Prioritizing tasks sounds simple enough. You can choose the most important ones, focus on those that have the biggest impact on ROI, or do what the client wants first. Or, you could always just wing it.
But what if all your tasks are important? What if the ones you focus on don't yield any ROI? What if the client's idea doesn’t work? What if winging it causes your whole project to go up in flames?
The reality is not knowing how to prioritize your tasks can ruin everything.
What you need is a rational way to prioritize so you can execute tasks in the most effective order. This article will help you do just that. It provides three steps to master prioritization. Follow them, and you’ll always know what to do next.
How to prioritize tasks
- Step 1: Choose a task prioritization method
- Eisenhower Matrix
- RICE prioritization
- MoSCoW
- Eat the Frog
- ABDCE
- Impact-effort matrix
- Pareto principle
- Weighted Shortest Job First
- Step 2: Use AI to automate ongoing task prioritization
St ep 1: Choose a task prioritization method
Some people have a natural aptitude for management and organization, while others don’t. If you’re part of the second group, the ability to prioritize project tasks may seem like an art. However, prioritization is more like a science.
Many prioritization masters use a task prioritization method to help them rank their tasks.
Why do you need a prioritization method?
To learn how to prioritize tasks, you need to understand the underlying “importance” of specific tasks compared to other ones — a tricky thing to do since “importance” isn’t very quantifiable.
Using a prioritization method helps you to quantify tasks based on a scoring system, which typically uses one or more of the following factors:
- Time
- Urgency
- Dependencies
- Available resources
- Impact
- Effort
As a result, you get a framework that ranks your tasks based on factors that are important to achieving your goal. While the degree of data validation can differ from technique to technique, this is a better alternative than guesswork.
To reap the benefits of task prioritization, you need to be able to choose the best prioritization technique for your needs.
The following eight prioritization strategies balance different factors to weigh tasks according to their urgency, importance, difficulty, or number of people they'll impact.
1. Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix (also known as the prioritization matrix), designed by Dwight D. Eisenhower, balances urgency and importance to rank tasks and clear busy calendars.
