If you blink in 2025, your favorite software rebrands itself as an AI company.
Spoiler: The engineers didn’t pull an all-nighter to rebuild the platform with AI. The marketers just swapped a few words on the homepage.
Nowhere is this more obvious than with CRMs.
Every CRM is suddenly an AI CRM. But test a few, and you’ll quickly find most are the same old systems — just with an “AI” sticker slapped on top.
And that’s a problem.
CRM companies promise a Lamborghini-level AI experience, lock businesses into year-long contracts, and then deliver a Honda Civic CRM.
Still, most businesses know they need AI. They just don’t know what it can actually do for them.
That ends here.
In this post, you’ll learn:
- what an AI CRM really is,
- what they can actually do for your business,
- and how leading AI CRM platforms measure up.
I’ll also give you an AI CRM evaluation checklist. So you can confidently choose a platform that works for your business.
Let’s jump in.
Why businesses need a CRM (even SMBs) and shortcomings of traditional CRMs
Let’s take a step back for a moment, and I’ll explain why businesses even need a CRM in the first place.
CRMs (customer relationship management systems) store every interaction your company has with prospects and customers — emails, calls, purchases, support tickets, renewals, and more.
Think of a CRM as your company’s collective memory. It remembers every promise made, every deal in motion, and every customer who might be at risk of leaving.
But at their core, they exist for one reason: to help businesses make more money.
They do that in three ways:
- Closing more deals. Sales reps can see every lead, every conversation, every deal in progress. They know which opportunities are hot, which are stalled, and exactly what it’ll take to move them across the finish line.
- Keeping more customers. Support and success teams don’t have to guess what’s going on. They see the entire history of an account — the tickets, the calls, the emails — so they can respond faster, fix issues sooner, and prevent churn before it happens.
- Improving performance. Company leaders finally get a clear picture of what’s working and what’s not. They can measure, forecast, and plan based on real data — not gut feeling. They can see how employees and sales reps interact with customers and provide feedback.
A good CRM helps teams guide leads through every stage of the sales pipeline — from first contact to closed deal.
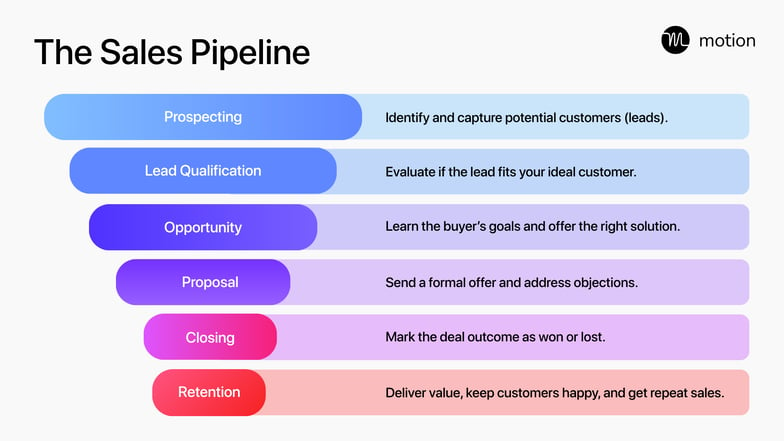
Here’s how that process typically works:
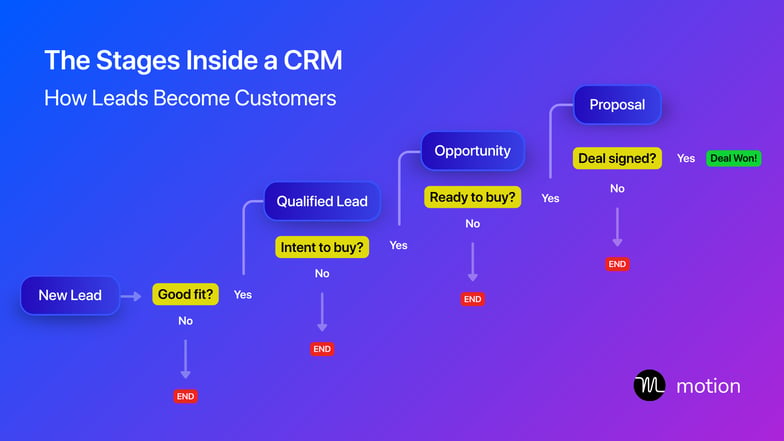
- New lead (prospecting): The CRM captures a new lead from a form, ad, or referral. If the person matches your target audience or fits your ideal customer profile, they move to the qualified Lead stage. If not, the record is marked as ended or disqualified.
