Every thriving organization has a heartbeat — a rhythm that keeps teams aligned and motivated.
But what is this pulse?
The answer is effective internal communication.
Gone are the days when employee interaction was limited to breakroom chats. Modern internal communication is the lifeblood of dynamic companies, as it helps ensure everyone marches to the same beat.
Dive in as we unravel what internal communication means, its significance, and methods for refining it in any corporate setting.
What does internal communication mean?
Internal communication is the exchange of information, ideas, and feedback within an organization. It encompasses the various interactions that happen among members of the same organization, be they departments, teams, or individuals.
Internal communication can include:
- Formal communication via memos, meetings, or official announcements
- Informal communication via chats, emails, and impromptu discussions
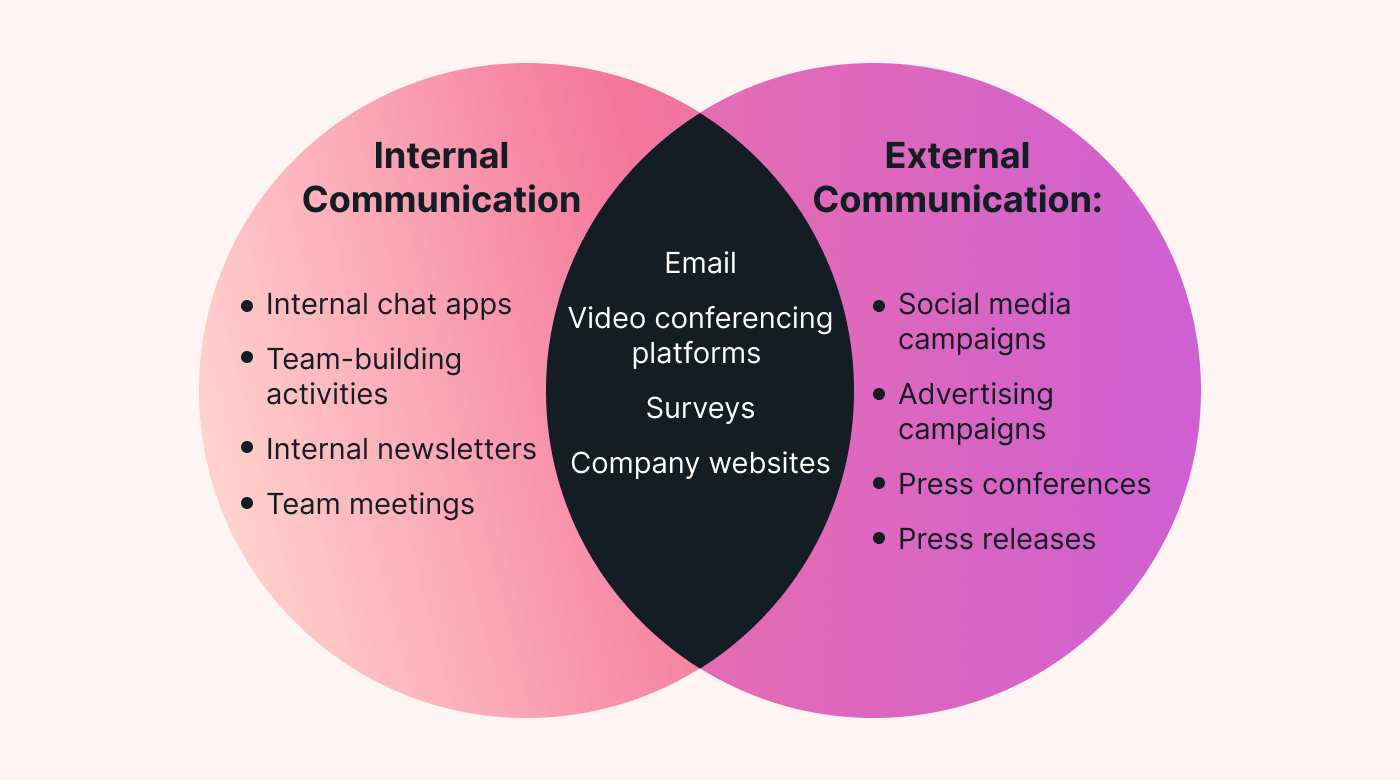
Internal vs. external communication
Internal and external communication are both critical components of an organization’s overall communication strategy, but they serve different purposes and audiences.
