In the fast-paced business world, orchestrating seamless production processes is essential to achieving success — but it's not always easy. You have different priorities to balance, conflicting deadlines, and teams of people to manage.
Enter production planning. From manufacturing to project management, effective production planning can help you improve resource allocation, reduce costs, and meet critical deadlines.
In this article, we’ll dive into the core principles of production planning. We’ll walk you through the methodologies you can use, the production planning princess, and the best practices you can follow to set yourself up for success.
What is production planning?
Production planning is the process of aligning resources and objectives to meet market demand. It helps you optimize your resources, reduce costs, and meet production deadlines as efficiently as possible.
The process involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and capacity planning to forecast future demand accurately. In doing so, you ensure you run an efficient production schedule.
For example, ensuring you have sufficient equipment, raw materials, and resources to meet customer orders as quickly as possible.
 |
Various factors influence production planning. From customer demands and external suppliers to technological advancements and regulatory factors, a lot can impact your production schedule.
This means that production planning is an ever-evolving process. You need to keep on top of all these external factors to ensure your production plan incorporates any changes and remains as efficient as possible (more on how to do this later).
Production planning methodologies
There are different types of production planning methodologies you can use depending on the specific needs and objectives of your business. Let's take a look at some standard methodologies in more detail.
Just-in-time (JIT) planning
JIT is an inventory management system. It focuses on minimizing waste by producing items as and when needed.
Let's say you're manufacturing a car. Instead of keeping a roster of airbags in your inventory, you only order them when you need them for production. It's a great way to keep inventory costs down, but it can be challenging to keep on top of.
If you don't have everything you need, you're constantly thinking about when to order new items and trying to align delivery dates with production schedules. It's a lot to manage, but can be done with an efficient production plan. And, as mentioned, it does bring inventory costs down.
Demand-driven MRP (DDMRP)
DDMRP is an inventory control process for optimizing your inventory levels. It’s based on real-time demand, ensuring you have the exact amount of resources and raw materials for the amount of products you make.
Like JIT, DDMRP is a great way to minimize inventory costs. But it does mean that you won’t have spare resources or materials around if and when you need them, so that’s something to consider if this is a good option for your business.
However, it benefits businesses that experience volatile production demand, have complex supply chains, or encounter variable lead times. Why? Because it allows you to get hold of the materials you need when you need them. You don’t waste time, money, or resources you don’t need.
Agile production planning
Agile project management methodology allows teams to work in short sprints and focus on continuous improvement. Because of this, Agile frameworks give you the flexibility to adapt to a fast-changing environment.
Take a look at a Kanban board as an example.
As an Agile framework, Kanban is flexible. It involves pulling tasks into a workflow and moving them through different stages of the project (or production) lifecycle.
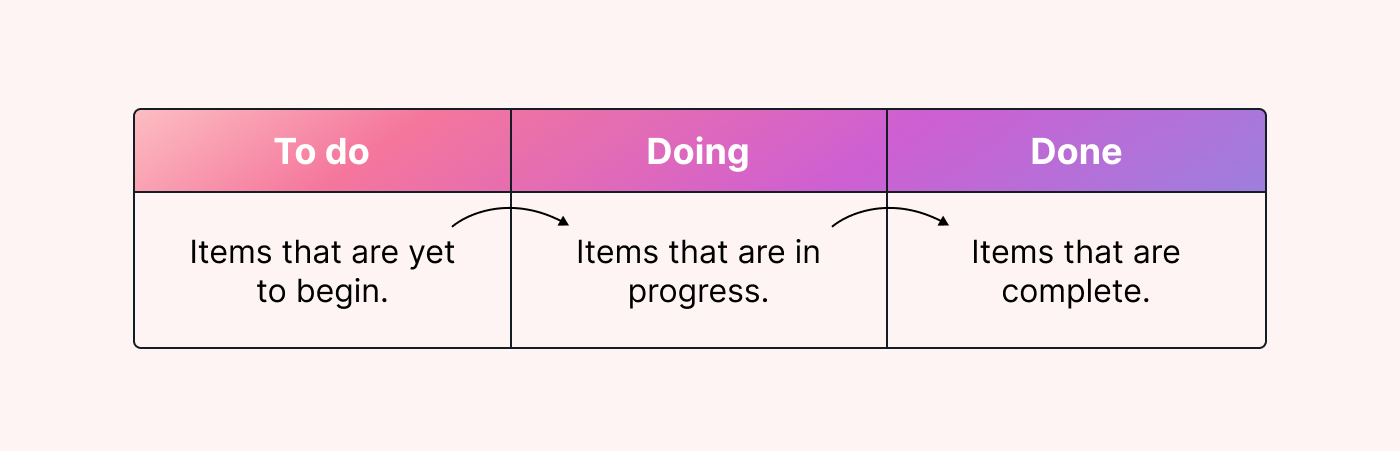 |
The great part is that you can update your workflow based on your current workload. How? By setting work-in-progress (WIP) limits.