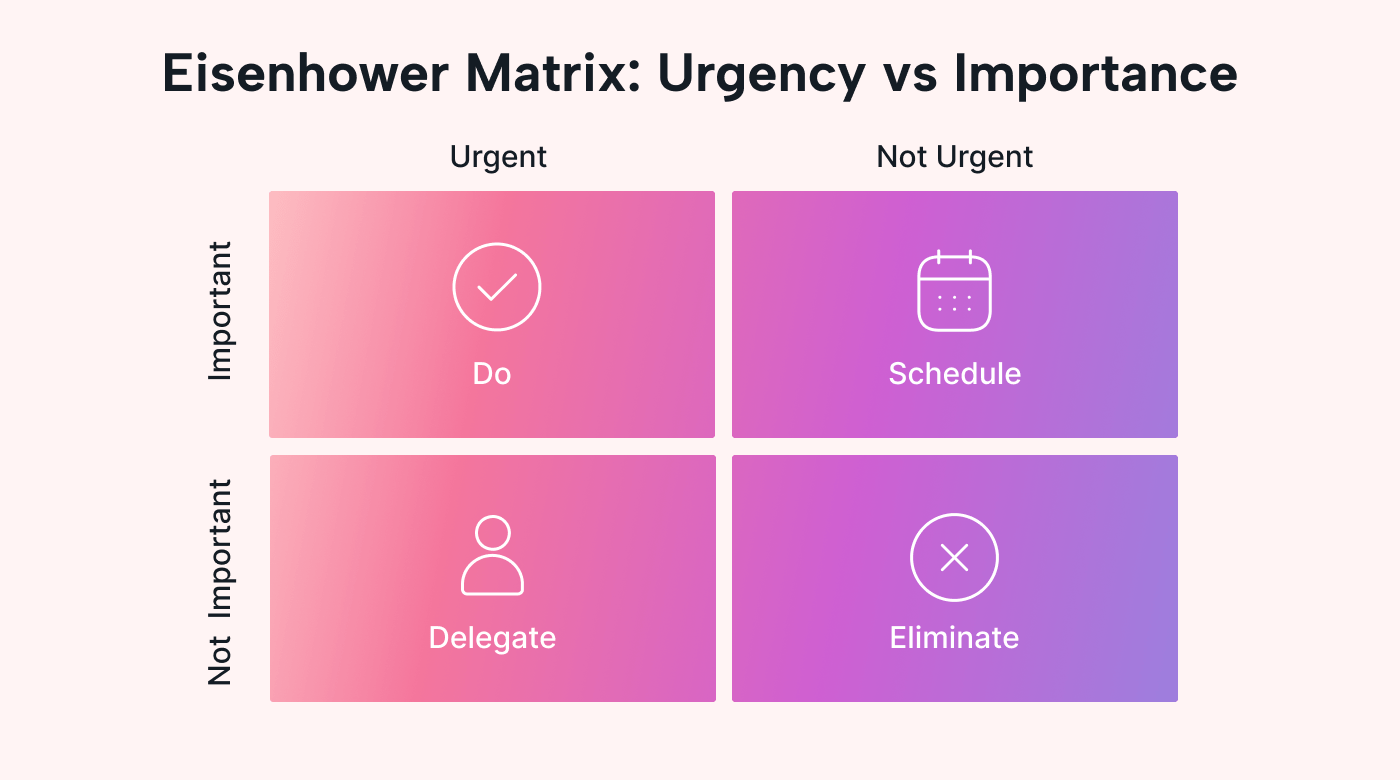
Urgency refers to how soon a task needs to be completed before you miss an imminent deadline or run into trouble. Importance refers to how valuable a task is for you, your team, or the company at large.
Comparing these two factors creates four categories for organizing your tasks. It then gives general instructions for how to handle the tasks in each category.
- DO – Urgent and important: These tasks are of the highest priority, so you should do them immediately or as soon as possible. Examples of highest-priority tasks include those with imminent deadlines.
- SCHEDULE – Not urgent, but important: These tasks should be done after you've completed the urgent and important tasks or scheduled into the next convenient time slot. Examples of high-priority tasks include business calls and personal tasks, like health checkups and exercise.
- DELEGATE – Urgent but not important: These low-priority tasks should be done last or delegated to other members of your team. Examples include long-term projects, non-urgent emails, or administrative tasks.
- ELIMINATE – Not urgent and not important: These tasks aren't directly related to your projects, are a waste of your time and effort, and should be removed from your daily list of to-dos.
Pros of the Eisenhower Matrix:
- Dividing tasks into the four categories is quick and easy.
- It helps avoid the mere urgency effect, which describes how people tend to prioritize urgency over importance.
Cons of the Eisenhower Matrix:
- It doesn't consider task dependencies.
- It can be difficult to quantify importance.
- If you have many tasks in each category, it's hard to prioritize them further.
You should use this method if:
- You only have a few tasks to work on.
- You tend to favor urgent tasks over important, high-priority tasks, and you want to balance these factors out.
2. RICE prioritization
The RICE prioritization method assigns numerical values to four factors that describe your tasks. You then calculate a RICE score for each of your tasks and prioritize those with the highest scores.
The RICE acronym stands for the following:
- Reach: The number of people affected by the task
- Impact: The potential benefit or value of the task
- Confidence: How confident you are in the methods or data you used to determine the reach and impact values
- Effort: The number of resources and amount of time you need to complete the task
To learn how to choose values for each factor, read our guide to RICE prioritization.
