Planning a schedule for a work project can be challenging. You’re trying to allocate your resources, plan your tasks, and make sure you deliver the end result by a certain date. It’s a lot to juggle.
Cycle time can help you manage this process. It gives you a better idea of how much time you need to complete a process, so you can effectively manage your schedule and dish out your resources.
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about cycle time. We’ll show you the cycle time formula, the benefits of using it, and how to overcome some of the common challenges.
What does cycle time mean?
Cycle time is a metric for measuring development speed in Agile projects. It helps teams predict how long their work will take from start to finish. This makes it easier to plan your schedule, allocate resources, and improve efficiency across your workflow.
We’ll look at these benefits (and a few others) in more detail later.
Cycle time can also pinpoint how long it’ll take to complete a certain task, process, or part of a product. It doesn’t always apply to an entire process, which means you can use it to find the average time spent on different areas of your work.
What is the formula for cycle time?
Here’s the formula you can use to calculate cycle time:
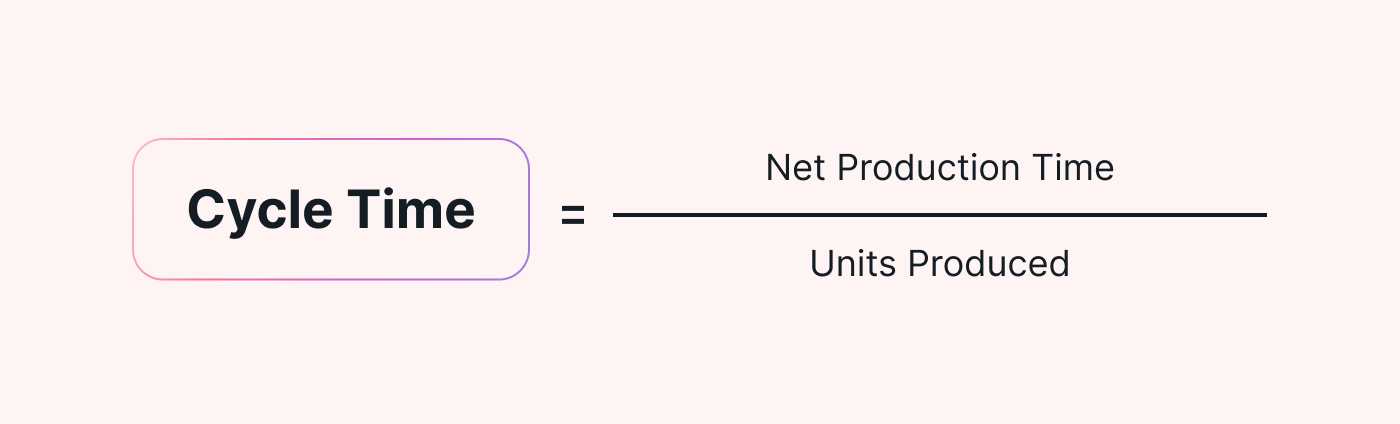 |
Net production time / Units produced = Cycle time
Net production time (NPT) is the total amount of time spent working on the task, meaning that it doesn't account for any breaks. When you add this figure to the formula, make sure you only add the total working time.
Now, let’s use an example to show how the formula works.
Imagine that you’re a project manager at a software development company. You have a new project on the horizon, but you need to estimate how long the project will take so you can update stakeholders and schedule the work accordingly.
This is where cycle time comes into play.
Using previous projects as a guide, you use the cycle time formula to estimate how long the next project will take. Here’s what you find:
- The net production time is an average of two weeks
- The average number of units produced is two
Based on this information, here’s what the cycle time looks like:
14 days / Two units = 7 days
In this situation, the average time for your software developers to create two units of work is seven days.
Why do we measure cycle time?
Let’s take a look at some of the benefits that come with measuring cycle time.
To provide accurate time estimates
Imagine that you’re trying to estimate the duration of a new project. It’s a totally new project and you don’t have any similar projects to review before making your estimation.
You’re estimating based on how long you think each task will take, but it’s not based on any concrete evidence. This makes it harder for you to make an accurate estimate for the project duration.