These limits help you control the work in your production schedule so your team isn’t overwhelmed. You can change these limits at any time to allow for more flexibility.
However, Agile isn’t for every production scheduling approach. It allows for more flexibility, but if you need structure and rigidity in your schedules, you’re better off using a more traditional form of production planning (like JIT or DDMRP).
Find out more about the Agile methodology here.
The production planning process
Now that we understand how production planning works, let’s walk through each step of the process.
1. Define planning objectives and goals
Start by establishing clear objectives and goals for the production planning process. These production goals should determine what you want to achieve from the process and how they align with your organization's mission and vision.
If you’re unsure where to start, look at the SMART goals framework. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
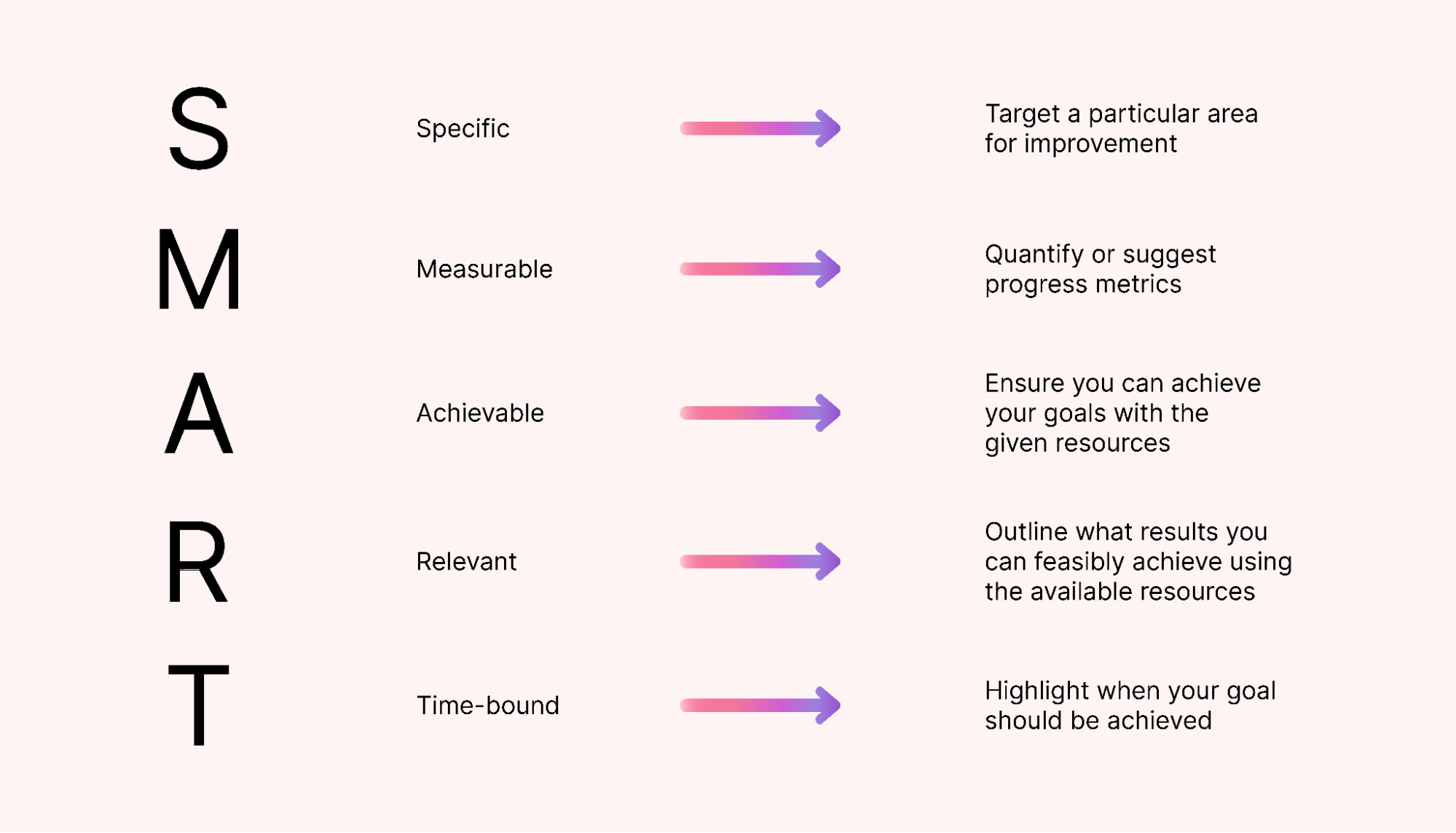 |
Using this framework, you can create clear, specific, and measurable goals for your production planning process. It also gives you direction, ensuring you know what you want to achieve and keeping you on track throughout the process.
