Delivering projects on time is easier said than done. There are conflicting deadlines to manage, resources to allocate, and unexpected hurdles to deal with.
The good news is that there’s one way you can make it easier to complete your projects on time — by identifying your lead time. When done well, it can help you minimize risk, improve resource allocation, and schedule realistic project deadlines.
In this article, we’ll be focusing on lead time in project management. We’ll show you what it is, how to calculate lead time in your own projects, and how to improve your lead time for a smoother and more efficient workflow.
What is lead time in project management?
There are a few different ways that businesses can use lead time. Manufacturers use it to calculate how long it takes to create and deliver a product; sales teams use it to estimate how long it takes to convert a lead into a paying customer; and so on.
In project management, lead time refers to the amount of time required to complete a specific task or activity within a project.
It represents the time between the start and end of a task, considering any dependencies or constraints that may affect its duration. For example, any potential delays, changes in resource availability, or changes to the project scope — all of which can affect the duration of each project task.
By identifying your project lead time, you get a good idea of how long your project will take. For this reason, lead time is often associated with the critical path method (CPM), which involves identifying crucial activities and their dependencies to determine the overall project timeline.
You can also use lead time to assess project feasibility, set realistic deadlines, and allocate your resources efficiently. Plus, it helps you identify potential bottlenecks or risks that may impact the project schedule.
What’s the difference between lead time and lag time?
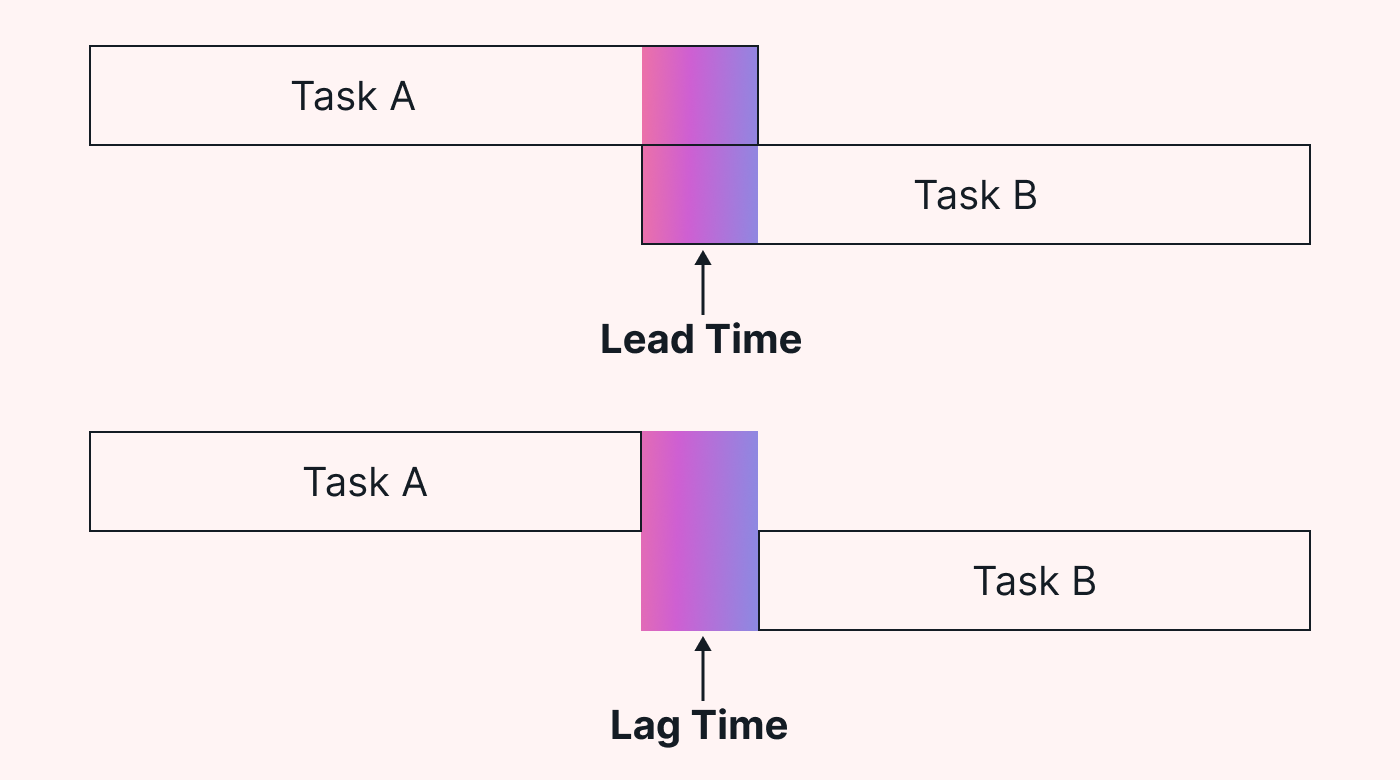
Lead time in project management is different from lag time. They’re both important scheduling techniques, but they represent different approaches to task sequencing.