But with the cycle time formula, you’re using real experience to inform your predictions. This means you’re in a better position to estimate a fairly accurate project duration.
When it comes to reviewing task duration and project timelines, it helps to use a platform that displays all this information in a simple format.
With Motion, for example, you can easily open your calendar and see exactly what’s in your schedule and how long each task takes to complete.
 |
This means you can easily review the duration of certain tasks and activities to easily calculate your net production time.
To improve processes
By measuring cycle time, you can identify areas where the process is slow or inefficient and take steps to improve it.
For example, if the cycle time shows that too much time is spent on a particular task or deliverable, you can reevaluate the time you’ll need to spend on certain tasks. As a result, you can be more effective with your time.
To allocate resources
Knowing the average cycle time of a process can help you plan your resource allocation.
Think about project management as an example. If you know roughly how long a project will take, you can assign the following resources:
- Capacity: You can figure out how much time each team member will spend working on the project.
- Budget: You can estimate how much money the project will need to run successfully and allocate the budget accordingly.
- Materials: You can make sure that all the necessary materials are available for the project.
- Equipment: You can identify the equipment that the team needs to complete the work and make sure it’s available for the duration of the project.
By having a clearer picture of how to allocate these resources, you’ll reduce waste, optimize your spending, and maximize your time.
What are the challenges of calculating cycle time?
Although measuring the average cycle time has its benefits, there are some hurdles to be aware of. Keep reading to see what these challenges are (and how to overcome them).
Defining process boundaries
It can be difficult to define the beginning and end of a process.
For example, let’s say that your team completes a project. You then use this information to estimate the cycle time for a future project. However, after feedback from stakeholders, the team has to go back and make changes to some of the deliverables.
In this situation, the changes should have been included in the net production time, but they weren't. This means that the cycle time calculation isn’t as accurate as it could be.
The good news is that there are ways to improve this process and make sure that you accurately record the NPT. Here are some of our tips:
- Identify what’s included in the process. Start by making sure you know what to include when estimating the NPT. If you add irrelevant tasks or information, you’ll skew the results of your calculation. So define exactly what tasks, processes, activities, and deliverables you’re adding to your formula so you know that you’re including the necessary information.
- Continually revisit cycle time formulas. To make sure your calculations are up to date, keep going back to make sure they’re up to date. For example, if there are any changes to a project or task after you’ve performed the calculation, go back and update it so it’s accurate.
Communication siloing
Communication silos form when different people or departments work separately from each other and don’t collaborate effectively. As a result, work can be duplicated, deliverables can be below quality standards, and deadlines can be missed.
Siloing is also a problem when you’re trying to calculate your cycle time.
Why?
Because if you don’t have the full picture, you won’t get an accurate calculation. And when teams aren’t communicating effectively, chances are you’ll struggle to get a clear picture of task duration and project completion.
Here are some ways you can prevent communication siloing to ensure your cycle time calculation is as accurate as possible.
- Use a collaborative platform. With a collaborative platform to manage your project, teams can keep in touch and see how everyone is progressing with their work. It provides transparency, which makes sure everyone’s on the same page and heading in the same direction.
 |
- Encourage open communication. Make sure everyone in the project team knows that communication is encouraged. Let everyone know who they can reach out to if they have queries, and provide an easy method of quick communication between members. For example, using a tool like Slack.
Cycle time FAQs
Do you still have some burning questions? You’re in luck. We’ve outlined some of the most frequently-asked questions about cycle time to give you the answers you’re looking for.
What is the difference between cycle time and takt time?