- Qualified lead: Once a lead is engaged and shows genuine interest — like requesting a demo or replying to outreach — the CRM flags them as having intent to buy. At this point, they move into the opportunity stage for active selling.
- Opportunity: If the prospect is ready to discuss pricing, terms, or a proposal, they advance to the pre-proposal stage. The sales team may send quotes, negotiate details, or customize the offer.
- Proposal: At the proposal stage, your team sends a formal quote or contract for review. The focus shifts from selling to securing commitment — clarifying terms, handling final objections, and confirming budget approval.
- Closed-won (or end): When the deal is signed, the record moves to closed-won — becoming a paying customer. If the deal falls through or the prospect stops engaging, it moves to end instead.
The flowchart below illustrates each of these stages and the requirements to progress from one stage to the next.
That’s the promise of a CRM. And for the most part, CRMs deliver on it.
The shortcomings of traditional CRMs
While almost every business should have a CRM, there are issues almost every team faces when using them. For example:
- Data entry is manual and time consuming. Reps spend hours logging calls, notes, and follow-ups instead of actually talking to customers. The irony? The more time they spend updating your CRM, the less time they have to build real relationships with customers.
- CRMs are difficult to use and set up. Most CRMs aren’t that user friendly. This is less of an issue for enterprise companies who can invest time and money in documentation and training, but it’s a huge challenge for smaller businesses (SMBs) who lack the time and money to fully train employees on how to use CRMs.
- Businesses use multiple tools that don’t sync data with the CRM. Sales, marketing, and support teams each have their own software and tools — email platforms, chat tools, billing systems, analytics dashboards — none of which talk to each other. So data lives everywhere and nowhere at once.
- Data inside CRMs is often missing or outdated. Thanks to the latter three issues, employees don’t always add or update data inside CRMs, especially at SMBs. Which means companies are paying for expensive, inaccurate software, and often, the CRM doesn’t actually contain the info they need.
How do AI CRMs solve these common shortcomings?
In theory, AI CRMs were built to fix what traditional CRMs broke.
- They automate data entry. AI handles much of the data entry. The AI can add new leads to your CRM. Update customer accounts with the latest call notes, meeting summaries, and emails. And move a lead through the stages of the sales pipeline.
- They’re actually easy to use. Modern AI CRMs include AI chats that can teach users how to use functionality they’re unsure of. And the AI can do tasks within the CRM upon request. For example, you can type into AI chat any notes you want to add to a customer account, and it will do it for you.
- They update data in real time. Instead of waiting for an employee to update the CRM (and they might forget to entirely), the AI updates data in real time. For example, once a customer signs a contract, the AI would update the customer account to reflect that it’s a closed deal.

In short, AI CRMs don’t just store information. They keep data accurate, organized, and up to date. They also help your team spend less time managing information and more time closing deals.
And that’s only the beginning. AI CRMs can handle multi-step, complex work that used to require manual effort — often across multiple tools.
Related: 10+ CRM Automation Examples and the Best Tools to Try
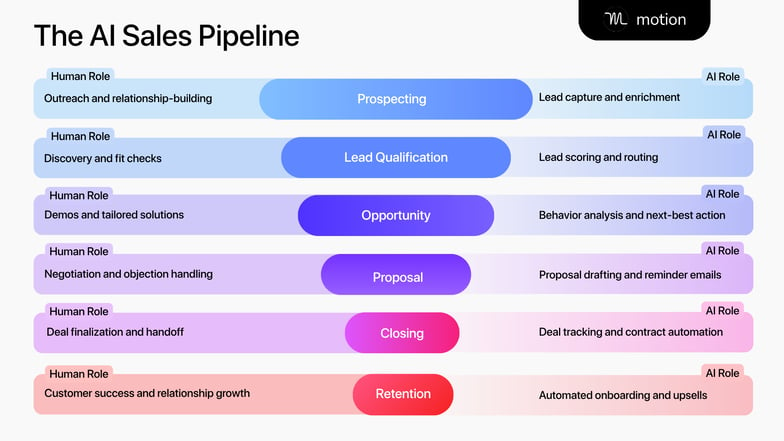
Because of this, AI fundamentally reshapes the sales pipeline.
That’s why we’ve mapped out an entirely new version of the traditional sales process: the AI sales pipeline.