Lead time allows for overlap between tasks and early starts of successor tasks, while lag time introduces a delay between the predecessor and successor tasks.
Here’s a visual that represents how it works:
 |
Let’s use software development to demonstrate how lag time works.
The completion of coding is a predecessor task, and the testing phase is the successor task. To allow for coding reviews and bug fixes, you introduce a two-day lag time between these tasks. That way, you have the time you need to review the coding before moving on to testing.
Why is lead time important in project management?
Let’s take a look at some of the reasons lead time is important in project management.
- To effectively plan and schedule work. Lead time provides project managers with a realistic understanding of how long each task or activity will take to complete. As a result, you can create accurate project schedules and timelines (or at least, as accurate as possible — nothing is free from unexpected delays and challenges).
- To allocate resources. By knowing the lead time for each task, project managers can ensure that the necessary resources (such as personnel, equipment, or materials) are available when needed. This prevents resource shortages and makes sure you effectively use the right resources at the right time.
- To identify and mitigate risks. By understanding the time required for each task, you can identify potential issues that could crop up as the project progresses. In doing so, you can create contingency plans to mitigate risks and minimize the impact.
- To assess project success. Lead time helps you assess project progress and efficiency. How? By comparing the planned lead time with the actual lead time (also known as schedule performance). It helps you evaluate project performance, identify areas for improvement, and make the necessary adjustments to keep the project on track.
How to calculate your lead time in project management
Let’s walk through the steps you can follow to calculate the lead time in your projects.
Define the start and end point of your task
The first step is to determine the start point of a task (which is typically the initiation of the task) and the endpoint (which is the completion of the task).
Follow these steps to clearly define the start and end points of your tasks:
- Define your task. Start by clearly defining the scope and objectives of each task in the project. This will make sure that you have a thorough understanding of what each task involves, which will help you determine the start and end points.
- Pinpoint the exact start point. Now, you can identify the task's start point, which involves pinpointing the action that initiates the task. This could be the completion of a predecessor task, a specific action, or a certain date in the project timeline.
- Identify when the task ends. The last step is to determine the task’s endpoint. To do this, you can review factors like task complexity, available resources, and any dependencies with other tasks. From here, you’ll have a good idea of the estimated completion date for each task.
- Estimate task duration. After pinpointing the start and end dates for your tasks, you can determine the actual duration it takes to complete the task. This can be based on historical data, estimates, or actual measurements from similar tasks or projects.
When it comes to visualizing the start and end points of your tasks, an online tool like Motion can help.
