Six Sigma is a useful tool for teams that want to reduce errors, improve their processes, and increase customer satisfaction.
But if you’re trying to find out what Six Sigma is and how the process works, you might be feeling pretty overwhelmed. There’s a lot of information out there and it’s filled with jargon and phrases that make it difficult to understand.
If you’re looking for a simple breakdown of the Six Sigma methodology, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll explain what Six Sigma is, why it’s important, and how to use it in your next project.
What is Six Sigma in simple terms?
Six Sigma is a system for improving quality and reducing errors in your processes, products, and services. The aim is to minimize mistakes and reduce variability to get as close to perfection as possible.
It grew out of a statistical method to reduce process variability to within plus or minus 3 standard deviations from the mean. That means only 3.4 defects per million products.
The system works by using data and statistical analysis to detect problems. Following the DMAIC framework (more on this later), you’ll logically identify and remove the causes behind any issues. You’ll eventually find the cause of the problem, and you can then put measures in place to improve it.
Let’s use the manufacturing process as an example.
Imagine you’re the production manager at a warehouse that makes cars. Over the last week, you’ve noticed that the number of cars produced is decreasing.
At this point, you’re asking yourself the following question: is there a way to increase production time and make more cars?
The answer is yes — and this is where Six Sigma comes into play.
Using the Six Sigma method, you can identify what’s slowing the manufacturing process down and figure out how to stop it. As a result, the manufacturing process becomes more efficient and you can increase the number of cars in production.
What is the Six Sigma formula?
Six Sigma uses the DMAIC framework (define, measure, analyze, improve, control) to identify and remove causes of process variation.
Let’s look at these in more detail:
Define
In this phase, you clearly define the problem or issues that you’re facing. For example, let’s say that you’re experiencing delays in your shipping process. The problem here is that you’re not shipping items on time and customers are receiving their items late.
You’ll also explore what your opportunities are for improvement, the metrics you’ll measure to make sure your improvements work, and what the customer requires from you.
Measure
In the measure phase, you’ll collect data to understand more about the issue and the extent of the problem. This involves gathering information from observations and surveys, and pulling data from your existing systems.
You’ll also set baseline metrics for comparison. After all, without a baseline, it’ll be hard to tell if your changes are successful.
Using the shipping example again, your baseline measurement might be shipping 50 orders a day. At the end of this process, you’re hoping that the number of daily shipments will increase.
Analyze
During the analysis phase, you’ll review the data you’ve collected to identify the root cause of the problem. You’ll uncover patterns, pinpoint trends, and highlight any inefficiencies that contribute to the issue.
The goal is to gain a deep understanding of the business process and determine the key factors that affect its current performance.
Improve
The improvement phase involves outlining all potential solutions and improvements. Solutions may involve redesigning your entire process, implementing new tools or technologies, or making changes to your workflow.
After identifying all the possible fixes, you’ll evaluate their effectiveness. Then, you can choose the best solution to fix the root cause of the problem and improve the process going forward.
Control
In the final phase, you’ll implement monitoring systems or control mechanisms to make sure your improvements are delivering the desired outcomes.
For instance, let’s say that you updated the shipping process to prevent bottlenecks and get more orders out the door. In the control phase, you might add a shipping tracker to see how many deliveries are sent each day. With this system in place, you can make sure that your improvements are doing their job and that they’re sustainable for the future.
Who uses Six Sigma?
Check out some of the industries that use Six Sigma to manage their projects.
- Manufacturing industry: Six Sigma (sometimes called Lean Six Sigma) has its roots in the manufacturing industry. It was created in 1986 by American engineer Bill Smith, who worked at Motorola at the time. Today, companies in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics use it to optimize their manufacturing processes. For example, in this study a food can manufacturing company improved its cash flow deficit by using Six Sigma.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry uses Six Sigma to improve patient safety, reduce medical errors, and streamline processes in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings. This healthcare study from BioMed Central shows how the Six Sigma framework reduced the duration and variability of clinic sessions.
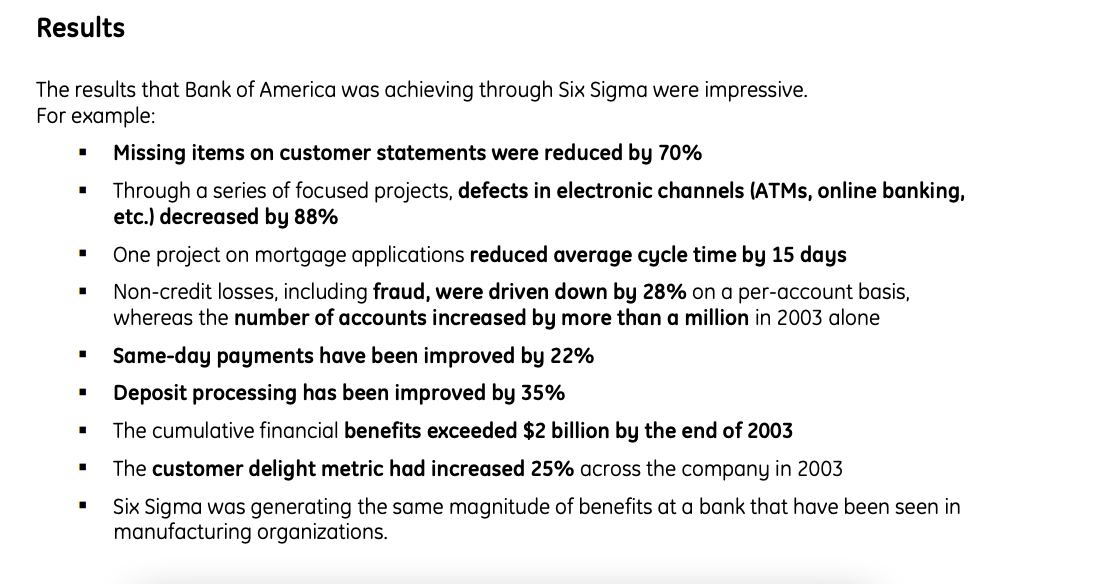
- Financial services: Banks, insurance companies, and financial institutions use Six Sigma to streamline processes and minimize errors in loan processing, underwriting, claims management, and customer service. Bank of America used Six Sigma and found that their average cycle time for mortgage applications was reduced by 15 days. Here are a few of the other benefits they found while using Six Sigma:
- Inventory management: Logistics and supply chain managers use Six Sigma to reduce lead times, improve order fulfillment accuracy, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. This study from the Journal of Advanced Research in Business and Management Studies shows how Six Sigma can optimize inventory management.