2. Analyze demand and forecast
With a clear picture of what you want to achieve from your production planning, you can now think about how to predict demand. This will help you forecast how many orders you’ll likely get, what resources you’ll need, and how to allocate them effectively.
There are a couple of ways you can approach this process:
- Review historical data. Look at previous production schedules to get an idea of how long the process takes, what resources and materials you might need, and how many orders you need to fulfill. This isn’t an exact reflection of your future production schedule, but it gives you a starting point to work from.
- Look at market trends. Take a step back and look at the marketplace. Are there any trends that influence your production schedule? There may be world events that might slow supplier deliveries. Or a new competitor on the market that could reduce your order volume? All of these elements can have an impact on demand.
3. Develop production schedule
Based on the information from your demand analysis, you can now start production scheduling.
Start by reviewing your current resources and production capacity. This will help you identify what to include in your production schedule, and what resources you might need to deliver your final products.
Here’s what the production schedule should include:
- Tasks and activities. The schedule should outline the sequence of tasks and activities your production team needs to complete to meet production targets. Consider factors like lead times and setup times to create an accurate timescale from start to finish.
- Costs. Keep a log of all the production costs, such as materials, equipment, and time spent. This will help you track your outgoing funds and ensure you're within budget.
- Inventory. Make a note of all materials, products, or other items that form your inventory. Tracking these items is vital for a successful schedule, as it shows you what you have available and what you might be missing.