Calculate each task's RICE score using the following formula:
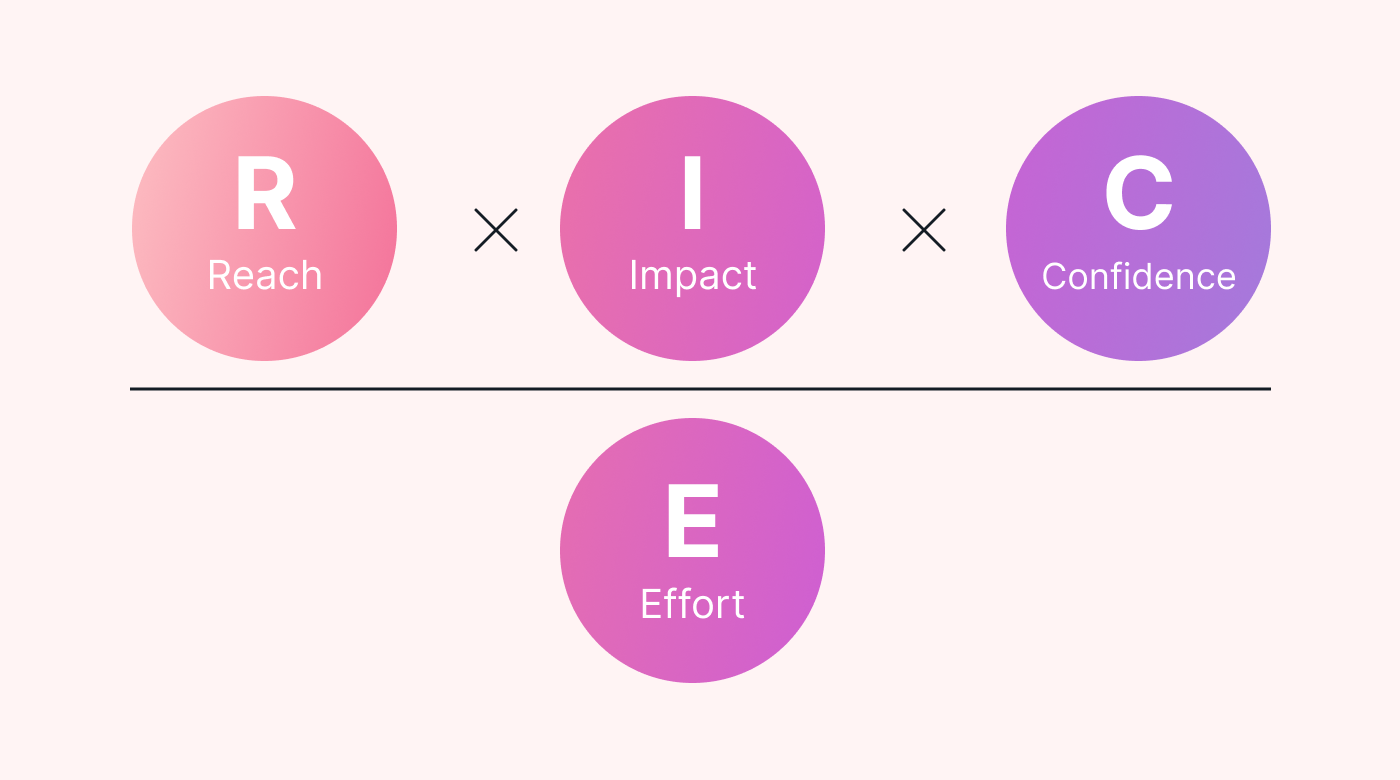
The task with the highest score wins the “top priority” spot in your to-do list.
Pros of the RICE method:
- It's a structured and quantitative method.
- It removes biases and subjective opinions, relying on measurable factors instead.
Cons of the RICE method:
- It doesn't consider task dependencies.
- It can be difficult to quantify qualitative factors, such as user experience.
- The values assigned to each factor may differ from person to person.
You should use this method if:
- You and your team have a standard scoring method.
- You're working with easily measured qualities, such as the number of clicks on a website link.
- You're not working on tasks that depend on each other.
3. MoSCoW
The MoSCoW method was created to prioritize the potential features of a product during its development. It's been adapted to apply to task prioritization.
