Are you tired of feeling lost in the complexity of your business operations?
Do you find it challenging to visualize how your organization's workflows are functioning and where there are gaps in the system?
It's time to take control of the situation and dive into process mapping.
In this guide, you’ll learn about the different types of maps and the benefits of each process. You'll also learn tips and tricks for overcoming common challenges that arise during the mapping process.
By the end, you'll be armed with the knowledge you need to create process maps that'll help you optimize your operations and smash goals.
So, let's get started.
What is process mapping?
Simply put, process mapping visualizes processes, outlining each step, decision point, and workflow handoff.
The purpose of process mapping is to provide the following:
- A clear understanding of how a process operates
- Identify areas of inefficiency or waste
- Find opportunities for improvement
Without a clear understanding of how processes work, companies may miss out on potential areas for optimization, which can lead to decreased profitability and lost competitive advantage.
For example, a manufacturing company that struggles with lengthy production times and high error rates decides to use process mapping. By mapping out each step in the production process, they could identify bottlenecks, such as redundant steps and unnecessary delays. This leads to higher profit margins and happy stakeholders.
What are the different types of process maps?
There are several types of maps to visualize workflows and identify areas for improvement.
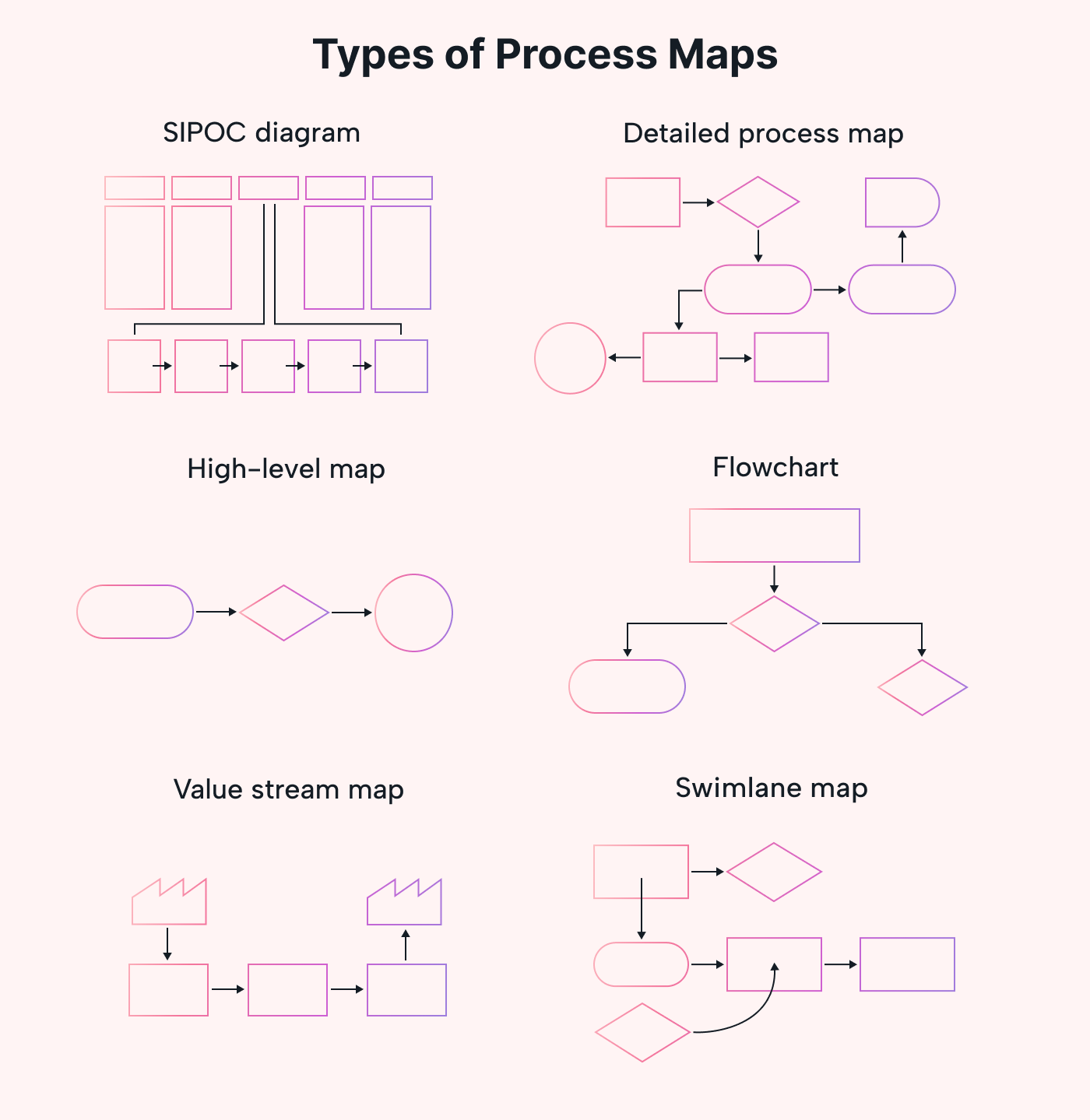 |
Here's a quick overview of the six main types of process maps:
- Flowchart
- Swimlane diagram
- Value stream map
- Business process model and notation (BPMN) diagram
- Data flow diagram
- Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers (SIPOC) diagram