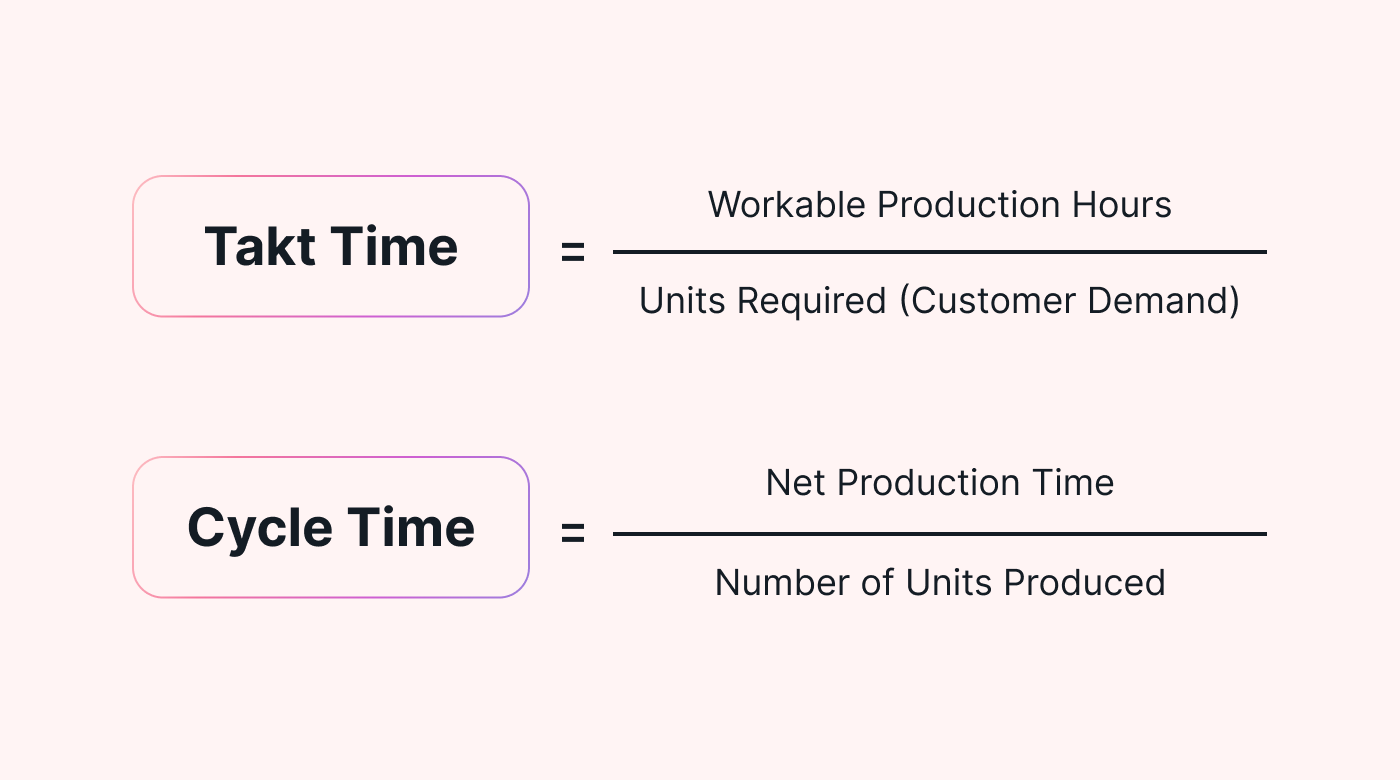
Cycle time is the time it takes to complete a single cycle of a process. Takt time, on the other hand, is the rate at which you need to complete a product or service to meet customer demand.
Takt time is calculated by dividing the available production time by the customer demand during that time.
 |
It helps teams locate areas of improvement in their production cycle and makes sure that customers are getting what they want as fast as possible.
What is the difference between cycle time and process time?
Cycle time includes all the time it takes to complete a process, while the process is focused on a specific development stage. For example, you might outline the process time for tasks to move through the ‘iteration’ stage of a project.
What is a normal cycle time?
There’s no ‘normal’ cycle time. It varies widely depending on the process, industry, and specific circumstances. For example, a manufacturing process may have a normal cycle time of 10 minutes to produce one unit of output. A customer service process may have a normal cycle time of 5 minutes to resolve a customer inquiry.
Track your cycle time with Motion
Cycle time is a useful metric for calculating the actual time spent on tasks, processes, and projects. It’s also a handy tool for predicting how long future items will take to complete. As a result, you can allocate resources, streamline your processes, and provide stakeholders with pretty accurate time estimates.
To track and manage how long your projects take to complete, take a look at Motion. With our intuitive platform, you can easily review all your tasks in a single location. Plus, you can manage your entire workflow, automate updates in your calendar, and track project progress in real-time.
Sign up for a free trial today.