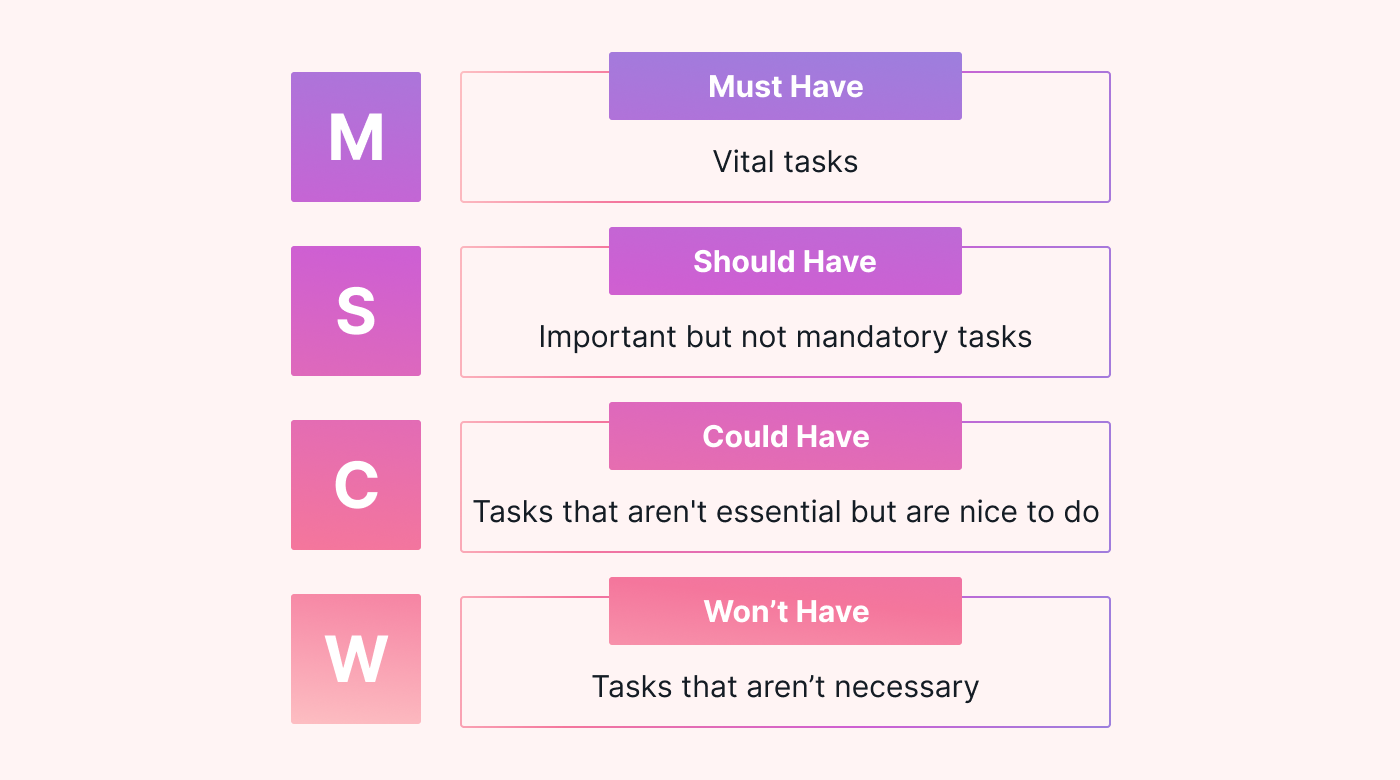
The MoSCoW method prioritizes the tasks that are most important and impactful for your clients and business. It divides tasks into four categories:
- Must have: These tasks are essential for other larger projects or stakeholders.
- Should have: These tasks are important but not mandatory. Not completing one of them won't do any damage to the business, but it will cause frustration and irritation until it's done.
- Could have: These tasks aren't essential, but they're nice to do eventually. Not completing one of them has a small impact on your team, clients, or business.
- Won't have: These are tasks that aren't needed. They don't have enough value to prioritize, so you can either put them on the back burner or drop them from your priority list entirely.
The four categories might feel similar to those of the Eisenhower Matrix, but the factors you consider are more focused on the task's impact and value than its urgency.
Pros of the MoSCoW method:
- It considers impact from the angle of usefulness for clients and business.
- Its categories are intuitive, making it easy to explain your priorities to colleagues.
Cons of the MoSCoW method:
- It doesn't consider the urgency of tasks.
- The impact level of a task can be subjective.
You should use this method if:
- You're choosing a feature to work on or implement into a product.
- You don't have multiple time-sensitive projects on the go.
4. Eat the Frog
The Eat the Frog technique comes from the famous Mark Twain quote, “If it's your job to eat a frog, it's best to do it first thing in the morning.”
According to this method, you tackle the most important, complex, or difficult task (or “eat the frog”) first. Then, you move on to the simpler tasks.

Pros of the Eat the Frog method:
- It's a simple method that allows you to get going quickly.
- Getting your most daunting task out of the way gives you momentum right at the start of your workday.
Cons of the Eat the Frog method:
- If you have multiple complex and important tasks, it can be difficult to know which to work on first.
- The most complex and difficult work isn't necessarily the most valuable task for your team or business.