We will go over each in more detail later, first let’s go over the symbols.
What are process mapping symbols?
Process mapping symbols are visual representations used in process mapping to illustrate different stages.
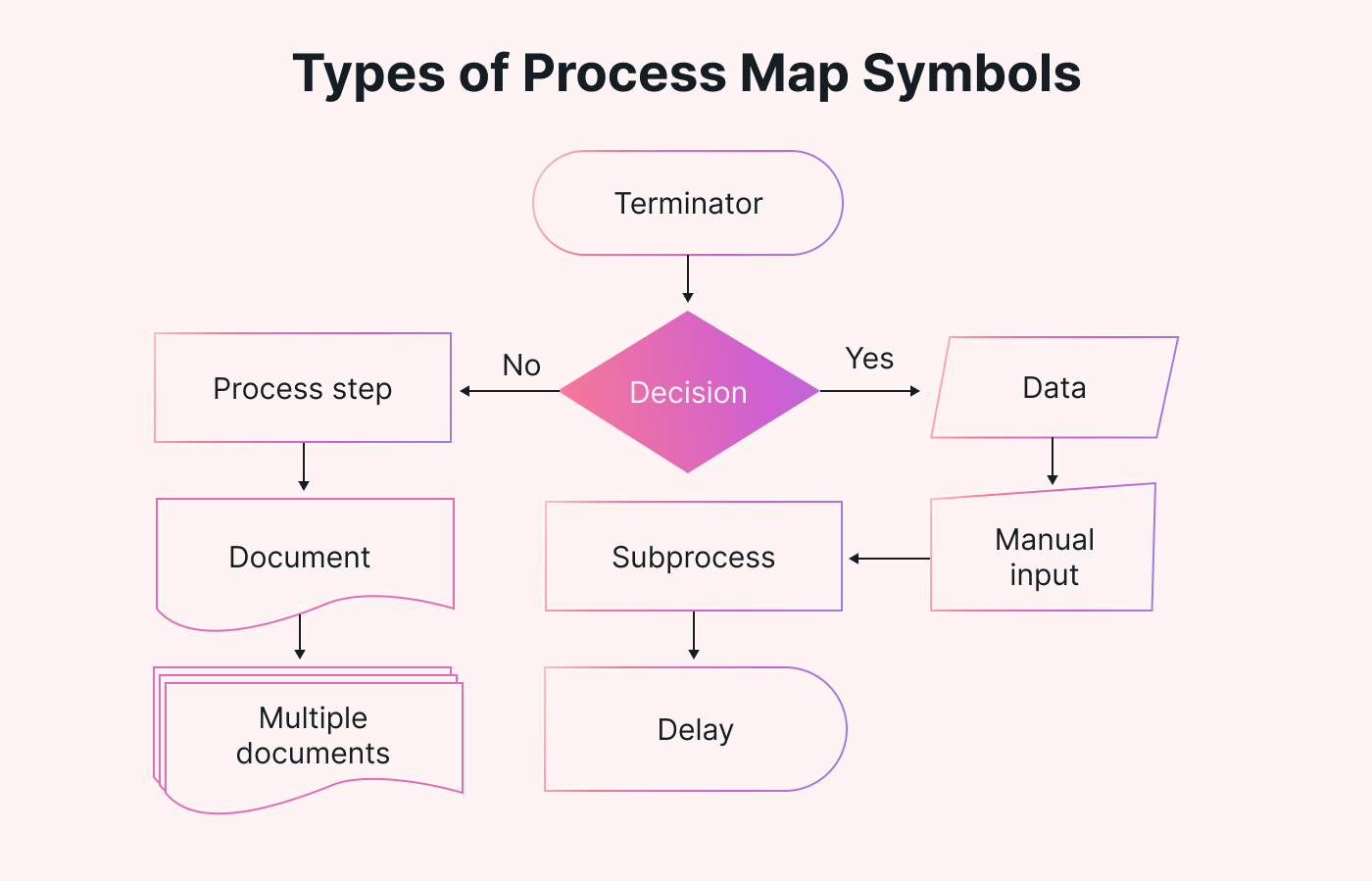 |
The nine main types of process map symbols are:
- Start/end symbol
- Process symbol
- Decision symbol
- Data symbol
- Document symbol
- Delay symbol
Each symbol represents a different action or decision within the process. These allow you to quickly identify where they are in the process and what actions are necessary.
When & why to use what process mapping type
Process mapping can be beneficial in a variety of scenarios.
 |
Below is a breakdown of the six main process maps and a summary of which to use and when.
Flowchart
Useful for: identifying bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies in a process.
Shows how a process is done from start to finish, typically in sequential order.
Great for determining the steps of a process and the people or departments involved.
Swimlane diagram
Useful for: identifying areas of overlap or miscommunication.
The swimlane diagram is useful for demonstrating the roles and responsibilities of different departments or teams.
Value stream map
Useful for: identifying areas for improvement and reducing lead time in a process.
Shows the process flow required to bring a product or service to a customer.
Great for identifying waste and inefficiencies in a process.
Business process model and notation (BPMN) diagram
Useful for: simulation of different scenarios to test process changes before implementing them in the real world.
Great for modeling complex processes and understanding interactions between different elements in the process.
Can highlight bottlenecks, redundancies, and other inefficiencies in a process.
Data flow diagram
Useful for: understanding how data flows through a system or process.