The AI Sales Pipeline shows how humans and AI work together across each stage of the sales process — combining automation with human judgment to move deals forward faster and more efficiently.
Not sure what multi-step, complex work your AI CRM can do? You’re not alone.
In this next section, I’ll share 18 examples of complex, multi-step work that AI CRMs can take on for your business.
18 AI CRM examples and use cases
AI lead generation and qualification use cases
Use case 1: Lead scoring and prioritization
AI CRMs evaluate every interaction a lead has with your business — website visits, demo requests, email replies, and sales calls — then combine that behavioral data with demographic and firmographic details such as:
- Company size and industry
- Job title and seniority
- Location and region
- Tech stack
- Annual revenue
- Whether they fit your ideal customer profile (ICP)
From these inputs, the system calculates two key metrics:
- Fit score: How closely the lead matches your ideal buyer profile
- Engagement score: How actively they’re showing interest in your brand
Those scores update automatically as new data comes in, giving teams a real-time view of who’s most likely to buy and when.
The impact?
Your sales team spends less time chasing bad leads and books more meetings with people who are actually interested. Marketing also gets clearer feedback on which campaigns bring in quality leads.
Example: When a lead views the pricing page multiple times, replies to a follow-up email, and works at a company that matches your target profile, AI can instantly recognize that pattern and rank them as high priority.
Use case 2: Data cleansing, enrichment, and deduplication
Bad data is one of the biggest reasons CRMs fail.
Over time, fields get skipped, contacts get duplicated, and your “source of truth” turns into an inconsistent, expensive mess.
AI CRMs solve this by continuously cleaning and enriching data in the background.
They can:
- Fill in missing firmographic fields like company size, industry, or revenue using trusted third-party data sources
- Identify and merge duplicate contacts (even when names or emails are slightly different)
- Standardize formats for names, phone numbers, and company domains
- Detect outdated information — such as job changes or company moves — and update records automatically
As a result, CRMs stay accurate and always up to date.
Example: If “Jon Smith” and “John Smyth” appear as separate contacts with similar emails and company info, AI recognizes they’re the same person and merges the records. It also fills in missing data, like the company’s headcount and tech stack, so teams always have a complete, up-to-date profile.
Use case 3: Lead sentiment and intent analysis
Every message a lead sends — whether it’s an email, chat, or social reply — contains signals about their interest level and buying intent.
AI CRMs analyze the tone, language, and context of those messages to detect:
- Sentiment: Positive, neutral, or negative tone
- Intent: How ready the person is to buy
If a lead starts using words like “timeline,” “budget,” or “implementation,” AI flags them as high intent. If the tone shifts toward hesitation or frustration, it detects that too — often before a human would notice.
These insights help sales teams prioritize outreach where it’s most likely to pay off, and help marketing automate timely responses or campaigns.
Example: When a prospect replies to a follow-up with, “We’re reviewing vendors and setting our budget this quarter,” AI interprets that as a strong buying signal. The lead gets routed to the right rep for immediate follow-up, while others with lower intent stay in nurture campaigns until they’re ready to re-engage.
Use case 4: Decision-maker mapping and approach plan
Even the best pitch fails if it never reaches the person who can say yes.
AI CRMs analyze communication trails — emails, meeting notes, call transcripts, and CRM activity — to identify who actually drives decisions versus who’s simply involved in the conversation.
It can detect patterns like:
- A director who replies selectively
- A VP who joins only key meetings
- A CFO who appears whenever pricing is discussed
From this data, the system infers who holds influence and assigns roles based on the DACI framework:
- Driver: Pushes the project forward
- Approver: Makes the final decision
- Contributor: Provides input or expertise
- Informed: Needs visibility but doesn’t influence the outcome
Once these roles are clear, AI can recommend the best next steps — which stakeholders to engage, how to reach them, and what messaging will resonate with each.
Example: If a rep is only communicating with a project manager, AI might flag the missing approvers and suggest looping in the VP of Operations and CFO. It can even generate tailored talking points for each role, helping the rep expand influence and move the deal forward faster.
Use case 5: Automated data capture and entry
Ask any sales rep what they dislike most about their CRM, and you’ll probably hear the same answer: data entry.
Logging calls, adding notes, copying meeting details, and updating fields takes valuable time away from selling — which is why so many CRMs end up full of incomplete records.