- It doesn't consider time sensitivity.
- Prioritizing the smaller tasks after you've “eaten the frog” can be difficult.
You should use this method if:
- You have complex projects or tasks that intimidate you so much that you struggle to work on anything at all.
- You have a main project you should be focusing on, but you keep getting distracted with admin work.
5. ABCDE
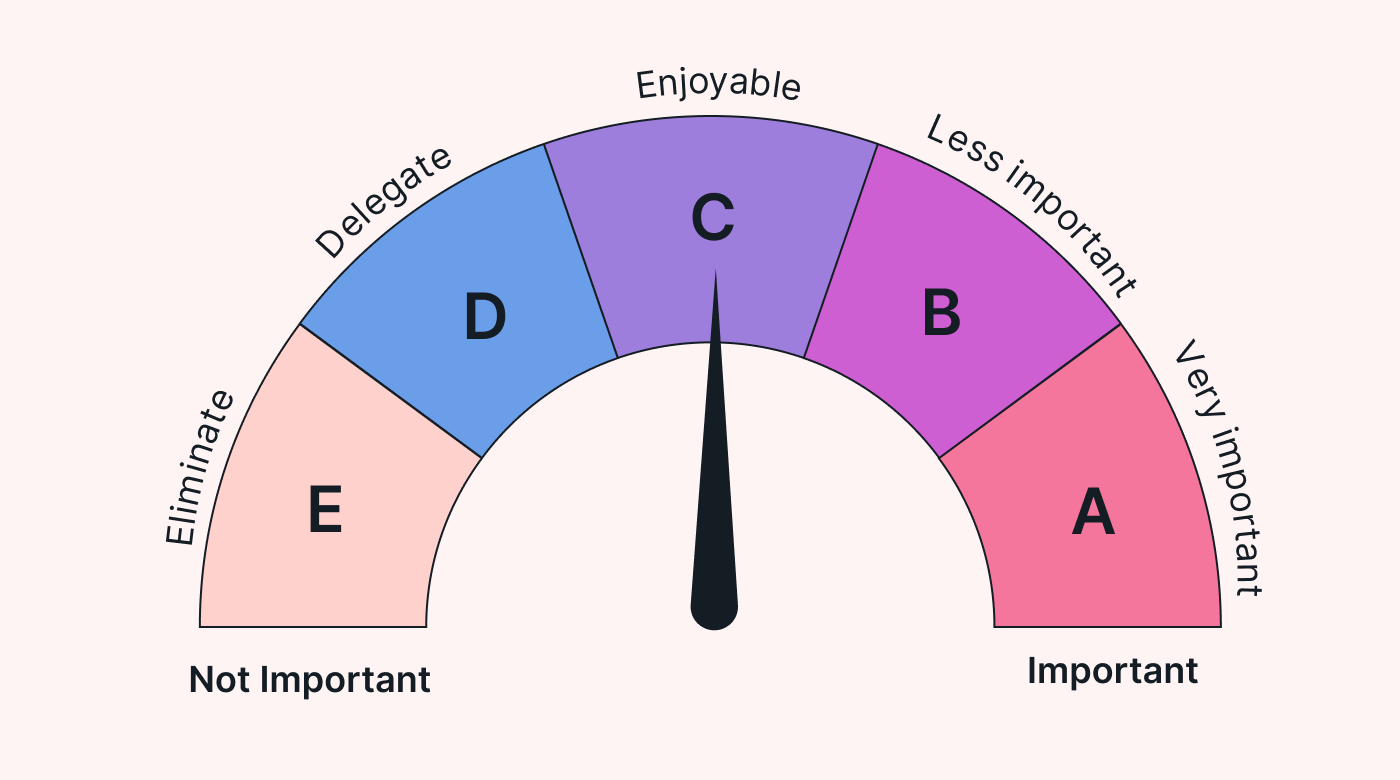
Brian Tracy's ABCDE method grades tasks by level of importance, where A is very important and E is not important.
With this method, you work on the A and B tasks first, then tackle the C tasks you enjoy, and only work on the D and E tasks if you have time left over. Otherwise, you'll delegate or delete these tasks.
- A – Very important: These are the very important tasks that carry a lot of value for your team or business.
- B – Less important: These are less important tasks that add a small amount of value to your team but aren't urgent or essential.