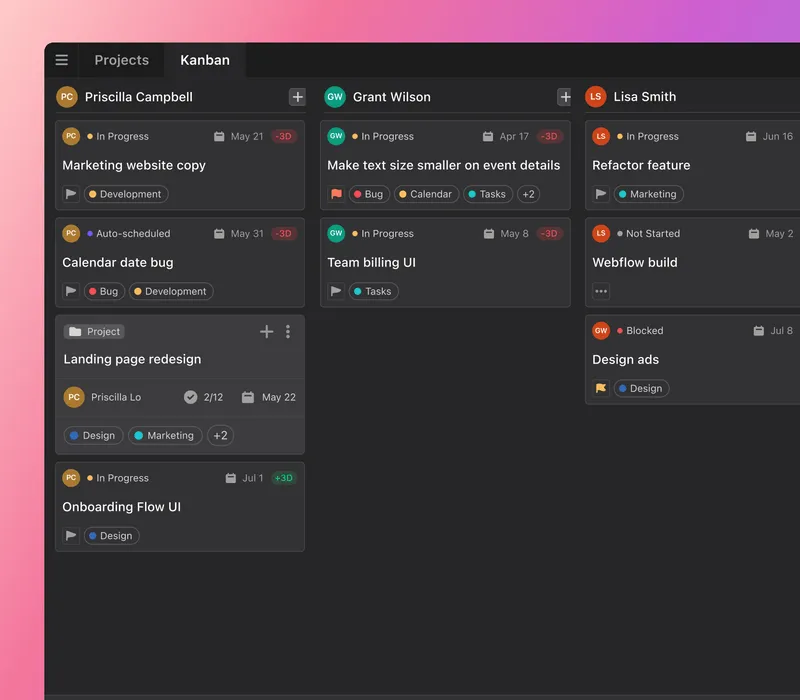 |
With our software, you can visualize all your tasks in one location and plot the start and end dates for each task.
Account for dependencies
When calculating lead time, you need to account for dependencies for each task. This means thinking about the time required for dependent tasks to be completed and how this can impact the lead time of other tasks.
Here are some of the types of dependencies you need to be aware of when identifying lead time:
- Finish-to-start. This is the most common type of dependency. It means that one task must be finished before the next task can start. For example, if task B is dependent on task A, then task A needs to be completed for task B to begin.
- Start-to-start. In this type of dependency, two tasks must either start simultaneously or have their start dates aligned. For instance, task A and task B must start at the same time for the work to be complete.
- Finish-to-finish. In this case, two tasks must either finish simultaneously or have their finish dates aligned. So, task A and task B must wrap up at the same time for the project to progress.
- Start-to-finish. This type of dependency is relatively rare. It means that one task must start for the other task to finish. If task B is dependent on task A, then task B can’t finish until task A starts.
Calculate lead time
With a clear picture of task durations and dependencies, you can now calculate lead time.
This involves adding the task duration (and the durations of any predecessor tasks) to obtain the total lead time.
Here’s how to use this calculation:
Task end date - task start date = task lead time
If you need to calculate lead time for multiple tasks within a project, repeat the above lead time formula for each task individually. Then, if you want to calculate your total project lead time, add all the individual task lead times together.
Improve your project lead time with these simple steps
Now that you know how to calculate lead time, take a look at some of the ways you can create a shorter lead time in your projects.
Keep an eye on progress
Lead time calculations are estimates. This means that they’re not foolproof, and you may need to update them as tasks progress.
This is why it’s so important to keep an eye on progress in real-time. If any unexpected challenges crop up or if you’ve incorrectly estimated task durations, you need to be on top of it. In doing so, you make sure that you have accurate lead time calculations throughout your project's lifecycle.
A good way to keep track of your lead time is to use a real-time work management tool like Motion. With our platform, you can easily see how your work is progressing and whether your task estimates are accurate. If things aren’t going to plan, we’ll let you know.