Can be helpful when designing or improving information systems and identifying opportunities for automation or integration.
Used to identify where data is lost, duplicated, or incorrectly used.
Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers (SIPOC) diagram
Useful for: understanding a process's high-level elements, what they produce and how that relates to the customers.
Shows the suppliers, inputs, process steps, outputs, and customers involved.
Used to identify key stakeholders and their needs and any constraints or limitations on the process.
6 steps for successful process mapping
To successfully map a process, you should follow a structured approach.
Here are six steps you can take to create a generic process map.
(Note: This can be applied to any process map)
Step 1: Determine the process to map
Determining which process you want to map is important before you start process mapping.
This can be any process within your organization, from a simple task, like onboarding new employees, to a more complex process like developing a new product.
The key is to choose a process that's essential, complex, or needs improvement.
Once you have identified the process, you can gather information and prepare to create the map.
Step 2: Gather information about the process
Gathering information about the process is crucial for successful process mapping. This involves gathering information about the process from the people involved in it.
 |
You can use various methods, such as the ones below, to gather this information:
- Observing the process in action
- Interviewing staff and process owners
- Reviewing process documentation and data
- Analyzing the process data and identifying key performance indicators (KPIs)
Document this information because you'll need it in a few steps.
Step 3: Define the scope and boundaries
In this step, you need to define the scope and boundaries of the process you are mapping.