- C – Enjoyable: These are tasks you find pleasure in doing and don't need much motivation to complete.
- D – Delegate: These are low-value tasks that you could delegate to a colleague if you run out of time before getting to them.
- E – Eliminate: These are tasks that add no value to your team and aren't essential or useful for your business. They have the lowest priority.
Pros of the ABCDE method:
- It's incredibly simple and intuitive.
- It includes an enjoyment factor for bonus tasks, which can motivate you through trickier jobs.
Cons of the ABCDE method:
- If you can't see the big picture, it's hard to accurately grade the importance of your tasks.
- If you aren't diligent with how you spend your time, you won't get past the bigger, more important tasks.
You should use this method if:
- You have the ability to grade your tasks' importance objectively.
- You're good at managing your time.
6. Impact-effort matrix
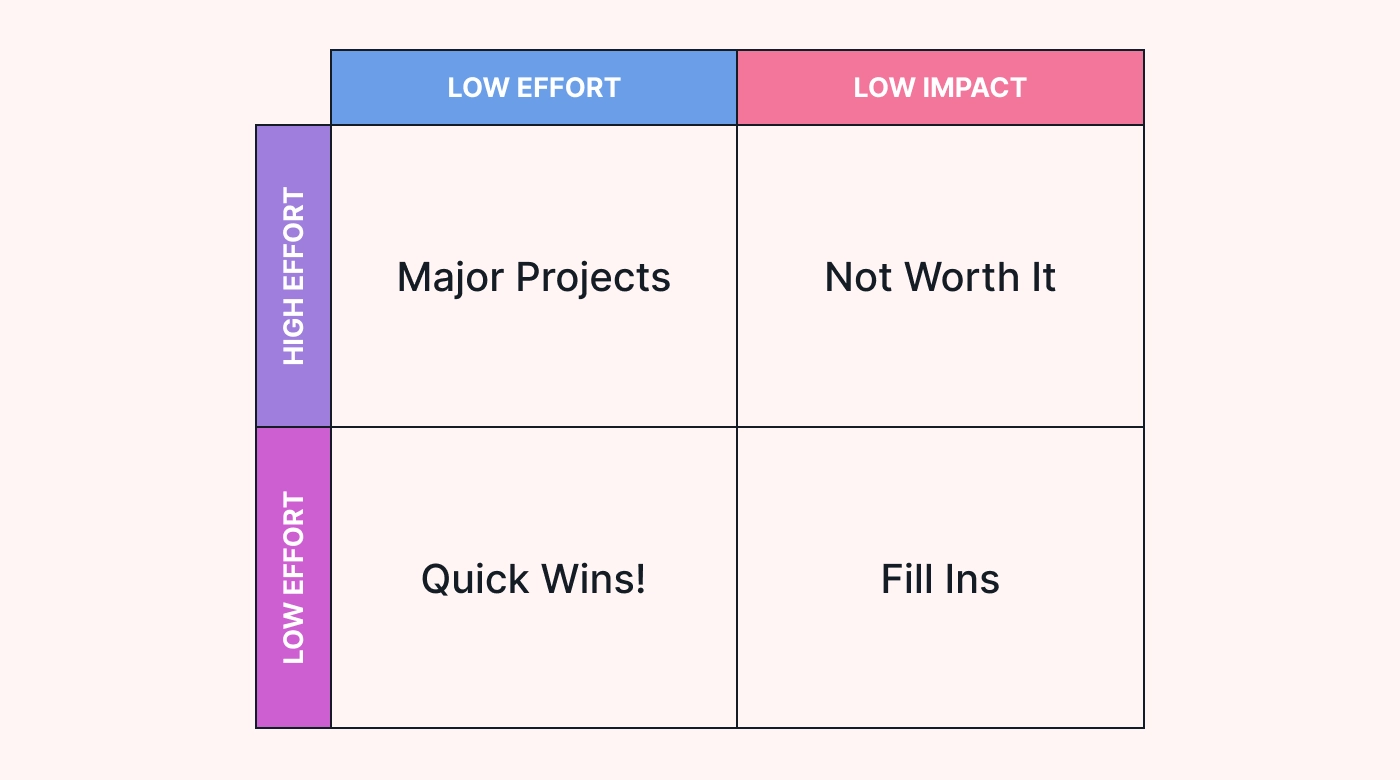
The impact-effort matrix (also called the value-complexity matrix) balances the impact of a task with the effort required to pull it off.