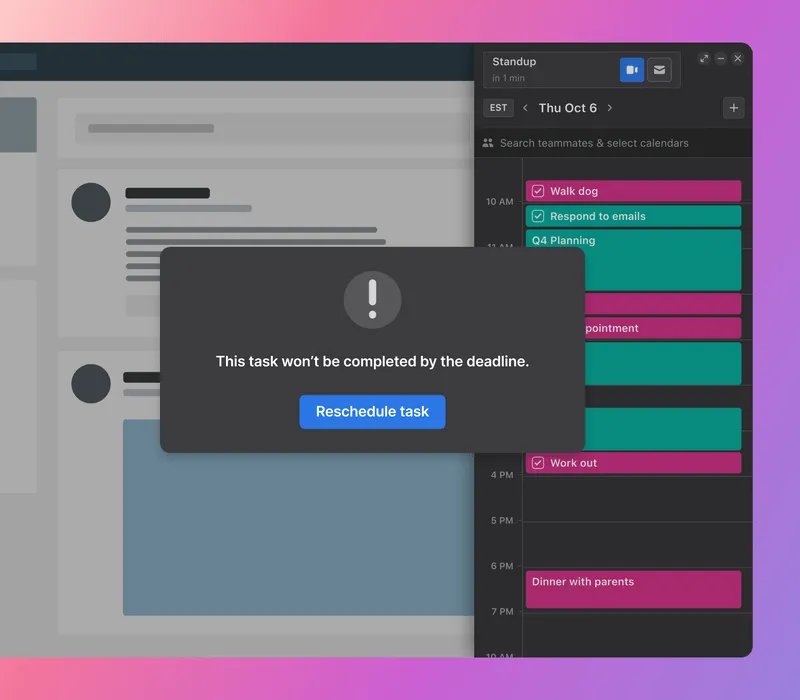 |
If you need to update your lead times for any reason, it’s easy to make the changes in Motion. Plus, when you amend the duration of one task, our system automatically updates the rest of your project schedule.
Automate your project
Automation eliminates the need for manual, repetitive tasks. It saves you time, streamlines your work, and as a result — helps you reduce lead time.
Think about it. The faster you can complete your tasks, the lower your lead time will be. Think about data entry as an example.
By automating the time-consuming process of data entry, you spend less time manually adding data to a system and more time actually working on the task. Throughout an entire project, this can significantly save time and speed up project progress.
So when it comes to finding a platform to manage your projects and track lead times, keep an eye out for automation. A platform like Motion, for example, can automate different elements of task management to speed up your workflow.
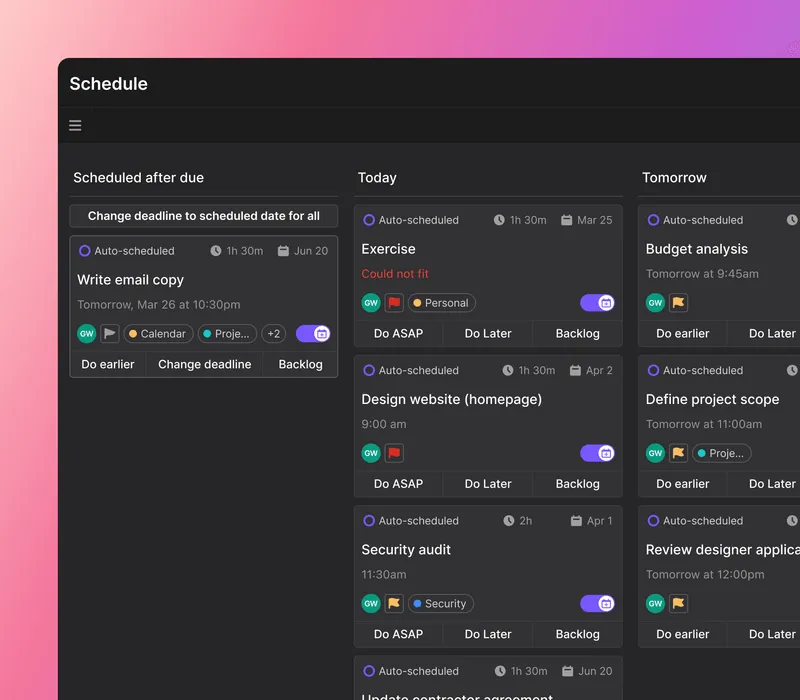 |
For example, you can automatically move tasks through the stages of the project lifecycle, assign certain tasks to specific people, or create automatic reminders and notifications.