AI CRMs eliminate that manual work by automatically extracting information from emails, calls, and meetings. They can identify:
- Contact details and job titles
- Deal stage changes and next steps
- Key points or pain signals mentioned in conversations
Once captured, this data is structured and added to the right fields instantly — no rep involvement required.
Example: After a customer call, AI can summarize the discussion, log attendees, update the deal stage with new budget or timeline details, and create a follow-up task automatically.
AI sales execution and forecasting use cases
Use case 6: Predictive forecasting and pipeline risk detection
Forecasting is one of the hardest — and most political — parts of sales.
Reps tend to be overly optimistic, managers downplay their numbers, and leaders are left trying to reconcile conflicting forecasts.
AI CRMs remove the guesswork, bias, and back-and-forth.They analyze every deal in the pipeline — including activity patterns, engagement frequency, deal velocity, sentiment, stakeholder mix, and historical close rates — to predict the likelihood of each opportunity closing on time.
Deals that appear healthy on the surface but show warning signs — like stalled communication or missing decision-makers — are flagged automatically.
Example: If a deal hasn’t had contact with a key stakeholder in 10 days or the budget conversation is overdue, AI highlights the risk and lowers the close probability. Another deal showing steady engagement might be rated 80% likely to close.
Use case 7: Rep performance insights
Most CRMs track outcomes — a deal closed or it didn’t — but not why some reps consistently outperform others.
AI CRMs change that by analyzing every interaction across the sales process to uncover patterns that drive success. Instead of surface-level activity metrics like “20 calls made,” they surface actionable insights such as:
- Which messages or cadences convert best
- Which deal stages reps move through most effectively
- Where each rep struggles or excels
These insights help managers coach more effectively and help reps understand their strengths and weaknesses.
Example: AI might reveal that one rep closes 45% of late-stage deals because they send ROI summaries within an hour of each demo, while another rep loses momentum due to long gaps between follow-ups.
Use case 8: Automatic lead routing and fair workload distribution
Manual lead assignment is often biased, outdated, or random — and that kills efficiency and morale.
AI CRMs eliminate the guesswork by automatically assigning new leads to the right reps and balancing workloads across the team.
They analyze factors such as:
- Past performance and win rates by segment or ICP
- Typical deal size and industry focus
- Current workload and available capacity
This ensures each lead goes to the rep most likely to convert — without overloading anyone.
Example: If one rep consistently wins mid-market construction deals and another performs best with enterprise tech accounts, AI routes new leads accordingly. When a rep’s pipeline starts to overflow, the system redirects incoming leads to teammates with capacity.
AI sales communication and productivity use cases
Use case 9: Personalized email drafting and outreach
AI CRMs can automatically draft and personalize sales emails based on deal stage, previous communication, and buyer context.
Messages adapt to where a prospect is in the funnel — whether it’s an initial outreach, a mid-deal check-in, or a late-stage proposal.
Example: After a discovery call, AI can instantly generate a follow-up email summarizing the discussion, addressing open questions, and confirming next steps. For a lead that’s gone quiet, it might draft a re-engagement email tailored to that person’s industry and specific challenges.
Use case 10: Meeting and pitch preparation
Many reps walk into meetings underprepared — juggling too many deals and too little time.
AI CRMs solve that by generating an automated briefing before every call. These summaries pull together:
- Recent emails and meeting notes
- Deal history and stage updates
- Key account details and decision-makers
- Relevant insights, such as industry trends or likely objections
Some systems even create tailored assets, like presentation decks, case studies or ROI examples that fit the account’s industry.
Example: Before a sales call, AI can create a one-page summary showing the client’s latest feedback, open questions, and potential concerns. It can even go a step further — pulling data from similar customers to build a short business case or presentation deck that shows potential return on investment (ROI) for the business owner, operations lead, CFO, or CMO.
Use case 11: Call transcription, summaries, follow-up emails, and CRM syncing
AI CRMs act as an assistant during and after meetings, handling the tedious work that often falls through the cracks.
They can:
- Record and transcribe calls automatically — no manual note-taking required
- Summarize key points, such as objections, budget, and next steps
- Identify action items and assign follow-up tasks to the right people
- Draft follow-up emails that recap the conversation and confirm commitments
- Update deal records with new details or stage changes
- Sync everything — recordings, summaries, and tasks — directly to the CRM for full visibility
Example: After a 45-minute call, AI can generate a concise summary noting that the buyer requested an updated quote and wants a follow-up next week. It automatically logs the transcript, creates the task, and drafts the email.