Defining the scope and boundaries is important because it guarantees everyone involved is on the same page about what is being mapped. It also helps prevent confusion and ensures that you accurately map the process.
To define the scope and boundaries of your process, you should consider factors such as:
- The start and end goals of the process
- The purpose of the process
- People involved
- Inputs and outputs needed
- Any constraints or limitations
Step 4: Write the sequence of steps for the process
In step 4 of process mapping, it's time to plot out the steps for the process. This involves taking the information gathered in step 2 and arranging it logically.
Pro-tip: flesh this out with as much detail as you can. Make sure to include every step.
Start with the first step and then progress through the process until a full sequence of steps from start to end is done.
Be mindful of potential decision points or forked paths in the procedure; ensure they're included in the sequence.
Step 5: Create the process map
Once the steps are identified, creating a visual representation of the process can be helpful, such as a flowchart or BPMN diagram.
Below is an example of a process map that follows a logical sequence.
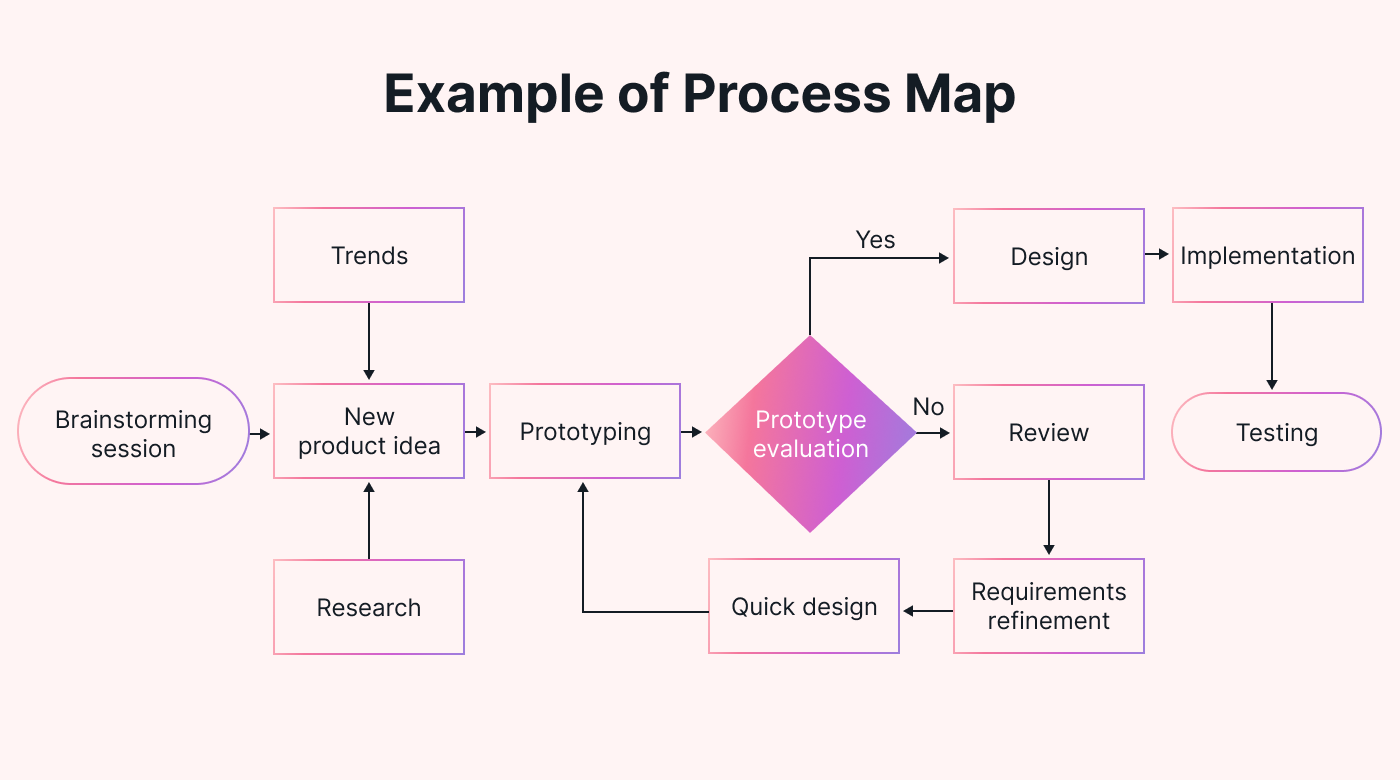 |
It's important to keep the map simple so that everyone involved can understand it.