It has the following four task categories:
- QUICK WINS – High impact and low effort: These are tasks that are worth investing time and energy into because even a small amount of work is rewarded.
- BIG BETS – High impact and high effort: These tasks are worth investing effort into carefully planning because they’ll have huge payoffs once you’ve completed them.
- FILL INS – Low impact and low effort: These tasks are easy to implement, but they aren’t always worth your time and resources and might be distracting you from your big picture.
- MONEY PIT – Low impact and high effort: These tasks are a waste of time and resources as they take huge amounts of work for little to no payoff.
Pros of the impact-effort matrix:
- The effort metric considers skill level, labor, time, and resources.
- It's a simple method that allows you to get started quickly.
Cons of the impact-effort matrix:
- Impact and effort levels are subjective and tricky to define.
- It doesn't take urgent tasks into account.
You should use this method if:
- You're working in a team and want a quick, collaborative game plan.
- You want to take resources into account while prioritizing.
7. Pareto principle
The Pareto Principle, or the 80/20 rule, is a powerful prioritization method that suggests that 80% of results come from 20% of efforts.
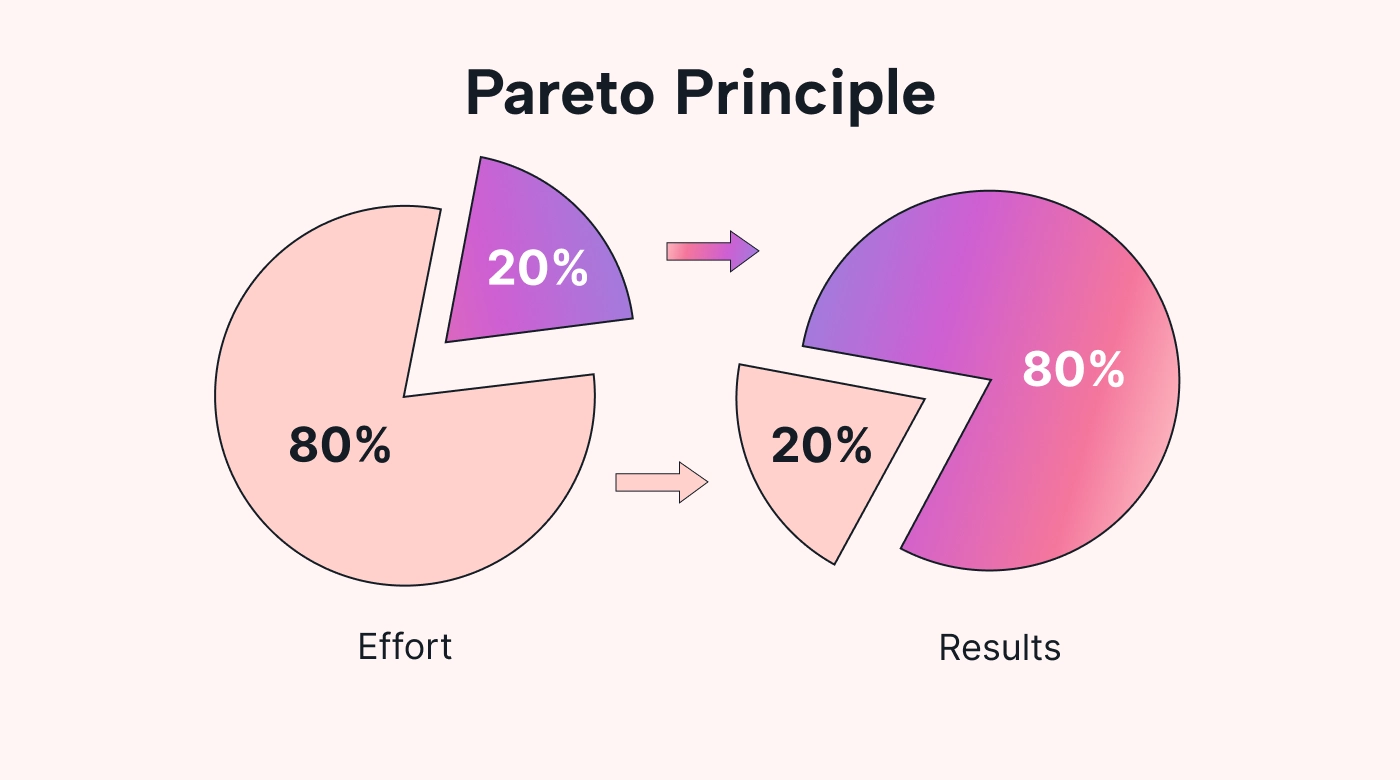
In a sales environment, this could mean that 80% of sales come from 20% of clients.