Use case 12: Customer churn prediction
Most companies only realize a customer is unhappy when they cancel. And by then, it’s too late.
AI CRMs help teams catch churn risk early.
To identify at-risk customers, they continuously monitor signals like:
- Product usage and engagement trends
- Support ticket volume and tone
- Email sentiment or slower response times
- Payment delays or contract renewal gaps
When risk indicators appear, the CRM flags the account, explains the reason, and recommends a proactive next step.
Example: If usage drops 30% over two weeks and recent support tickets show negative sentiment, AI can flag the account as “at risk” and suggest a personal check-in from the account manager.
Use case 13: Renewal and expansion automation
Renewals and upsells often get overlooked — buried under new deals and daily priorities.
AI CRMs prevent that by tracking contract timelines, customer behavior, and usage patterns to automate renewal and expansion workflows.
They can:
- Auto-create renewal opportunities based on contract terms or expiration dates
- Monitor product usage to flag churn risks or upsell potential
- Trigger tailored plays, such as check-in reminders or upgrade offers
- Sync billing, support, and contract data so teams see everything in one view
Example:If a customer’s contract renewal date is 30 days away and usage has increased 20% month over month, AI can automatically generate a renewal opportunity, notify the account owner, and draft an upsell email highlighting the expanded usage.
Use case 14: Next-best action recommendations
AI CRMs don’t just track activity. They can help sales teams decide what to do next.
By analyzing recent behavior, communication patterns, and deal history, AI predicts which action is most likely to move the relationship forward.
Common recommendations include:
- Sending a case study or ROI example after a pricing conversation
- Scheduling a follow-up call after a demo
- Offering a trial extension when engagement starts to drop
These recommendations appear directly in the CRM workflow, helping teams take smarter, faster action.
Example:If a prospect visits your pricing page twice in one day but hasn’t replied to recent emails, AI might suggest sending a follow-up that includes an ROI example and limited-time discount.
Use case 15: Product and service recommendations
Upsells and cross-sells often happen inconsistently — or not at all.AI CRMs make them automatic by analyzing each customer’s behavior, purchase history, and product usage to spot natural opportunities for add-ons or upgrades.
They can:
- Identify when customers approach usage limits
- Flag complementary products based on what similar customers buy
- Recommend personalized upgrade offers or bundles
Example:If a customer frequently exceeds their plan limits, AI can suggest an upgraded tier and generate a personalized email offering an incentive to switch early.
Use case 16: Customer sentiment monitoring
Most CRMs track what customers do. AI CRMs also track how they feel.
By analyzing tone and language across emails, chats, and support tickets, AI can detect shifts in customer sentiment — from excitement to frustration or confusion.
It alerts teams to emerging risks or opportunities before they escalate.
Example: If a long-time customer suddenly writes, “We’ve been waiting weeks for this update,” AI flags the message as negative sentiment and notifies the account owner. Conversely, if a new customer leaves positive feedback, it can tag the account as a potential advocate and suggest a review or referral request.
AI insight and analysis use cases
Use case 17: Sales performance analysis
AI CRMs can help you understand what makes your best salespeople successful — and where others can improve.
By reviewing sales activity, emails, and meeting transcripts, the AI spots the patterns behind strong (and weak) performance.
AI can:
- Identify winning habits, like quick follow-ups or clear next steps after calls.
- Highlight problem areas, such as poor discovery questions or slow responses.
- Track momentum metrics that affect revenue — like days in stage, average deal size, how fresh next steps are, and how quickly reps follow up after meetings.
- Suggest next actions to fix those issues, like sending a follow-up reminder or refreshing a stalled deal.
- Compare performance across individuals or teams to find what works.
Example: AI might show that one rep consistently closes mid-size clients because she sends a short recap email with ROI proof points right after every demo. Another rep, who talks most of the time during calls, struggles to convert — and the system flags that her follow-ups are often delayed.
Use case 18: Understand why customers buy (or don’t)
Your CRM holds a goldmine of customer feedback, but it’s often buried in notes, call logs, and emails.AI CRMs make that data searchable and actionable.
Teams can ask questions like:
- “How many prospects mentioned price as a concern this month?”
- “Which features come up most in positive feedback?”
- “Why do deals stall at the proposal stage?”
AI aggregates this input across every interaction, revealing patterns that improve sales, marketing, and product decisions.
Example:If 25% of lost deals mention “limited weekend support,” AI surfaces that trend automatically in a weekly summary. Leadership can then decide whether expanding service hours could increase win rates.