Here’s a breakdown of the differences between the two:
 |
Purpose
Internal communication
- Targets the members within the organization.
- Aims to inform and engage employees, promote organizational culture, drive alignment, and enhance productivity and collaboration.
- Includes staff meetings, intranet posts, corporate newsletters, and team-building activities.
External communication
- Targets audiences outside the organization.
- Aims to build the company’s brand, communicate with customers or stakeholders, manage public relations, and market products or services.
- Includes press releases, marketing campaigns, customer service interactions, and stakeholder reports.
Audience
Internal communication
- Is primarily directed at employees, though it can also include contractors or partners closely affiliated with the company.
External communication
- Targets a broader audience, including customers, investors, suppliers, media, regulators, and the general public.
Channels
Internal communication
- Uses platforms like company intranets, internal chat apps (Slack, Microsoft Teams, etc.), internal newsletters, and town hall meetings.
External communication
- Relies on public-facing platforms, like company websites, social media, advertising campaigns, press conferences, and public statements.
Content and tone
Internal communication
- Is more informal and can include details specific to company operations.
- Focuses on company policies, updates, achievements, and other matters of internal interest.
External communication
- Is usually more formal and polished.
- Focuses on presenting the company to the external world in the best possible light.
Feedback
Internal communication
- Encourages a two-way flow of information, allowing employees to respond, offer feedback, or voice concerns.
External communication
- May not always be two-way, especially in the case of mass media communication. However, platforms like social media now allow for more direct engagement and feedback from external audiences.
Why is good internal communication so important?
Effective internal communication within a company is essential for the following reasons:
Offers direction and alignment
It helps ensure that everyone in the organization understands the company’s goals, values, and priorities.
Enhances collaboration
Clear communication between teams or departments can foster collaboration and prevent misunderstandings or duplicated efforts.
 |
Improves morale
Transparent and open communication can boost employee morale and engagement. When employees feel informed and listened to, they’re more likely to feel valued and motivated.
Strengthens problem-solving
Open channels of communication allow for the quick identification and resolution of issues. These things can be particularly critical during crises.
Helps with change management
When there are changes in an organization — whether it’s a new product, a change in leadership, or a company-wide restructuring — effective internal communication helps to smoothly navigate the change management process.
An effective way to give feedback
A solid internal communication plan allows for two-way communication. Management can share information downward, while employees have channels to provide honest feedback or voice their concerns upward.
Promotes a unified company culture
Effective internal communication helps to build a shared company culture in which everyone feels like part of a larger mission.
Reduces turnover rates
When employees are kept in the loop and understand their roles, they tend to feel more secure and engaged in their jobs. This can lead to greater employee satisfaction and reduced employee turnover, ultimately saving companies time and resources in hiring and training.
Strengthens trust
Transparency in communication helps to build trust between management and employees. When leadership communicates openly about both successes and challenges, a sense of trust and partnership results.
Methods of internal communication
Internal communication encompasses a wide range of tools, methods, and interactions for fostering dialogue, sharing information, and aligning employees with organizational goals.
