Process analysis is a systematic approach to examining how work is performed within an organization.
It involves breaking down processes into their individual components, studying each step, and identifying areas for optimization.
By thoroughly understanding the flow of work, businesses can pinpoint bottlenecks, eliminate redundancies, and implement strategies to enhance productivity and reduce waste.
At its core, process analysis is about doing more with less. It's a powerful tool that enables organizations to achieve greater efficiency, boost profitability, and deliver superior products or services to their customers.
The importance of process analysis cannot be overstated, as it provides a structured framework for continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Understanding the fundamentals of process analysis
Process analysis is a comprehensive discipline that encompasses various techniques and methodologies.
It starts with defining the specific process or processes to be analyzed, setting clear objectives, and gathering relevant information.
This info can come from various sources, like process documentation, stakeholder interviews, and data collection methods such as surveys, observations, and focus groups.
Once the necessary data has been gathered, the next step is to map out the process visually.
This can be done through the creation of process flowcharts, which provide a clear representation of the steps involved, decision points, and inputs and outputs.
By visualizing the process, it becomes easier to identify areas for improvement and potential bottlenecks.
Flowcharts are particularly useful because they offer a bird's-eye view of the entire process, allowing stakeholders to see how different steps are interconnected.
This visual representation can reveal inefficiencies that may not be immediately apparent when looking at individual steps in isolation.
Additionally, flowcharts can serve as a communication tool, helping to align team members and stakeholders on the current state of the process and the desired future state.
Why perform process analysis?
The main benefit of business process analysis is to improve efficiency or gain a better understanding of how a business functions. However, a process analysis usually has specific goals.
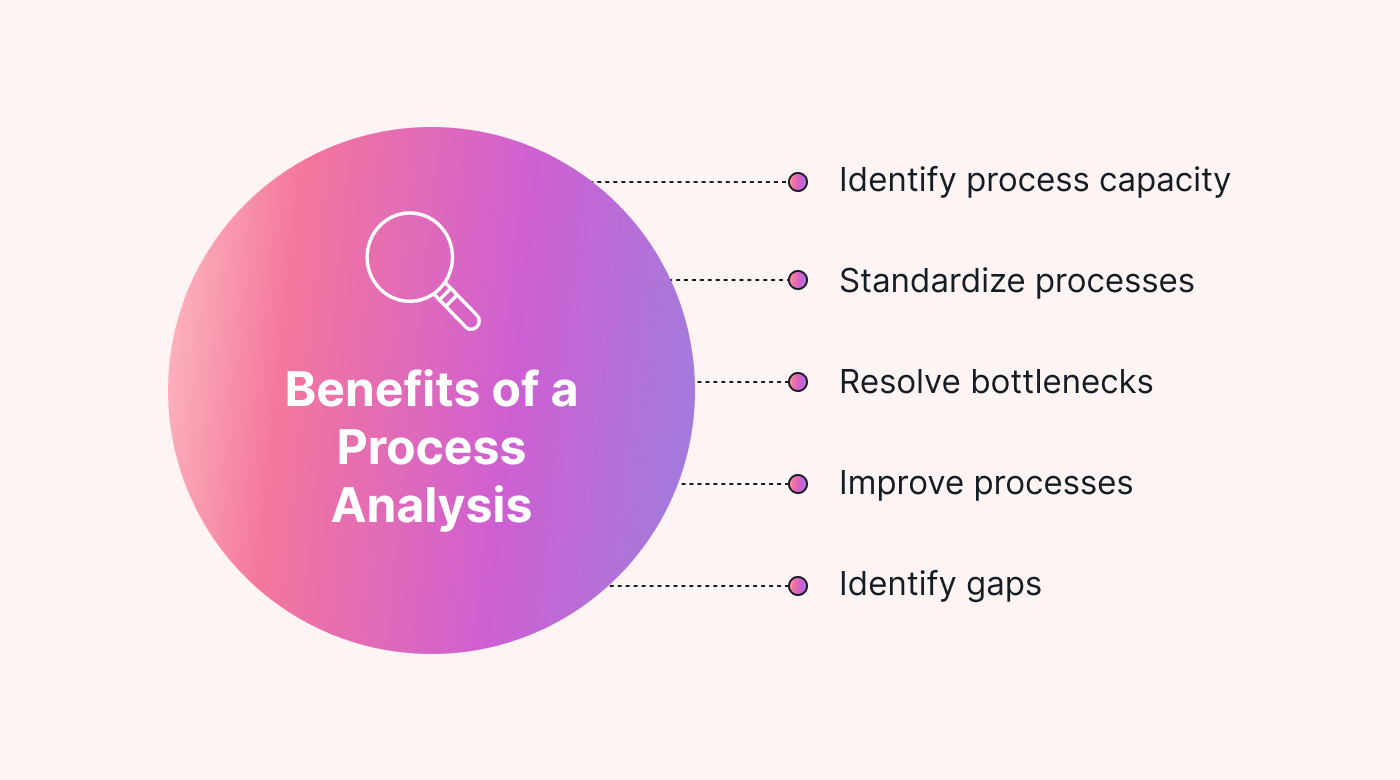
- Identify process capacity - There may be a functional limit to existing processes that limits your overall business operations.