Top AI CRM Tools in 2025: Reviewed
How I reviewed these AI CRMs
To make this guide genuinely useful for businesses, I focused on practicality — not theory.
I reviewed the leading AI-powered CRMs on the market to understand how they actually help businesses work faster, close more deals, and deliver better customer experiences.
For each platform below, you’ll get:
- A quick intro to the tool and its standout AI features
- Pricing details (where available)
- An overview of which businesses each CRM is best suited for
That said, I can’t “stress test” these tools the way your own team could. I can demo them, analyze capabilities, and explain how we use ours at Motion — but your business, workflow, and sales process will look different.
So instead, this section gives you an informed overview of each tool — plus a checklist you can use to evaluate them yourself.
How to use the checklist
Use this checklist as a guide while you’re evaluating AI CRMs — whether you’re browsing websites, trying free versions, or joining sales calls.
Bring it with you when you meet with vendors. It’ll help you ask smart, specific questions about how each platform works and whether it actually fits your business.
You’ll quickly see which use cases each CRM supports, where features are missing, and which tools best align with your priorities — not just what the salesperson wants to show you.
Pro tip: Before you start testing, identify which AI use cases matter most to your business. That way, you can focus your demos on the features that will actually save time and drive revenue.
Free tool: Grab your free checklist here.
What to look for when testing AI CRMs
Beyond use cases, here are a few other factors worth evaluating:
- Ease of use: Is it simple enough that your team will actually use it every day?
- Real AI value: Does it automate meaningful work?
- Revenue impact: Would it realistically help you book more jobs or close more deals?
- Feature depth: Does it cover the use cases that matter most to your business?
- Integrations: Does it connect easily with your existing tools (email, scheduling, billing, etc.)?
- Price-to-value ratio: Do the AI features justify the cost?
- Real-world feedback: What are users in your industry saying about it?
Reviewing 7 Top AI CRM Tools for 2025
Now that you know what to look for, let’s review the leading AI CRMs available today.
Each summary below highlights what the tool does well, where it may fall short, and which type of business it’s best suited for.
Salesforce AI CRM (Einstein + Copilot)
Salesforce has been the CRM standard for years. With Einstein and Copilot, it now layers AI across nearly every part of the platform.
AI features
Einstein scores leads, predicts revenue, and flags at-risk deals. Copilot adds a chat-style assistant you can ask questions like:
- “Which deals are likely to close this month?”
- “Summarize my top opportunities for the week.”
It’s a powerful system built for teams that want deep analytics, forecasting, and automation.
Best use cases
- Lead scoring and prioritization
- Forecasting and pipeline risk detection
- Rep performance insights
- Decision-maker mapping
- Call summaries and insights (through integrations)
Pros
- Enterprise-level analytics and flexibility
- Massive integration ecosystem
- Powerful automation once fully set up
Cons
- Expensive: And AI features often cost extra
- Steep learning curve for smaller teams
- Heavy setup and admin requirements
Pricing
Core CRM plans start around $25–$80 per user/month, with Einstein + Copilot AI features available as paid add-ons that can raise total cost above $150 per user/month.
Ideal customer
Large, enterprise companies that already use Salesforce or have the resources (and patience) for a robust, highly customizable system.
HubSpot AI CRM
HubSpot is one of the most popular CRMs for small and midsize businesses. It combines marketing, sales, and service tools in one platform, with built-in AI.
AI features
HubSpot’s Smart CRM uses AI to score leads, recommend follow-up actions, draft emails, and summarize customer interactions.
The new AI assistant also helps with content writing, deal analysis, and sales outreach.
Best use cases
- Automated follow-ups and next-best action recommendations
- Lead scoring and prioritization
- Renewal and upsell reminders
- Customer sentiment and engagement tracking
Pros
- User-friendly and simple to onboard
- All-in-one business platform for marketing, sales, and service teams
- Automations that genuinely reduce manual work for SMB teams
Cons
- Advanced AI features require higher-tier pricing
- Some users feel the AI insights are basic and occasionally inconsistent
- Lacks the customization and analytical depth of enterprise CRMs like Salesforce
Pricing
HubSpot offers a free plan with basic CRM functionality. Paid plans start around $20 per seat/month and go up to $90+ per seat/month for professional and enterprise tiers, where AI features are more robust.
Ideal customer
Service businesses that want a reliable, all-in-one CRM with AI. It’s perfect for teams that care more about ease and real-world efficiency than deep customization or complex data modeling.