Here are some examples of popular internal communication methods:
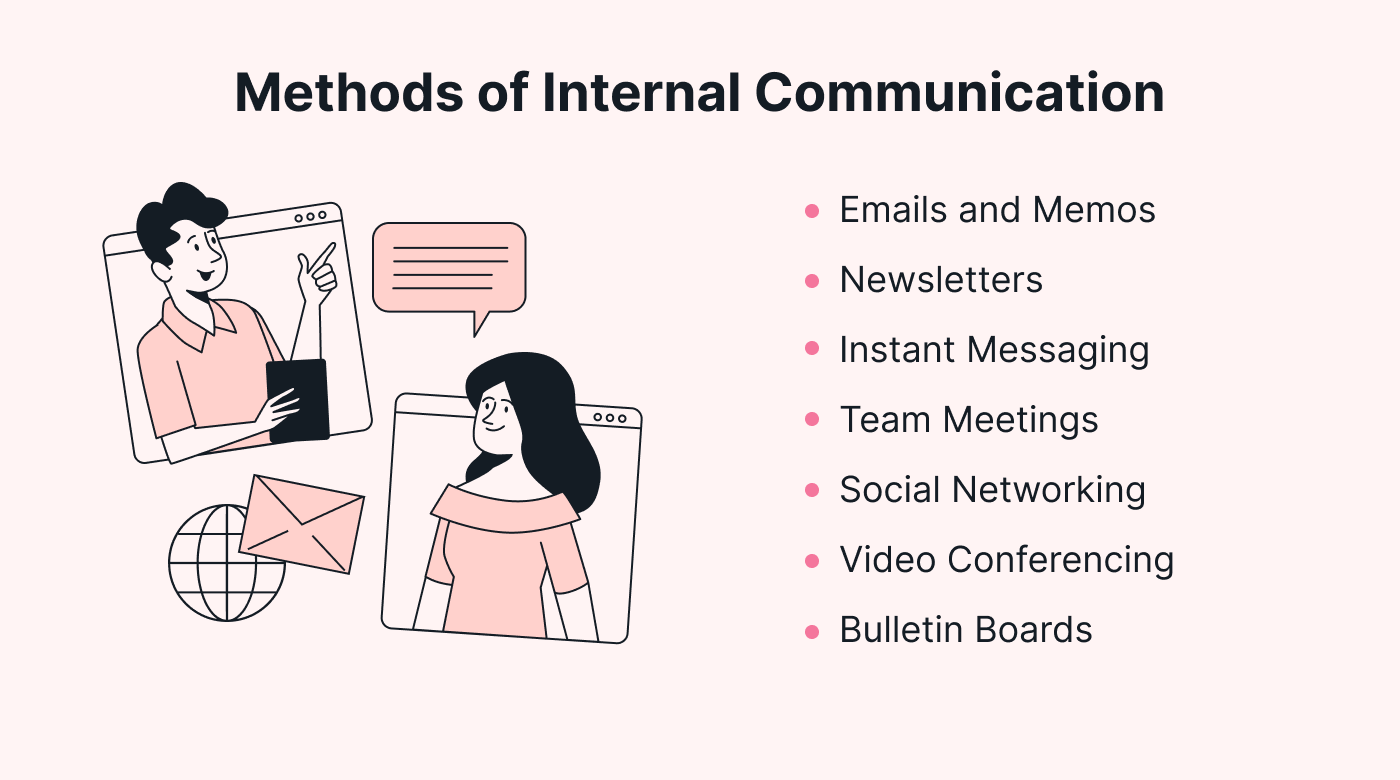 |
Emails: Often used for company-wide announcements, policy updates, or specific departmental communications.
Newsletters: Periodic updates that can include company news, employee spotlights, and other organizational updates.
Instant messaging: Includes platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or WhatsApp for Business, and are used for real-time, informal communication among employees.
Team meetings: Regular meetings within a team or department to discuss ongoing projects, challenges, and updates, or larger company-wide meetings where executives share company updates or future visions or address employee questions.
Social networking: Company-specific platforms or channels on larger platforms (like a Facebook Group for employees) that allow for social interaction and sharing.
Video conferencing: Tools like Zoom, Google Meet, or Webex, all of which are used for virtual meetings; these are especially important for remote teams or geographically dispersed companies.
Bulletin boards: Physical or digital boards for posting news, updates, or important notices.
Internal blogs or forums: Platforms on which employees can share insights, updates, or topics of interest.
Training sessions: Events or courses designed to upskill or inform employees about specific topics.
Feedback and suggestion boxes: Tools or systems where employees can submit ideas, feedback, or concerns either anonymously or openly.
Employee surveys: Tools used to gather feedback from employees on various topics, from job satisfaction to opinions on company initiatives.
Employee onboarding programs: Introductions and training for new employees to get them acquainted with company culture, policies, and their roles.
Collaboration: Tools like Motion, Trello, or Asana where teams can collaborate on projects, share updates, and track progress.
Employee recognition programs: Communication that highlights employee achievements, milestones, or exceptional performances.
Crafting an internal communication strategy
Here’s a step-by-step guide to crafting an effective internal communication strategy and fostering a connected, informed, and engaged workforce:
 |
1. Set clear objectives
Determine what you aim to achieve. This might include improving employee engagement, increasing employees’ understanding of company values, facilitating change management, or enhancing inter-departmental collaboration.