Step 6: Analyze & implement improvements
Once you have created the process map, it's time to analyze it and identify areas of improvement. Look for steps that are redundant, unnecessary, or need improving.
You may also want to consult with employees involved in the process to get their input.
After identifying areas for improvement, it's time to implement them. This may involve:
- Changing the sequence of steps
- Cutting unnecessary steps
- Or introducing new technology
Successful process mapping examples
Understanding the steps involved is essential, and seeing them in action helps to see the benefits of this practice.
Below are two practical examples of successful process mapping and how it can benefit each scenario.
Example 1:
Let's say you work for a manufacturing company that produces widgets or apps. You decide to create a process map to get a better understanding of the process and identify areas for improvement.
After creating a detailed process map, you notice several areas where the process could be streamlined.
For example, you identify that the testing process could be improved by implementing automated testing equipment. This could cut down on the overall time required and improve the accuracy of the tests.
Example 2:
Another example could be a restaurant looking to enhance its customer service. The manager creates a process map for the dining experience, from when customers enter to when they leave.
After creating the process map, the manager identifies numerous areas where the dining experience could be improved. For instance, they notice that waitstaff could be more attentive to customers' needs, especially during peak hours. They also note that the kitchen could benefit from a more efficient ordering process to reduce wait times for food.
With these insights, the manager decides to implement new training for the waitstaff and streamline the ordering process in the kitchen.
Successful process mapping: tips for overcoming common challenges
There are a few common challenges that you might encounter when process mapping. However, by following some key tips, you can overcome these challenges and ensure your process mapping efforts succeed.
Communicate the importance of process mapping
Make sure all team members understand why process mapping is important and what the end goal is. Explain how it can:
- Improve efficiency
- Reduce costs
- Improve customer satisfaction
Involve team members in the mapping process
The ones who know the process are the people who do it daily. Involving them in the mapping process can help you identify areas for improvement and ensure that the process map accurately reflects how the process works.
Define clear objectives
Before you begin the process mapping, make sure you have clearly defined objectives. This will help you stay on track and ensure the process map meets your needs.
Keep the process simple
Process mapping can become overwhelming if you try to include too much detail. Keep the process map simple and focus on the most significant steps. This will help you identify areas for improvement more easily.
Review and update the maps regularly
Once the process map is complete, reviewing and updating it is essential. This will help you identify new areas for improvement and ensure that the process map accurately reflects the current process.
Start process mapping today
Process mapping is invaluable for any organization seeking to streamline its operations and increase efficiency. By following the steps above, you can make informed decisions about running your business more smoothly. You can identify areas for improvement as well as for capitalization. However, combining it with the right tools can further enhance its effectiveness.
Consider incorporating Motion into your workflow to enhance your process mapping journey further.
Motion can enhance your process mapping and workflow
Motion is an AI-powered rock star app designed to help you optimize your time and streamline your workflow.
Below are a few major ways Motion can beef up your workflow.
- Motion seamlessly integrates with process mapping by providing a centralized platform where you can manage your tasks, deadlines, and project schedules.
- With Motion's task management features, you can easily prioritize your process improvement initiatives. And schedule them within your calendar. This allows for better coordination and ensures that process improvement efforts are effective.
- Motion facilitates collaboration by providing features such as shared calendars, task assignments, and real-time updates.
Motion's task prioritization, scheduling, and collaboration features provide a holistic approach to project management. It’s the perfect blend of process mapping and task execution in a unified platform.
Discover how Motion can streamline your operations, improve efficiency, and drive success. Start your 7-day free trial.