- Standardize processes - Creating a single way of performing similar processes can reduce costs and improve training efficiency.
- Resolve bottlenecks - Resources or information may be tied up, slowing or stopping a process.
- Modify processes - Understanding the processes in place can make introducing new elements easier.
- Identify gaps - Is there an incomplete process, or is something missing entirely?
How to perform a process analysis
To an extent, every analysis will be different. However, there are a few key elements that every analysis should include.
Process modeling is a significant part of the analysis, which reveals factors that impact as-is processes. The models are then adjusted to find potential improvements.
Process analysis is usually performed on-site, where processes can be directly observed and measured. Analysis will also often involve interviews with workers performing the processes.
What are the steps of a process analysis?
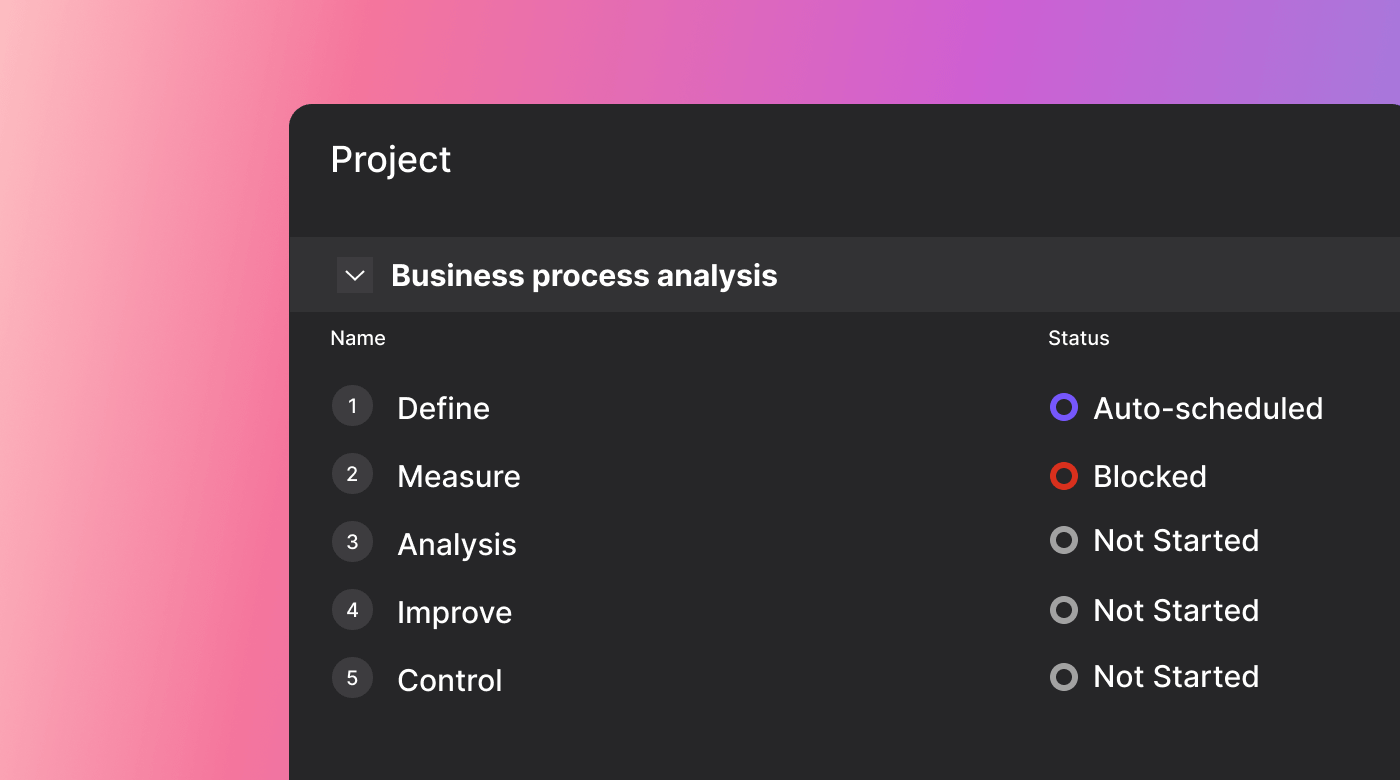
In general, business process analysis is broken down into several stages. The later stages, particularly improve and control, may be considered part of process management.