Find out more about creating a detailed production schedule.
4. Look for (and manage) risks in your production process
Before your production process goes live, consider any risks you might face.
production flow. For example, any disruptions to the continuous flow of production and interruptions in your supply chain.
Having a clear picture of potential challenges allows you to implement contingency plans. As a result, you're much better prepared when things don't go to plan.
To identify potential risks, you can create a risk matrix.
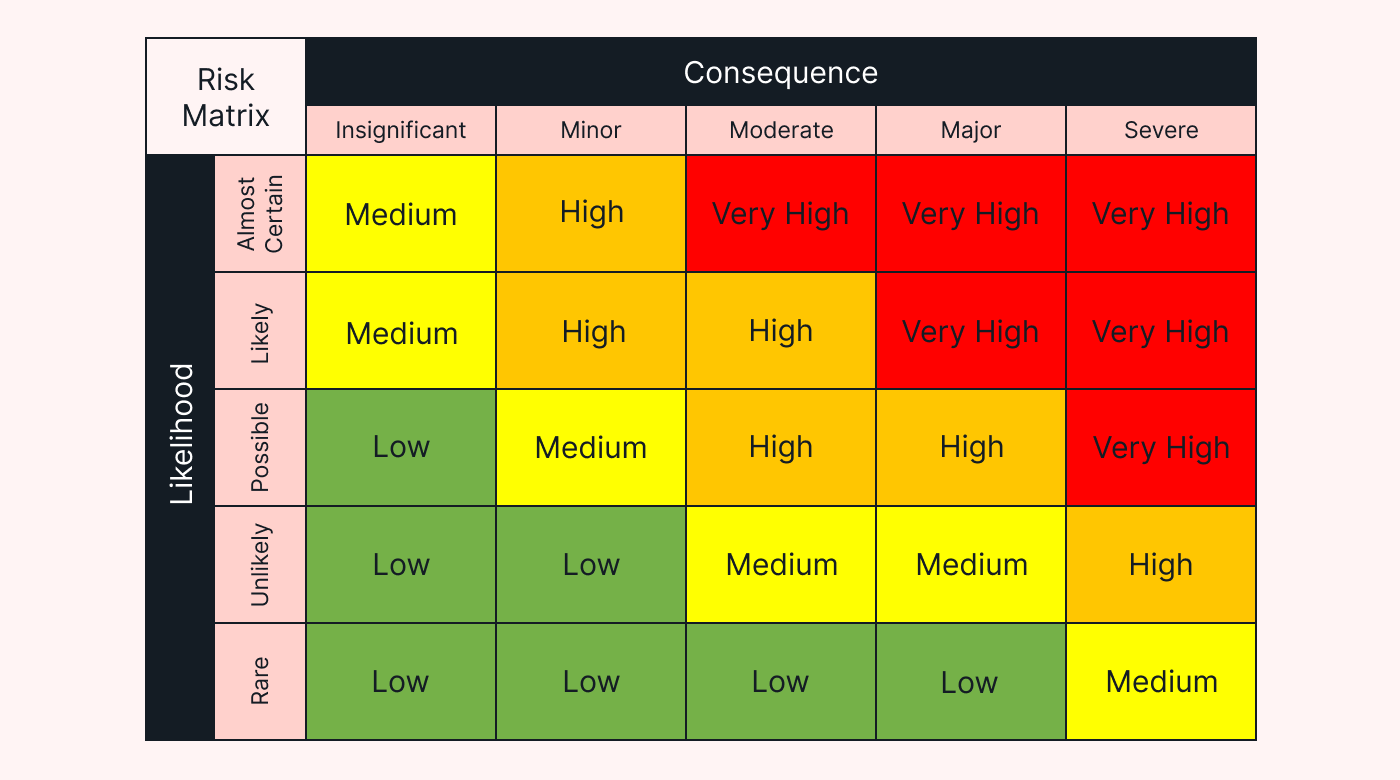 |
Find out more about how to create an effective risk management process.
Tips, tools, and techniques for better production planning
Here are some tips for creating and managing a successful production plan.
Collaborate
As the adage goes, teamwork makes dreams work.
To run an effective production schedule, you must collaborate with your production team to deliver products on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
This is where using a collaborative platform to manage your production process can be helpful.
Take a look at Motion as an example. Production teams can easily visualize their schedule, share updates, and keep up to date on the latest developments in the production plan.
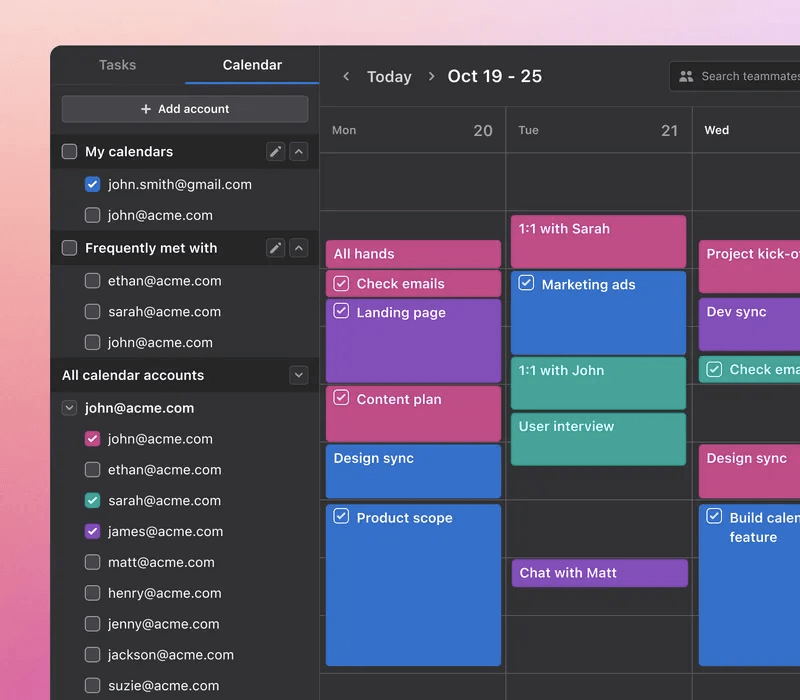 |
As a result, production teams can streamline their efforts and work together more efficiently.
Visualize the process
It helps to have a clear visual of the production process to keep on top of things. That way, you can see how the process is going in real time (and whether there are bottlenecks).
Again, having a centralized platform to visualize all this information is helpful. With an online tool like Motion, the entire production team has real-time visibility of the production schedule. As a result, they can easily see if they're on track to deliver the finished product on time and within budget.
