs can be carried over from project to project.
What is the downside of the RACI model?
For simple projects, it doesn't always make sense to create a formal RACI model and roll it out to the team. The role defining and implementation can prove cumbersome. Sometimes a "less is more" strategy works better if you seek immediate results. .
As with any tool, misapplying or misusing RACI can confuse the issue: for example, can that accountable person really approve a scope change? Making sure that the most important decisions have accountable assigned to someone with the authority to actually decide is crucial.
Misuse of RACI also often leads to misuse of meetings. Failing to declare and stick to the purpose of the meeting can be a major waste of time. It’s important for meeting participants to know why they are there – is it to make a decision, to solve a problem, or just to be briefed?
Also, for organizations relying on support resources, another RAM model may be more applicable, such as CARS, which recognizes support roles. And some frameworks in the Agile project management methodology have responsibility and accountability built in, and thus may not need a separate model.
What is the best way to present a RACI chart?
There are multiple ways to present and share a RACI chart. .Whatever format is chosen, it should be understandable and readily available to team members.
Some useful features of a RACI presentation tool include the ability to customize and color-code cells to highlight priority items. Color-coding team member cells can help the project manager see whether anyone is responsible or accountable for too many items. If using an electronic tool, real-time editing capability helps teams see updates as you enter them.
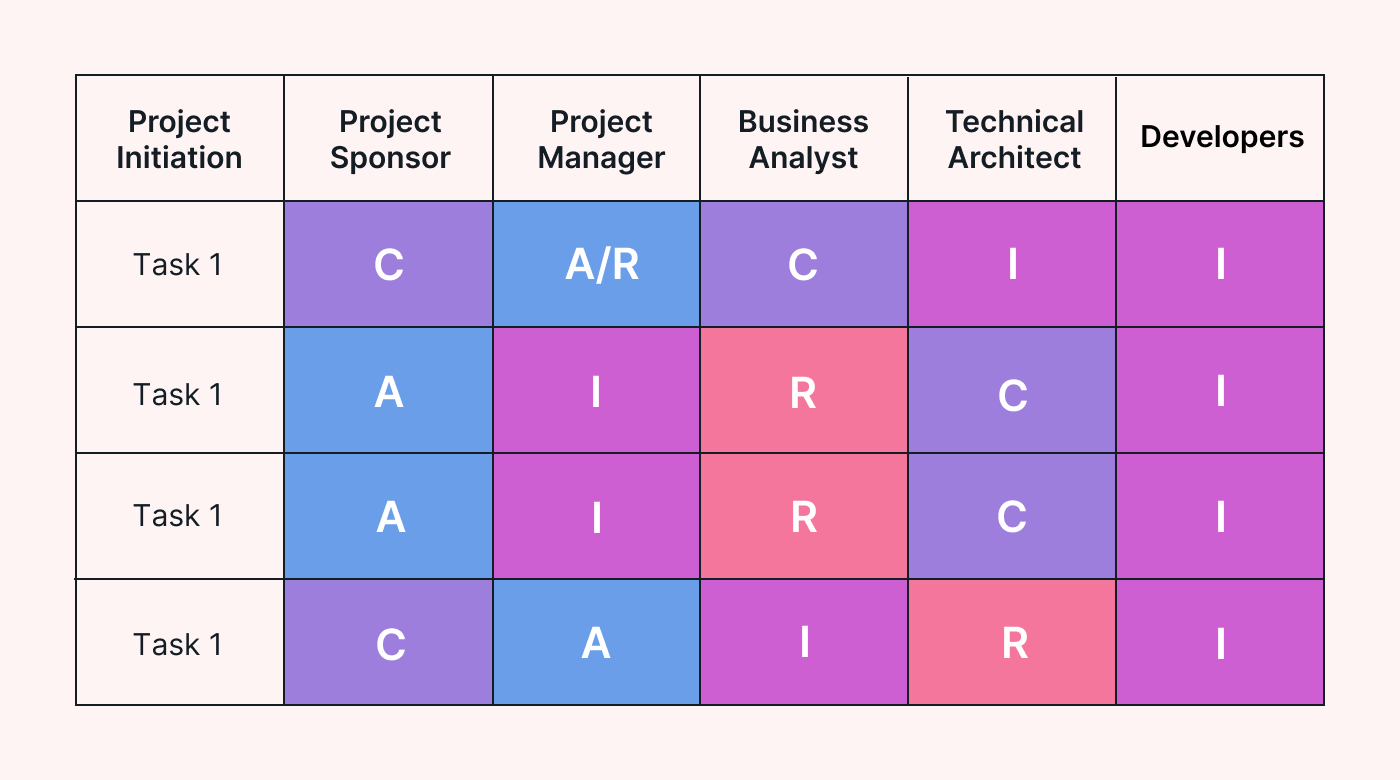
Some matrices include columns for each role, with rows for each task. Others label columns for each team member and rows for each task, then label the role type using its first letter. Here are some popular presentation options:
- Spreadsheet: Spreadsheets are easy to customize and update. Their rows and columns are perfect for RACI chart purposes and they are easy to update and share.
- PowerPoint: PowerPoint slides are a popular format for engaging and informing team members about project details. However, regularly updating and sharing changes with everyone can be cumbersome. People could accidentally view an outdated deck.
- Images: Images may provide information at-a-glance, but they are difficult to update.
- Software tools and templates: Some project management platforms provide RACI matrix templates. A template makes it easy to assign items, track updates, and share the chart with everyone.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Do you still have questions about RACI diagrams? Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about RACI.
Can you have more than one responsible in a RACI matrix?
- Yes, you can. Each task must have at least one responsible person. But it is OK to have more than one responsible person, as long as the responsible members are clear about what each is supposed to contribute.
Can someone be both R and A in a RACI chart?
- Yes, they can. Assigning accountability and responsibility to one person for simple tasks can streamline work and approval. However, the accountable person carries the consequences if something goes wrong or the task finishes late. For this reason, managers or senior leaders usually hold the accountable role.
What kinds of projects can benefit from RACI
- Nearly all projects can benefit from RACI, or a similar RAM model. But it is especially useful for projects that require significant cross-functional involvement, such as marketing, product development and finance on a new product development project. It’s also especially important for complex projects with lots of task dependencies. A RACI tells those who owns the dependent tasks, or the tasks you depend on.
 |
How do you create a RACI matrix?
- Creating a RACI matrix is easy, especially with one of the many free, customizable spreadsheet or slide presentation matrix templates. Embed your RACI chart as a document into Motion so everyone can easily access the chart anytime, anywhere.
Motion can help take RACI assignments to the next level
Are you ready to take tracking roles and assignments in RACI to the next level? You have lots of projects. They all might have multiple tasks, with changing priorities. You have people assigned. Motion can help you get a handle on all your projects, tasks, people and changing priorities.
Using AI, it can plan and replan your and your team’s schedules, automatically prioritizing work so you don’t have to. You can block off time for deep work and personal commitments. Motion automatically builds and rebuilds your schedule based on changing priorities. It automatically finds time for a meeting that works for all your selected participants.
Add tasks, subtasks, and team members. Then, watch as Motion uses the power of AI to build a schedule for each team member automatically, and prioritizes tasks according to importance. What happens if someone's schedule changes? Motion reorganizes the schedule and re-creates each team member's daily schedule without a single mouse-click.
More than 30,000 users around the world already use Motion. Try Motion now to help you harness its power to manage your projects and schedules.