These are just a few examples, but you can apply the principles and methodologies of Six Sigma to almost any industry or organization.
Why is Six Sigma important?
Take a look at some of the benefits businesses experience when using Six Sigma.
- To improve quality control: The goal of Six Sigma is to get as close to perfection as possible. This means that it helps businesses improve quality across the board. From the products you sell to customers to your internal business processes, Six Sigma reduces variables to improve quality.
- To increase efficiency: By identifying and eliminating bottlenecks and removing redundancies, you can be more efficient with your time. As a result, you can improve productivity, and deliver products and services to customers more quickly. For example, if you use an intelligent online work scheduling tool like Motion, you can eliminate the process of managing your schedule every day and increase your efficiency by 137%.
 |
- To make informed business decisions: Six Sigma promotes a culture of evidence-based decision making. In other words, all of the decisions you make are based on reliable data rather than assumptions or guesswork. This means you’re making informed decisions that are in the best interests of the company.
How do you perform a Six Sigma project?
A Six Sigma project usually follows a project charter with these steps:
 |
Let’s walk through these steps in more detail.
1. Outline your business case
The first step is to outline the business case for improving the process, product, or service.
A business case is used to convince decision-makers to approve the work. It’ll show them why you want to make improvements and why it’s necessary in the first place.
The business case should define the following information:
- How the customer is impacted by the problem you’re facing
- How long they’ve been impacted
- The benefits of making improvements
- The risks of not making improvements.
If you’re new to writing a business case, don’t worry. Here are some tips to get you started on the right foot:
- Be concise. Your business case should be short, to the point, and easy to understand. That way, it’s easy for decision-makers to review important information. Keeping it simple also reduces the risk of misinterpretation, which can cause problems when trying to get approval.
- Demonstrate the value. Management will want to know how the changes will benefit the business. If it doesn’t benefit the business, it’s unlikely you’ll get approval to make changes. So, to show decision makers why it’s worth doing, use concrete evidence and offer data-backed predictions to show them why it’s beneficial to the success of the company.
2. Write a problem statement
A Six Sigma problem statement outlines the problem you’re trying to overcome. It provides the entire organization with a clear and simple overview of what the challenge is and the impact it's had on the business.
Problem statements look slightly different for every project, but here are the key elements you’ll want to include in your own statement:
- The challenge: What’s the problem you’re facing?
- Timeframe: When and where was the problem discovered and for how long has it been an issue?
- Impact: How has it impacted the business or the end user?
- Importance: Why is it important to fix it?
Here’s an example of a problem statement to demonstrate:
In the last six months, online subscriptions have decreased by 40% resulting in a loss of $5,000.
3. Write your goal statement
After writing your problem statement, you can now write your goal statement.
A goal statement establishes what the end result should be and when it should be complete. It’s like the other side of the coin to your problem statement. The problem statement outlines the issue, while the goal statement outlines how to solve it.
To create an effective goal statement, it helps to use SMART goals.
SMART is an acronym for specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. It’s a goal-setting framework that helps project management teams create clear and precise goals.
 |
Here’s an example of a SMART goal:
To increase online subscriptions by 40% over the next six months by improving the online sign-up process.
This goal statement is simple but clear. You know exactly what you want to achieve, how you plan to achieve it, and when it’s due.
4. Create your project scope
Project scope outlines all the goals, milestones, deliverables, tasks, and deadlines for an upcoming project.
When it comes to Six Sigma, creating the project scope is a vital part of the process. It sets boundaries for your work, aligns the project team, and makes sure that everyone has a clear picture of what the project involves.
Here are a few best practices you can follow to create a simple project scope for your Six Sigma project:
- Add your goals: Clearly outline what your goal is for the project. This will make sure that all the work throughout the project aligns with the goal. You can use the information you’ve already gathered in your business case, your problem statement, and your goal statements to determine what the project goals should be.
- Establish project boundaries: Determine the boundaries and limitations of the project so team members know what they should (or shouldn’t) do. For example, if managing a construction project, you might state that all work must be carried out within a certain location. Anything beyond that location isn’t covered by the scope. By defining these boundaries, you prevent scope creep (when changes are made to the project without approval) and make sure everyone on the project team is on the same page.
- Identify deliverables: Outline the deliverables that’ll be completed by the end of the project. These can be tangible products, documents, reports, or any other measurable outcomes. For example, if you're implementing a software project, the deliverables may include a functional software system, user documentation, or training materials.
Find out more about defining project scope in this article: How to Successfully Manage a Work Project (and Impress Your Team and Boss).
Use Motion to manage your Six Sigma projects
Six Sigma is a useful tool for any business that wants to minimize errors, decrease customer issues, increase customer satisfaction, and streamline its processes.
To help manage the Six Sigma process, consider using Motion’s AI-powered calendar. With our platform, you can easily track your workflow, schedule tasks, and identify areas of process improvement.
Sign up for the free trial to get started.