- Define - Identify the processes you’re interested in and begin to describe them. You may begin by diagramming as-is processes.
- Measure - Begin collecting data to measure the functions of existing processes. Doing so allows you to compare them to metrics like KPIs. Efficiency is a common metric to consider, though the specifics will depend on the process and its goals.
- Analyze - Begin to analyze your findings. You might use various types of analysis, diagrams, models, or consultations with team members to gain insight into processes.
- Improve - Identify problems and then create potential paths to improvement. In general, the analysis will include several options for improvements. Specific steps to be taken are then determined in collaboration with other stakeholders.
- Control - Determine if the implemented changes had beneficial effects. This step may include quality control. You may even perform a follow-up process analysis down the line.
A real-world process analysis example: Thai milk collection
Business process analysis is a very complex endeavor. However, it may be easier to understand with a simple example. This basic business process analysis considered milk collection in Thailand as part of collecting, processing, and distributing milk to consumers.
The process analysis in this example followed the steps we outlined previously in the article, starting with understanding the current operation process and collecting data.
Define
To understand the specific process of collecting milk, some broader context regarding the business of selling milk in Thailand is necessary.
Process analysts interviewed business owners and process managers. With that information, the analysts created a process diagram using a public-domain business process modeling method.
Measure
Once they understood the specifics of the process, it was possible to measure its different parts and collect more detailed data about operations.
Analysts also identified factors that impacted the process, from local regulations to requirements regarding delivery times. Further direct interviews with stakeholders played a big part in this step.
Analysis
The analysts produced diagrams that offer a more detailed look at the factors impacting milk collection.
Specifics of the process also mapped out, including requirements for testing the milk and the equipment required.
Improve
The analysis revealed several areas of potential improvement. Some were outside the scope of the specific process, such as connecting dairy farmers with veterinarians to produce more nutritious milk.
Fundamental improvements were suggested, such as long-term planning and the introduction of real-time tracking.
Control
This particular example didn’t include a follow-up. However, analysts should theoretically return to the same collection center after implementing changes.
Then they can then assess which suggestions were implemented, and what effects those changes had. Based on those findings, further refinements may be suggested.
Take a step to streamline your own daily processes
Business process analysis is a complex field that has its own specialists and methods.
However, anyone who wants to improve their business and reduce inefficiencies in their work can use the approach.
Not only will it help you gain a better understanding of how you operate, it will help you do things better.
Keeping the complexities of a business process analysis straight can be difficult. It’s made a lot easier by using tools like those provided by Motion.
It can help keep you on task, communicate with team members, and organize data.
You can streamline that business process as a project using Motion’s Intelligent Calendar, especially if you're constantly reprioritizing tasks.
The cutting-edge AI will manage those decisions for you.
Sign up for Motion and see the difference it can make in managing the tasks for process analysis or any other project.

Alli is Content Writer and Strategist who has worked in SaaS since 2017. She’s worked with brands like BombBomb, Animalz, SupportLogic, and Copy.ai. Alli lives in Colorado with her husband, daughter, and two dogs.