Zoho AI CRM (Zia)
Zoho CRM is one of the most affordable AI-enabled CRMs on the market. It has a built-in AI assistant — called Zia — automates tasks and delivers insights.
AI features
Zia handles predictive lead scoring, forecasts deal outcomes, detects anomalies in your pipeline, and suggests the best time to contact prospects.
It can also analyze sentiment from emails and chats to flag when a customer might be unhappy or at risk of churn.
Best use cases
- Lead scoring and prioritization
- Forecasting and pipeline risk detection
- Customer sentiment tracking
- Smart reminders and workflow suggestions
Pros
- Budget-friendly and feature-rich for the price
- AI works automatically — little setup required
- Integrates well with Zoho’s full business app suite (email, accounting, forms, etc.)
Cons
- Interface can feel dated compared to modern CRMs
- AI insights can be inconsistent for small datasets
- Customization is limited beyond the Zoho ecosystem
Pricing
Plans start around $20 per user/month, with Zia AI tools available in the Enterprise and Ultimate editions.
Ideal customer
Zoho is ideal for teams that value affordability, automation, and simplicity over advanced analytics or heavy customization.
Pipedrive AI CRM
Pipedrive is built for simplicity. It’s designed to help small sales teams stay organized and move deals forward without the heavy setup or complexity of larger CRMs. Its AI Sales Assistant adds a layer of automation and insight on top of that clean foundation.
AI features
The AI Sales Assistant analyzes pipeline activity, identifies stuck deals, and suggests the next actions reps should take. It can also generate performance summaries and surface patterns in lost opportunities.
The AI tools are practical, and most users find them genuinely helpful for day-to-day deal management.
Best use cases
- Lead scoring and prioritization
- Next-best action recommendations
- Automated follow-ups and reminders
- Deal performance insights
Pros
- Very easy to learn and navigate
- Quick setup — ideal for teams without a dedicated CRM admin
- Affordable pricing and solid mobile app experience
Cons
- AI insights are more basic than enterprise systems.
- Limited reporting options compared to larger CRMs
- Some integrations and advanced automations require paid add-ons.
Pricing
Plans start at $14 per user/month, with AI features available in higher tiers like Advanced and Professional.
Ideal customer
Small service businesses that want a straightforward, sales-focused CRM with helpful automation.
Freshworks AI CRM (Freddy AI)
Freshsales, part of the Freshworks suite, is a CRM designed for businesses that want automation and ease of use.
Its built-in AI assistant, Freddy AI, helps sales teams focus on the right leads and stay on top of every deal.
AI features
Freddy AI scores leads based on engagement, predicts which deals are most likely to close, and suggests next steps for reps.
It can also automate data entry, summarize conversations, and alert users to stalled opportunities.
Best use cases
- Lead scoring and prioritization
- Predictive forecasting and risk detection
- Automated follow-ups
- Next-best action suggestions
Pros
- Affordable and easy to set up
- Combines CRM, calling, and email in one system
- Good automation features for smaller teams
Cons
- Limited AI depth compared to larger CRMs
- Smaller integration ecosystem
- Occasional syncing or reporting delays reported by users
Pricing
Plans start at $15 per user/month, with Freddy AI included in the Pro and Enterprise tiers.
Ideal customer
SMBs that want an affordable, all-in-one CRM with reliable automation and straightforward AI — without needing extensive configuration or IT support.
Close AI CRM
Close is a sales-focused CRM built for teams that prioritize calls, emails, and speed. It’s popular with agencies and service businesses that rely on proactive outreach rather than inbound leads. Its AI features are designed to make that outreach faster and more consistent.
AI features
Close uses AI to write and personalize follow-up emails, predict the best time to reach out, and summarize call transcripts.
It also automates repetitive admin tasks like logging activities and updating deal stages.
Best use cases
- Automated post-call follow-ups
- Call summaries and transcription
- Next-best action recommendations
- Lead scoring and prioritization
Pros
- Designed specifically for outbound sales and calling-heavy teams
- Simple, fast interface
- Streamlined automations that save time on admin work
Cons
- Lacks broader marketing and service features
- Fewer customization options than larger CRMs
- AI tools are still developing — practical but not predictive
Pricing
Plans start at $49 per user/month, with AI capabilities included in higher-tier plans.
Ideal customer
Small to midsize service businesses or agencies that rely on consistent follow-ups and outreach. And want a CRM that helps reps stay efficient without extra complexity.