Consider using Agile frameworks
Agile is a flexible approach to project management. It emphasizes collaboration, continuous improvement, and delivering value to customers in shorter cycles of work. As a result, you can reduce your lead time by delivering work incrementally (instead of in one go at the end of the project).
There are different Agile methodologies you can use to structure your projects. Here are a couple to choose from:
- Kanban. Kanban is a visual Agile framework. It uses columns to represent the different stages of your workflow, with tasks moving through them depending on how they’re progressing. It helps teams manage their workflow, identify bottlenecks, and improve efficiency. By visualizing the status of each task, you can use this framework to identify your lead times and keep track of task progress in real-time. It’s also a great way to limit your work-in-progress and make sure your project team isn't overburdened with tasks.
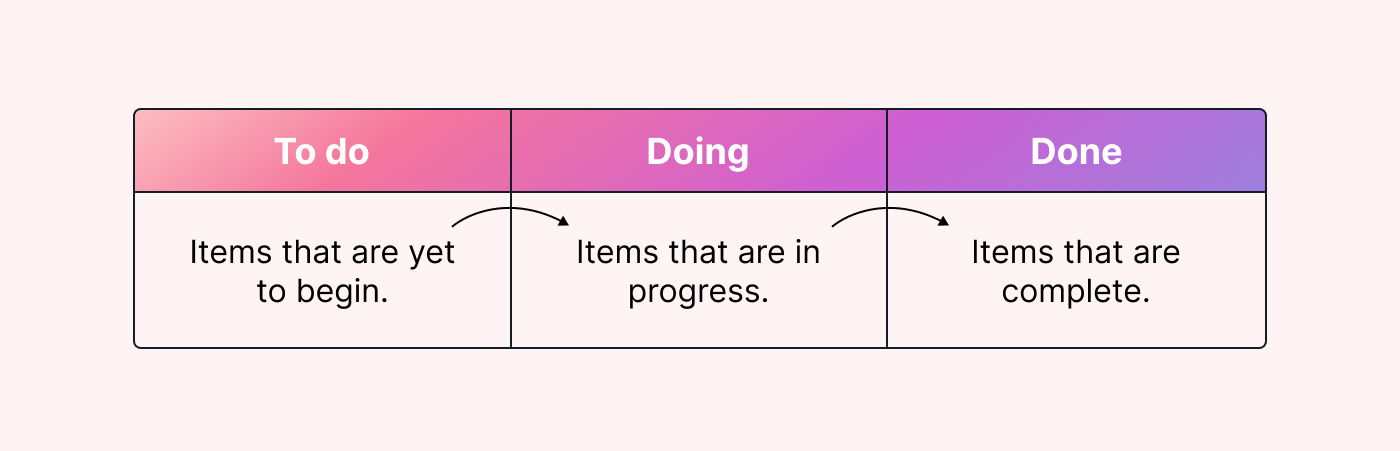 |
- Scrum. In Scrum, everyone works together to achieve a common goal in short cycles called sprints. The process follows specific steps involving daily meetings and frequent reviews to adapt to changes. As a result, you can ensure you’re working as efficiently as possible to deliver the most value. You can find out more about Scrum in project management here.
Use Motion to track your lead time
Lead time is an important metric for project success. It shows you how efficient your workflow is, how well you’re allocating resources, and whether you’re on track to complete specific tasks throughout the project.
Consider using a tool like Motion to make tracking your lead time easier. With our online work management tool, you can easily track and monitor lead time for all your projects. Add task durations, share updates with your project team, and keep up to speed with progress in real-time.
Sign up for a free trial to see how it works.