Begin with a brainstorming session with key stakeholders. List the outcomes you want to see from the internal communication strategy. Once you’ve completed this list, prioritize these outcomes and set tangible metrics for each.
2. Identify your audience
Recognize that your organization may consist of groups with varying needs. Segment your audience by department, role, or location to tailor your messages appropriately.
Conduct a brief survey or use existing HR data to determine your workforce’s demographics and preferences. Group them based on similarities to create targeted communication campaigns.
For instance, remote workers might need a different communication touchpoint than on-site employees.
3. Choose the right communication channels
Choose channels based on your audience’s preferences and the nature of the content.
A tool like Motion might be effective for tech-savvy teams, while a production floor might benefit more from bulletin board announcements. Remember, one size doesn’t fit all.
4. Determine content types
What kind of information do employees need and want? This can range from company news, policy updates, and training content to employee spotlight stories.
Hold focus group discussions or feedback sessions. Understand what kinds of information employees value most. This will help you tailor content that’s both engaging and informative.
5. Establish a content calendar
Outline when and how frequently you’ll communicate. Use a tool like Motion to map out a communication timeline. Assign responsibilities to team members for content creation, approval, and dissemination.
 |
For instance, designate every first Monday of the month for company news and the third Thursday for employee spotlights. Regularity can create a rhythm that employees come to expect.
6. Document the strategy
Create a written document outlining strategy, objectives, channels, and protocols. Regularly update it based on changing objectives or audience feedback. It will serve as a reference and help ensure continuity.
7. Measure and analyze
Determine key metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of your communication efforts. Use analytics from digital platforms, like the number of views or email open rates.
For physical interactions, post-meeting or post-event surveys can be invaluable. Convert this data into insights. For instance, use it to determine which topics get the most engagement.
8. Review and adjust
Schedule quarterly review meetings with your communication team. Discuss the analytics, gather feedback, and recalibrate the strategy accordingly.
For example, if video messages have a particularly high engagement rate, consider increasing the frequency or variety of such content.
Tips for improving your internal communication
Here are some strategies for refining your team’s internal communication:
Ensure clarity and understanding
Ever read a work email and thought, “What did they mean by that?”
Making sure everyone on a team is on the same page cuts down on misunderstandings and time wasted deciphering such messages.
Encourage an open-door policy
A welcoming atmosphere helps team members more freely share their insights, leading to a more collaborative and inclusive environment.
Encourage leaders and managers to be approachable and available for discussions, fostering an environment where employees feel their voices matter. For example, set aside specific hours in which you are available for casual chats.
Use multiple channels
Not every platform is suitable for every kind of communication. Instant messages can be great for quick queries, but longer, more detailed discussions may be better suited for face-to-face meetings.
Whether it’s email, messaging, or a good old-fashioned meeting, choose wisely.
Consolidate channels to avoid overload
It’s easy to feel like you’re drowning in a sea of apps and notifications. Having too many tools can lead to missed messages and wasted time.
Motion streamlines communication by offering several collaborative tools in one place, helping teams stay in sync without the clutter.
Encourage feedback
Create ways for employees to share their thoughts and concerns, like surveys or feedback forms. Keep in mind that some employees may feel more comfortable providing feedback anonymously.
However, it’s also not enough to just collect feedback. Showing that changes are made based on feedback reinforces trust and encourages continued communication.
Set clear expectations
Outlining clear business goals from the get-go ensures everyone knows their role and can contribute effectively. Whether it’s for a specific project or a general task, having written guidelines or expectations can be a reference point for everyone.
Take your internal communication to the next level with Motion
Internal communication has transformed from simple break room chats to sophisticated interactions that drive organizations. A company’s success hinges on ensuring every department, team, and individual exchanges information and ideas effectively.
Motion steps in as a solution tailored to today’s modern corporate landscape by consolidating communication and facilitating seamless interactions while eliminating the clutter of excessive channels. Whether it’s task alignment or scheduling meetings, Motion’s unified platform ensures everyone stays connected, understands their role, and works toward the collective vision.
Ready to experience an internal communication transformation? Sign up for Motion’s free 7-day trial.