Attio AI CRM
Attio is one of the newer CRMs on the market, built for teams that want a modern, flexible platform with intelligent automation. Attio is a more AI-forward platform than other platforms we’ve reviewed here.
AI features
Attio uses AI to enrich contact data, identify relationships between people and companies, and summarize customer interactions.
It can detect key insights from emails and notes, automatically updating contact profiles with relevant context.
Best use cases
- Contact and company enrichment
- Relationship mapping and account insights
- Meeting and communication summaries
- Context-aware recommendations
Pros
- Modern, intuitive interface with minimal setup required
- Flexible database-style customization
- Continuous product updates and responsive support
Cons
- Smaller integration library than established CRMs
- AI capabilities still expanding
- Lighter on advanced sales forecasting and analytics
Pricing
There is a free plan. Paid tiers start around $29 per user/month.
Ideal customer
Small businesses or agencies that want a sleek, customizable CRM with smart automation — and prefer a modern user interface.
The final verdict: The Top 3 AI CRMs in 2025
After comparing the leading platforms, here’s how they stack up for small and midsize businesses — based on usability, real AI value, pricing, and overall impact.
1st place: HubSpot AI CRM
The best all-around option for SMBs.
HubSpot strikes the right balance between powerful automation and everyday usability.
Its AI tools are approachable, practical, and genuinely helpful for smaller teams — and its unified marketing, sales, and service ecosystem makes it easy to manage the entire customer journey in one place.
2nd place: Pipedrive AI CRM
The most user-friendly CRM for small sales teams.
Pipedrive’s AI tools are simple but effective, helping reps focus on the right deals without overcomplicating workflows.
It’s affordable, quick to set up, and ideal for service businesses that want automation without the enterprise overhead.
3rd place: Zoho CRM (Zia)
The best budget-friendly AI CRM.
Zoho’s Zia assistant delivers meaningful automation at a fraction of the price of larger systems.
It’s a great fit for teams that want predictive insights and workflow suggestions without sacrificing affordability — though it’s less polished than HubSpot or Pipedrive.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about AI CRMs
What is an AI CRM?
An AI CRM is a customer relationship management system that uses artificial intelligence to automate tasks, analyze data, and provide insights that help teams sell, market, and support customers more effectively.

How does AI improve CRM systems?
AI eliminates manual work like data entry, lead scoring, and follow-up tracking. It can analyze patterns across your customer data to predict outcomes, recommend next steps, and surface insights your team might otherwise miss.
What are the main use cases for AI in CRM?
Common use cases include lead scoring, forecasting, customer sentiment analysis, automated follow-ups, data enrichment, and identifying at-risk customers or upsell opportunities.
Which companies offer the best AI CRMs in 2025?
Top performers for SMBs include HubSpot Smart CRM, Pipedrive (AI Sales Assistant), and Zoho CRM (Zia). For larger teams, Salesforce Einstein + Copilot leads in power and customization.
What’s the difference between a traditional CRM and an AI CRM?
Traditional CRMs store and organize customer data.
AI CRMs automate many of the tasks that teams used to do manually within a CRM. They can automatically add and update customer data, perform actions (like writing and sending emails), and analyze data for you.
Can AI CRMs integrate with my existing tools?
Yes. Most AI CRMs integrate with common tools like Gmail, Outlook, Slack, accounting software, and scheduling platforms.
Are there free AI CRMs?
Sort of. HubSpot, Zoho, and Attio all offer free or low-cost tiers with basic AI features, but eventually you’ll need to upgrade and pay.
What are the risks or downsides of using AI in CRM?
AI insights are only as good as the data you feed them. Poor data quality can lead to bad recommendations. Some CRMs also lock advanced AI tools behind expensive plans.
How do I choose the right AI CRM for my business?
Start with your team size, workflow, and top use cases. Use our checklist to compare options based on ease of use, automation quality, integrations, and price-to-value ratio — and test the top few with free trials before committing.

The bottom line: The right AI CRM will automate work and increase sales.
For most small and midsize businesses, the right AI CRM system saves hours each week, keeps data clean, and helps teams follow up faster and more intelligently.
The key is choosing one that fits how your business actually works.
Start small.
Focus on the AI features that solve your biggest bottlenecks and issues — like forecasting or follow ups — and expand from there.
The companies that do will spend less time managing data and more time doing what matters: building relationships, closing deals, and growing faster.