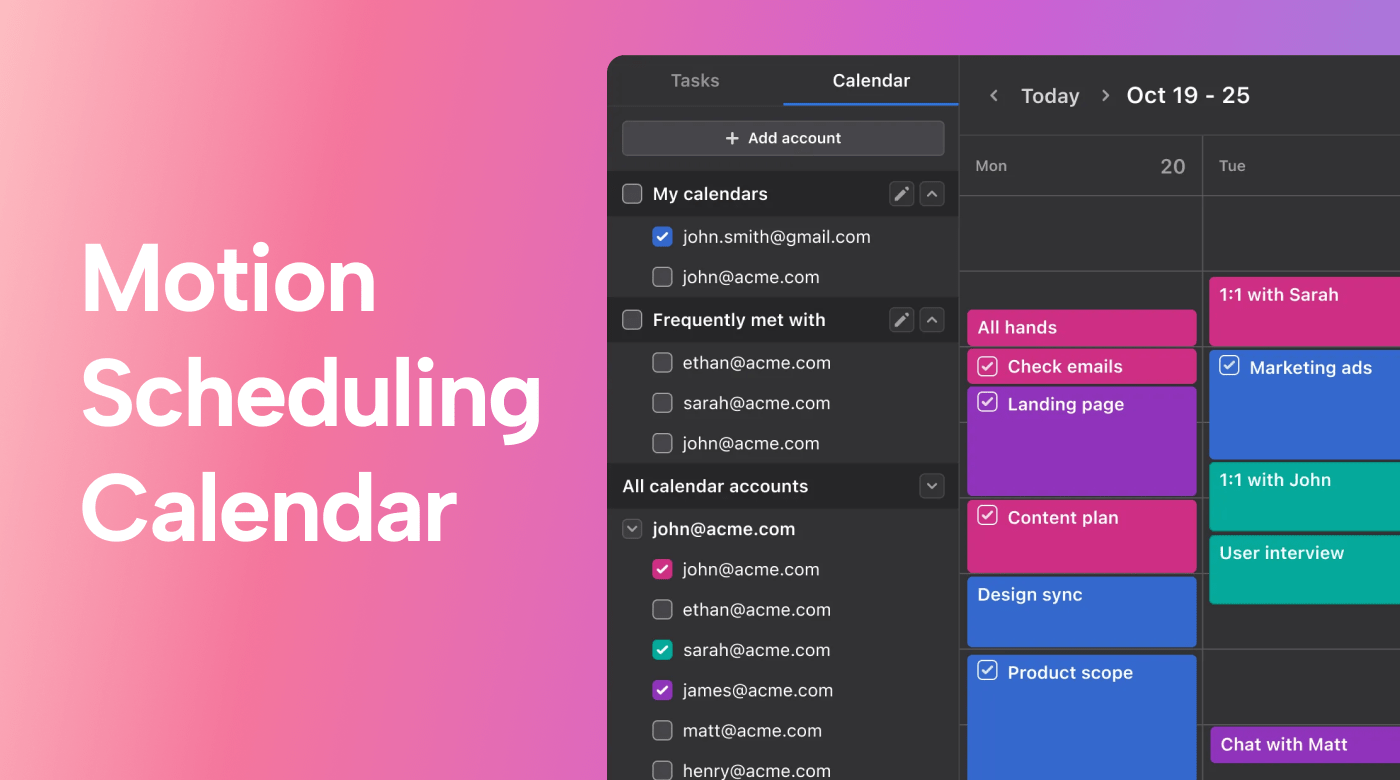 |
And because Motion is an online tool, team members see the most up-to-date version of the schedule. If you make changes, it automatically updates the platform for everyone to see.
Automate your processes
To streamline your production process even more, consider using automation. This will save you time, speed up your production process, and reduce human error.
How? If a platform is automatically moving things along, it reduces the chance of human error.
Automation is included in most production software. Here are some of the tools to look out for:
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. An ERP system is an operations platform that helps companies manage their processes and analyze resource availability. Most ERP systems will provide automation, but review the tool's functionalities to be sure.
- Material requirements planning (MRP) software. MRP platforms help businesses manage their materials and resources throughout manufacturing. They review production schedules, lead times, and demand forecasts to help you identify what resources and when you need them. Automation can do this without manually placing an order — the system takes care of it for you.
- Task management software. Task management platforms can help you plan and manage all the activities in your production schedule. Depending on the platform, you can automate different parts of this process. For example, marking a task as complete automatically sets the next one in motion (pun intended — find out more about Motion's Task Manager here).
Use Motion for production planning
By now, you should have a good understanding of production planning. You know what it is, the methodologies to bring it to life, and the steps you can follow to get your production schedule up to scratch.
The next step is to use your newfound knowledge to create your production plan. This is where Motion can help.
Motion is an online work management tool that can streamline your organization, improve collaboration, and boost productivity.
Give Motion a try with our 7-day free trial to see how we can help you with your production planning.