To apply the Pareto Principle, list all your tasks and identify the top 20% that will produce the most significant results.
Pros of the Pareto Principle:
- Focuses on impactful tasks that contribute to results.
- Helps users quickly find critical tasks that generate the most value with minimal effort.
Cons of the Pareto Principle:
- It can be hard to tell which tasks are in the top 20% without conducting a detailed analysis.
- The principle doesn't directly address task urgency or dependencies.
You should use the Pareto Principle if:
- You need a fast way to boost productivity and focus on high-value tasks.
8. Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF)
WSJF is another powerful prioritization method, especially in Agile and Lean environments. It prioritizes tasks based on their cost of delay and job duration so that those with the highest economic impact are completed first.
In a marketing campaign, critical tasks such as creating ad content, landing page design, and audience targeting can be assigned a WSJF score. If creating ad content has the highest cost of delay and shortest job duration, it should be prioritized to maximize the campaign's effectiveness quickly.
To use WSJF, calculate each task's cost of delay and divide it by the job duration. Then, tackle the tasks with the highest WSJF scores first.
Pros of WSJF:
- Prioritizes tasks based on impact and duration, handling the highest-benefit ones first.
- Uses a structured approach to prioritizing tasks in Agile and Lean environments.
Cons of WSJF:
- Accurate estimation of both cost of delay and job duration is challenging.
- Ignores qualitative aspects not tied to economic impact.
You should use WSJF if:
- You need Agile prioritization.
- Your projects consist of complex tasks with varying economic impacts and durations.
- You need a method that balances the urgency and economic benefits of critical tasks.
Step 2: Use AI to automate ongoing task prioritization
You've got your priorities in order. So, now what?
You can make the most of your prioritized task list by enlisting the help of digital tools. Project management software like Motion's AI can help you move from planning to action. Its AI scheduling features automate the management and planning of tasks.
Motion automatically plans your day by scheduling your daily tasks by deadline and priority level. All it needs is your tasks and calendar events, and Motion will create an optimized schedule for you every single day. Motion will also send a calendar reminder when a deadline is approaching or if you've overbooked yourself.
Get more done each day, feel less overwhelmed, and have more time for what matters. With Motion managing your schedule, you can confidently switch between tasks, knowing you're always focused on your top priorities.
Use AI to allocate and manage your team's tasks
What Motion can do for you, it can also do for your teams.
If you manage a team, you can create projects and list the required tasks along with their priority levels. Once you assign a task to someone, Motion will lock it into their schedule. And if new super-important tasks come up, Motion will rearrange the assigned person's calendar to accommodate them.
Your team never has to worry about prioritizing their own workloads, and you don’t have to worry about them missing deadlines — Motion is on top of it.
All this is in an easy-to-use project management tool that integrates with many other tools, helping your team focus on work, not planning.
Keep your daily priorities in order with Motion
With practice, you'll become better at knowing which tasks and projects will provide the highest value and should be your number one priority. Having additional prioritization techniques in your arsenal helps you take control of your responsibilities at work and unlock impactful productivity.
Knowing how to prioritize daily and weekly tasks is the first step to tackling your to-do list. Managing your priorities is the next step on your road to success.
Motion makes it easy to keep your priorities in order by scheduling tasks in order of importance and priority. Once you've set an importance level, Motion uses the power of AI to create an optimal schedule for you to follow.
Try out Motion for free today.

Hailing from South Africa, Richard Reynolds is a seasoned project & product management writer at large (last sighted in Vietnam!) With 5+ years experience in the field, a BA in Psychology, and education in Biz Mgmt & Professional Project Management, Richard remains passionate about simplifying complex project concepts with seasoned professionals and newbies alike.




